1-3 Additional Practice Piecewise Defined Functions Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
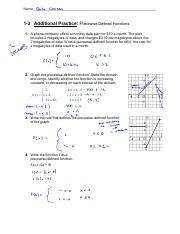
Table of Contents
1-3 Additional Practice Piecewise Defined Functions: Answer Key & Comprehensive Guide
Piecewise functions, those mathematical chameleons that change their behavior depending on the input, can seem daunting at first. But with practice and a clear understanding of the underlying concepts, you'll master them in no time. This comprehensive guide provides detailed solutions to 1-3 additional practice problems focusing on piecewise defined functions, along with explanations to solidify your understanding. We'll cover evaluating functions, graphing them, and understanding their applications.
Understanding Piecewise Defined Functions
Before diving into the practice problems, let's refresh our understanding of piecewise functions. A piecewise function is defined by multiple sub-functions, each applicable over a specific interval of the domain. It's essentially a collection of functions stitched together. The key is to identify which sub-function to use based on the input value (the x-value).
General Form:
A piecewise function is typically represented like this:
f(x) = { g(x), if a ≤ x < b
h(x), if b ≤ x ≤ c
i(x), if x > c }
This indicates that the function f(x) behaves as g(x) when x is between a and b (inclusive of a, exclusive of b), as h(x) when x is between b and c (inclusive of both), and as i(x) when x is greater than c. The intervals are crucial; they dictate which sub-function to apply.
Practice Problems & Solutions
Let's tackle three practice problems, gradually increasing in complexity. For each problem, we'll provide a step-by-step solution and explain the reasoning behind each step.
Problem 1: Evaluating a Piecewise Function
Consider the function:
f(x) = { 2x + 1, if x < 2
x² - 3, if x ≥ 2 }
Evaluate: a) f(1) b) f(2) c) f(4)
Solution:
a) f(1): Since 1 < 2, we use the first sub-function: f(1) = 2(1) + 1 = 3
b) f(2): Since 2 ≥ 2, we use the second sub-function: f(2) = (2)² - 3 = 1
c) f(4): Since 4 ≥ 2, we use the second sub-function: f(4) = (4)² - 3 = 13
Problem 2: Graphing a Piecewise Function
Graph the following piecewise function:
g(x) = { -x + 3, if x ≤ 1
2x - 1, if x > 1 }
Solution:
To graph this function, we'll graph each sub-function separately, paying close attention to the intervals.
-
-x + 3, if x ≤ 1: This is a linear function with a slope of -1 and a y-intercept of 3. We graph this line, but only for x-values less than or equal to 1. At x = 1, the y-value is 2. Include a solid dot at (1, 2) because it's included in this interval.
-
2x - 1, if x > 1: This is also a linear function with a slope of 2 and a y-intercept of -1. We graph this line only for x-values greater than 1. At x = 1, the y-value would be 1, but we don't include this point because the inequality is strictly greater than. Use an open circle at (1, 1) to indicate this.
By combining these two graphs, you'll see a discontinuous piecewise function with a "break" at x = 1.
Problem 3: A More Complex Piecewise Function
Analyze and graph the function:
h(x) = { |x|, if x < -1
x², if -1 ≤ x ≤ 2
4, if x > 2 }
Solution:
This problem introduces absolute value and a constant function, making it more challenging.
-
|x|, if x < -1: This is the absolute value function, but restricted to x-values less than -1. The graph will be the positive portion of the absolute value function to the left of x = -1. Use an open circle at (-1, 1).
-
x², if -1 ≤ x ≤ 2: This is a parabolic function, and we only need to graph the portion from x = -1 to x = 2 (inclusive). At x = -1, y = 1, and at x = 2, y = 4. Use solid dots at (-1, 1) and (2, 4).
-
4, if x > 2: This is a horizontal line at y = 4 for all x-values greater than 2. Use an open circle at (2, 4).
By carefully plotting each piece and paying attention to the open and closed circles at the boundaries, you will obtain the complete graph of the piecewise function. The graph will show distinct sections that meet (or don't meet) at the boundaries defined by the conditions.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
Piecewise functions aren't just abstract mathematical entities; they have real-world applications in various fields. Understanding their properties and nuances will enhance your problem-solving abilities.
1. Modeling Real-World Scenarios:
Piecewise functions are ideal for modeling situations where different rules apply depending on the input. For example:
-
Tax brackets: Income tax calculations often use piecewise functions, where different tax rates apply to different income levels.
-
Shipping costs: Shipping costs might involve a base rate plus a per-item charge or different rates depending on the weight or destination.
-
Cellular phone plans: Many phone plans have a fixed cost for a certain amount of data and then a higher rate for data exceeding the limit.
These scenarios perfectly illustrate the usefulness of piecewise functions in modeling non-linear and discontinuous relationships.
2. Calculus Applications:
Piecewise functions play a significant role in calculus. Understanding their behavior is crucial for topics like:
-
Limits and continuity: Determining limits and whether a function is continuous at points where the function definition changes.
-
Derivatives: Calculating derivatives of piecewise functions requires careful consideration of the different sub-functions and their derivatives.
-
Integrals: Integrating piecewise functions involves breaking the integral into separate integrals over the different intervals.
3. Computer Programming:
In computer programming, piecewise functions often translate into conditional statements (if-else structures). This allows programmers to implement logic where different actions are performed based on the value of a variable.
4. Signal Processing:
Piecewise functions are essential in signal processing for representing signals that change abruptly or have different characteristics in different time intervals. For example, square waves or signals with sharp transitions.
Tips for Mastering Piecewise Functions
-
Careful Interval Analysis: Always carefully examine the intervals defined for each sub-function. Make sure you understand which sub-function applies to each x-value.
-
Pay Attention to Open and Closed Circles: When graphing, meticulously use open circles for exclusive inequalities (< or >) and closed circles for inclusive inequalities (≤ or ≥). This accurately represents the function's behavior at the boundary points.
-
Practice Regularly: The best way to master piecewise functions is through consistent practice. Work through many examples, gradually increasing the complexity.
-
Visualize the Graph: Creating a graph of the piecewise function helps to understand its behavior and identify any discontinuities or interesting features.
-
Break Down Complex Problems: If you encounter a complex piecewise function, break it down into smaller parts. Analyze each sub-function independently before combining them.
By following these tips and consistently practicing, you will build a strong foundation in understanding and working with piecewise defined functions. Remember, the key is to approach each problem systematically, focusing on the intervals and the specific sub-function applicable to each input value. With dedicated effort, you'll conquer these mathematical chameleons!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Two Attributes That Define A Threat Are
Mar 28, 2025
-
Monster Synthesis Activity Answer Key Pdf
Mar 28, 2025
-
Shadow Health Hypertension And Type 2 Diabetes
Mar 28, 2025
-
Bob Golomb Attributes His Success As A Car Salesmen To
Mar 28, 2025
-
Turning Right And Accelerating To 30 Mph Takes About
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1-3 Additional Practice Piecewise Defined Functions Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
