1-3 Skills Practice Locating Points And Midpoints Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
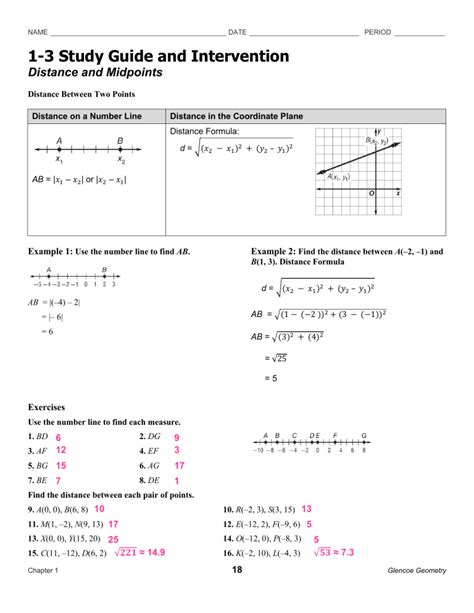
Table of Contents
Mastering 1-3 Skills Practice: Locating Points and Midpoints – A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential skills of locating points and midpoints, crucial concepts in geometry and coordinate systems. We'll explore various methods, provide ample practice problems with detailed answer keys, and offer strategies for mastering these skills. Whether you're a student striving for academic excellence or an enthusiast keen to enhance your mathematical abilities, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to tackle any challenge related to point and midpoint location.
Understanding the Coordinate Plane
Before we dive into locating points and midpoints, let's review the fundamental concept of the coordinate plane. The coordinate plane, also known as the Cartesian plane, is a two-dimensional surface formed by two perpendicular number lines: the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical). Their intersection is called the origin, represented by the coordinates (0,0).
Points on the coordinate plane are identified using ordered pairs (x, y), where 'x' represents the horizontal position (distance from the y-axis) and 'y' represents the vertical position (distance from the x-axis). Positive x-values are to the right of the origin, negative x-values to the left. Positive y-values are above the origin, and negative y-values are below.
Example: The point (3, 2) is located 3 units to the right of the origin and 2 units above it. The point (-1, -4) is located 1 unit to the left of the origin and 4 units below it.
Locating Points on the Coordinate Plane
Locating a point on the coordinate plane is straightforward:
- Start at the origin (0, 0).
- Move horizontally along the x-axis the number of units indicated by the x-coordinate. Move to the right for positive x-values and to the left for negative x-values.
- Move vertically along the y-axis the number of units indicated by the y-coordinate. Move up for positive y-values and down for negative y-values.
- The point where these movements intersect is the location of the ordered pair.
Practice Problems:
Locate the following points on a coordinate plane:
- (2, 5)
- (-3, 1)
- (0, -4)
- (4, 0)
- (-2, -3)
Answer Key:
- Start at (0,0). Move 2 units right, then 5 units up.
- Start at (0,0). Move 3 units left, then 1 unit up.
- Start at (0,0). Move 0 units horizontally, then 4 units down.
- Start at (0,0). Move 4 units right, then 0 units vertically.
- Start at (0,0). Move 2 units left, then 3 units down.
Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment
The midpoint of a line segment is the point that divides the segment into two equal parts. To find the midpoint, we average the x-coordinates and the y-coordinates of the endpoints.
Midpoint Formula: Given two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂), the midpoint M is calculated as:
M = ((x₁ + x₂) / 2, (y₁ + y₂) / 2)
Practice Problems:
Find the midpoint of the line segment connecting the following pairs of points:
- (2, 4) and (6, 8)
- (-1, 3) and (5, -1)
- (0, 0) and (4, -6)
- (-3, 2) and (-7, -4)
- (5, -2) and (-1, 6)
Answer Key:
- M = ((2 + 6) / 2, (4 + 8) / 2) = (4, 6)
- M = ((-1 + 5) / 2, (3 + (-1)) / 2) = (2, 1)
- M = ((0 + 4) / 2, (0 + (-6)) / 2) = (2, -3)
- M = ((-3 + (-7)) / 2, (2 + (-4)) / 2) = (-5, -1)
- M = ((5 + (-1)) / 2, (-2 + 6) / 2) = (2, 2)
Advanced Applications: Distance and Slope
Understanding midpoints and points on a coordinate plane forms the foundation for more advanced geometrical concepts. Two key concepts built upon this foundation are:
1. Distance Formula: The distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) is calculated using the distance formula, derived from the Pythagorean theorem:
Distance = √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²)
2. Slope: The slope of a line segment connecting two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) represents its steepness and is calculated as:
Slope = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
Practice Problems Incorporating Distance and Slope:
- Find the distance between the points (1, 2) and (4, 6).
- Find the slope of the line segment connecting the points (-2, 3) and (4, -1).
- Find the midpoint of the line segment and then calculate the distance from the midpoint to each endpoint for the points (2, 5) and (8, 1). Are these distances equal? What does this tell you?
Answer Key:
- Distance = √((4 - 1)² + (6 - 2)²) = √(3² + 4²) = √25 = 5
- Slope = (-1 - 3) / (4 - (-2)) = -4 / 6 = -2/3
- Midpoint M = ((2+8)/2, (5+1)/2) = (5,3). Distance from M to (2,5): √((5-2)² + (3-5)²) = √13. Distance from M to (8,1): √((8-5)² + (1-3)²) = √13. Yes, the distances are equal. This confirms that the midpoint indeed divides the line segment into two equal parts.
Real-World Applications of Locating Points and Midpoints
While seemingly abstract, the skills of locating points and midpoints find practical applications in numerous fields:
- Mapping and Navigation: GPS systems rely heavily on coordinate systems to pinpoint locations. Midpoint calculations can be used to find the halfway point between two destinations.
- Computer Graphics: Computer-generated images and animations are built using coordinate systems. Locating points and midpoints is fundamental in defining shapes, movements, and transformations.
- Engineering and Construction: Engineers use coordinate systems to design and construct buildings and infrastructure. Precise point location is essential for accuracy and safety.
- Game Development: In video games, characters and objects are positioned and moved using coordinates. Midpoints can be crucial in calculating collision detection and pathfinding.
- Data Analysis: In statistical analysis, data is often represented visually on coordinate systems. Understanding points and midpoints can help interpret trends and patterns.
Tips and Strategies for Mastering Point and Midpoint Location
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering these skills. Work through numerous problems, varying the types of coordinates used.
- Visualize: Always visualize the coordinate plane when solving problems. Drawing a sketch can help you understand the relationships between points.
- Check Your Work: After solving a problem, carefully check your work. Ensure that your calculations are accurate and your answers make sense in the context of the problem.
- Use Technology: Utilize online calculators and graphing tools to verify your answers and gain a better visual understanding of the concepts.
- Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask for help from a teacher, tutor, or classmate if you're struggling with a concept.
This guide provided a thorough exploration of locating points and midpoints, incorporating practice problems with answer keys and real-world applications. By mastering these fundamental skills, you lay a strong foundation for more advanced geometrical concepts and pave the way for success in various academic and professional pursuits. Remember that consistent practice and a clear understanding of the underlying principles are crucial for achieving proficiency in this area of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Virtual Lab Electrochemical Cells Answer Key
Mar 11, 2025
-
3 04 I See What Doesnt Belong
Mar 11, 2025
-
Causes Of The Civil War Slotted Notes Answer Key
Mar 11, 2025
-
Read The Following Excerpt From Federalist
Mar 11, 2025
-
A Computer Typically Connects To A Router Via A
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1-3 Skills Practice Locating Points And Midpoints Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
