1-3 Skills Practice Locating Points And Midpoints Answers
Onlines
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
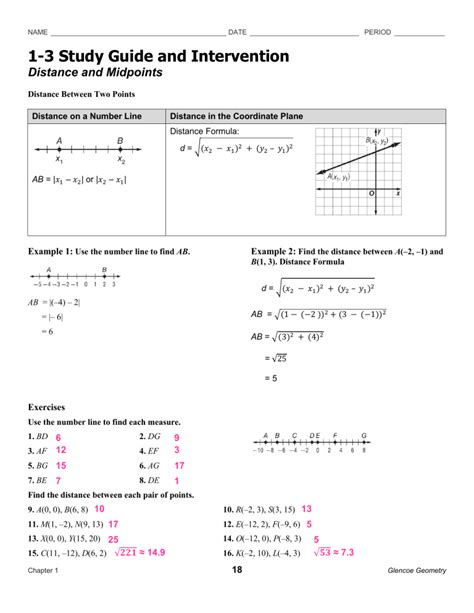
Table of Contents
Mastering Coordinate Geometry: A Deep Dive into Locating Points and Midpoints
Coordinate geometry, a fundamental branch of mathematics, forms the bedrock for understanding spatial relationships. Proficiency in locating points and midpoints is crucial for success in higher-level mathematics and related fields like computer graphics, engineering, and physics. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed exploration of these core concepts, supplemented with illustrative examples and practice exercises to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Cartesian Coordinate System
Before delving into point and midpoint location, let's establish a strong foundation in the Cartesian coordinate system. This system, named after René Descartes, uses two perpendicular lines – the x-axis (horizontal) and the y-axis (vertical) – to define a two-dimensional plane. The point where these axes intersect is called the origin, denoted as (0,0).
Every point on the plane is uniquely identified by its coordinates, an ordered pair (x, y). The x-coordinate represents the horizontal distance from the origin, while the y-coordinate represents the vertical distance. Positive values indicate movement to the right (x) or up (y) from the origin, while negative values indicate movement to the left (x) or down (y).
Example: The point (3, 2) is located 3 units to the right of the origin and 2 units above it. The point (-1, -4) is located 1 unit to the left and 4 units below the origin.
Locating Points on the Coordinate Plane
Locating points on the coordinate plane is a straightforward process:
- Identify the x-coordinate: This value determines the horizontal position.
- Identify the y-coordinate: This value determines the vertical position.
- Plot the point: Starting from the origin, move horizontally according to the x-coordinate and then vertically according to the y-coordinate. The intersection of these movements marks the location of the point.
Practice Exercise 1: Plot the following points on a coordinate plane: (2, 5), (-3, 1), (0, -2), (4, 0), (-1, -3).
Calculating the Distance Between Two Points
Determining the distance between two points on a coordinate plane involves applying the distance formula, derived from the Pythagorean theorem. Given two points, (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂), the distance 'd' between them is calculated as:
d = √[(x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
Example: Find the distance between points A(2, 3) and B(6, 7).
- Substitute the coordinates: d = √[(6 - 2)² + (7 - 3)²]
- Simplify: d = √[4² + 4²] = √(16 + 16) = √32
- Simplify further (if possible): d = 4√2
Practice Exercise 2: Calculate the distance between the following pairs of points:
- (1, 4) and (5, 8)
- (-2, 3) and (4, -1)
- (0, 0) and (3, 4)
Finding the Midpoint of a Line Segment
The midpoint of a line segment is the point that divides the segment into two equal parts. Given two points, (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂), the midpoint (xₘ, yₘ) is calculated using the midpoint formula:
xₘ = (x₁ + x₂) / 2 yₘ = (y₁ + y₂) / 2
Essentially, the midpoint's x-coordinate is the average of the x-coordinates of the endpoints, and similarly for the y-coordinate.
Example: Find the midpoint of the line segment connecting points C(-2, 5) and D(4, 1).
- Apply the midpoint formula: xₘ = (-2 + 4) / 2 = 1 yₘ = (5 + 1) / 2 = 3
- The midpoint is (1, 3).
Practice Exercise 3: Find the midpoints of the line segments connecting the following pairs of points:
- (3, 7) and (9, 1)
- (-4, 2) and (6, -2)
- (0, 5) and (8, 0)
Advanced Applications and Problem Solving
The concepts of locating points and midpoints form the foundation for solving more complex problems in coordinate geometry. Here are a few examples:
1. Determining if points are collinear: Three or more points are collinear if they lie on the same straight line. This can be verified by calculating the slopes between consecutive pairs of points. If the slopes are equal, the points are collinear.
2. Finding the equation of a line: Knowing the coordinates of two points on a line allows you to determine its equation using the point-slope form or the slope-intercept form.
3. Solving geometric problems: Many geometric problems, such as finding the area of a triangle or the length of a diagonal in a rectangle, can be easily solved using coordinate geometry. For instance, the area of a triangle with vertices (x₁, y₁), (x₂, y₂), and (x₃, y₃) can be calculated using the determinant formula.
4. Applications in 3D Coordinate Systems: The concepts extend naturally to three-dimensional spaces, involving the x, y, and z axes. Similar formulas can be applied to locate points and calculate distances and midpoints in 3D space.
Real-World Applications
The skills learned in locating points and midpoints have wide-ranging practical applications:
-
Computer Graphics: Creating and manipulating images on a computer screen relies heavily on coordinate geometry. Points represent pixels, and calculations involving points and midpoints are essential for transformations, animations, and other visual effects.
-
Mapping and GPS: GPS systems rely on coordinate systems to pinpoint locations on Earth. Calculating distances and midpoints between locations is crucial for navigation and route planning.
-
Engineering and Construction: Coordinate geometry is used extensively in surveying, construction, and architectural design to accurately determine positions, distances, and sizes.
-
Game Development: Video games use coordinate systems to represent the positions of game objects, characters, and the environment. Calculations involving points and midpoints are used extensively for movement, collisions, and other game mechanics.
Conclusion: Continuous Practice is Key
Mastering coordinate geometry requires consistent practice. The more problems you solve, the more comfortable you'll become with locating points, calculating distances, and finding midpoints. Start with the basic exercises provided in this guide and gradually progress to more challenging problems. Don't hesitate to consult additional resources and seek help when needed. By consistently applying these principles, you'll build a solid foundation in coordinate geometry that will benefit you in various mathematical and real-world applications. Remember, the key to success lies in understanding the fundamental concepts and consistently practicing their application. With dedication and perseverance, you will undoubtedly master these essential skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does Set And Coordinate Distribution Objectives Mean
Mar 25, 2025
-
Check All Possible Effects Of This Selective Pressure
Mar 25, 2025
-
Welcome To Yellowstone Park Is An Example Of A
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Is Not True Of Cooking Foods In A Microwave
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Term Institutionalization Can Be Defined As
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1-3 Skills Practice Locating Points And Midpoints Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
