11.7 8 Configure A Dsl Internet Connection
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 8 min read
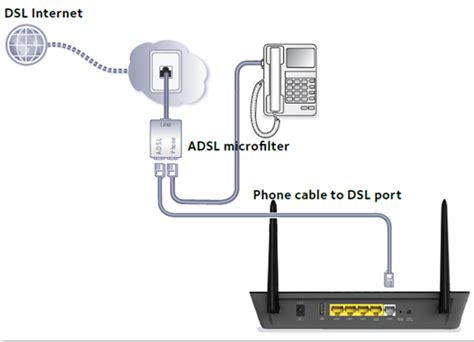
Table of Contents
Configuring a DSL Internet Connection: A Comprehensive Guide
Connecting to the internet via DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) might seem daunting, but with the right steps, it's a straightforward process. This comprehensive guide walks you through the entire process, from initial setup to troubleshooting common issues. We'll cover everything you need to know to get your DSL connection up and running smoothly.
Understanding Your DSL Setup: The Foundation
Before diving into the configuration, let's establish a strong foundation by understanding the core components involved in setting up a DSL internet connection. This includes:
1. Your DSL Modem: The Gateway to the Internet
The DSL modem is the crucial piece of hardware that translates your phone line's digital signals into data your computer can understand. It acts as the bridge between your home's phone line and the internet. Ensure your modem is compatible with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and the type of DSL service you've subscribed to. There are different types of DSL (ADSL, VDSL, etc.), and incompatibility can prevent a connection.
2. Your Router (Optional but Recommended): Sharing the Connection
While a modem is sufficient for a single device, a router allows you to share your DSL internet connection among multiple devices (computers, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, etc.) simultaneously. A router creates a local area network (LAN) within your home, enabling wireless connectivity and improved network management. Most modern routers also include features like firewalls for enhanced security.
3. Ethernet Cables: The Wired Connection
Ethernet cables provide a stable and high-speed wired connection between your modem, router (if used), and your devices. Wired connections generally offer superior performance and reliability compared to wireless connections. Use high-quality cables to avoid connection drops or slow speeds.
4. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP): The Service Provider
Your ISP is the company that provides the DSL internet service to your home. They'll supply you with your modem (sometimes), username, and password, which are essential for connecting to the internet. Contact your ISP if you have trouble locating these details or need technical assistance. They are your primary resource for troubleshooting.
Step-by-Step DSL Internet Connection Configuration
Now, let's walk through the practical steps of configuring your DSL internet connection. This process is generally similar across different ISPs, but minor variations might exist.
1. Physical Connections: Setting up the Hardware
- Connect the phone line: Plug the phone line from your wall jack into the DSL modem's corresponding port.
- Connect the modem to the router (if applicable): Use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem to your router's "WAN" or "Internet" port.
- Connect your devices to the router: Connect your computers, smartphones, tablets, etc., to the router either via Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi.
2. Modem Configuration: Getting Online
Once the physical connections are established, you need to configure your modem. This usually involves:
- Powering on the modem: Plug in the power adapter and wait for the modem's lights to indicate that it's receiving a signal and is connected to your ISP. The lights usually have specific meanings, referred to in the modem's manual.
- Accessing the modem's interface: Many ISPs provide a default gateway IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) for modem access. Open a web browser and type this address into the address bar. You will be prompted to log in with a username and password. These details can often be found on a sticker on the modem or in the documentation provided by your ISP. Some modems automatically configure themselves after receiving a signal from the ISP.
- Checking connection status: Once you've accessed the modem's interface, verify that it has established a connection to your ISP. Check for signal strength, signal to noise ratio (SNR), and other relevant parameters. If you encounter problems during this phase, refer to your modem's documentation or contact your ISP's technical support.
3. Router Configuration (if applicable): Setting up your Network
If you're using a router, you'll need to configure it after the modem is connected. This often involves:
- Accessing the router's interface: Similar to the modem, you'll need to access your router's interface via a web browser by entering its IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Refer to the router's documentation for specific instructions.
- Setting up the Wi-Fi network: Configure your router's Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and password. Choose a strong password to secure your network.
- Configuring security settings: Enable a robust security protocol (like WPA2 or WPA3) to protect your wireless network from unauthorized access.
- Advanced settings (Optional): Explore your router's advanced settings to configure features like Quality of Service (QoS), port forwarding, guest networks, and parental controls, as needed.
4. Verifying Internet Connectivity: Testing Your Connection
After completing the setup, test your internet connection. Try browsing the web, checking your email, or streaming videos. If your internet connection is functioning correctly, you should be able to access online resources without issue. If you experience problems, refer to the troubleshooting section below.
Troubleshooting Common DSL Internet Connection Problems
Despite careful setup, you might encounter issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
1. No Internet Connection: The Most Common Problem
If you can't connect to the internet, check the following:
- Modem and router lights: Ensure that the lights on your modem and router indicate that they are properly connected and functioning.
- Physical connections: Double-check all cable connections to ensure they are secure and properly plugged in.
- ISP service status: Verify that your ISP's service isn't experiencing an outage. Check their website or contact their customer support.
- Username and password: Confirm that you've entered the correct username and password for your ISP account.
- Firewall settings: Ensure that your firewall isn't blocking internet access. Temporarily disable your firewall to see if this solves the problem. If it does, you will need to configure your firewall rules appropriately to allow internet access.
2. Slow Internet Speed: Optimization Strategies
Slow internet speeds can be frustrating. Consider these factors:
- Line quality: Poor line quality can significantly impact your DSL speeds. Contact your ISP to discuss potential issues with the line.
- Network congestion: Heavy network traffic can slow down your speeds. Try connecting at off-peak hours to see if speeds improve.
- Interference: Wireless interference from other devices can affect your internet speed. Try moving your router or using a wired connection.
- Outdated equipment: An older modem or router might not be able to handle modern internet speeds. Consider upgrading your equipment.
- Too many devices: Having many devices connected simultaneously can decrease individual device speeds. Consider disconnecting some devices if speeds are unusually slow.
3. Intermittent Connection: Addressing Dropouts
Intermittent connections can stem from several sources:
- Line quality issues: Similar to slow speeds, poor line quality can cause intermittent connection drops. Contact your ISP to investigate line problems.
- Power fluctuations: Power outages or surges can disrupt your internet connection. Consider using a surge protector to safeguard your equipment.
- Modem or router problems: A faulty modem or router can lead to intermittent connections. Try rebooting your equipment, and if the problem persists, consider replacing the faulty device.
- Software conflicts: Software conflicts on your computer might disrupt internet connectivity. Restart your computer to resolve software issues.
4. Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems: Enhancing Wireless Performance
If you are experiencing Wi-Fi connectivity problems:
- Router placement: Poor router placement can significantly reduce Wi-Fi signal strength. Place the router in a central location, away from obstructions like walls and large metal objects.
- Wireless interference: Other wireless devices operating on the same frequency (2.4GHz or 5GHz) can interfere with your Wi-Fi network. Try switching to the less congested frequency or changing your Wi-Fi channel.
- Wi-Fi signal strength: Weak Wi-Fi signal strength can lead to connectivity problems. Consider using a Wi-Fi extender or mesh network to improve coverage.
- Password issues: Ensure you are using the correct Wi-Fi password to connect to the network.
Advanced DSL Configuration Options
For users seeking more control over their DSL connection, some advanced configuration options are available:
- Quality of Service (QoS): This feature prioritizes certain types of network traffic, ensuring smooth streaming or online gaming, even with high network usage. This is a router-specific setting.
- Port Forwarding: This allows you to forward specific ports to devices on your network, enabling access to services running on these devices from the internet. This is also typically done via your router's interface.
- Dynamic DNS: If you have services running on your network that need to be accessible from the internet, dynamic DNS can provide a consistent domain name even if your public IP address changes.
Conclusion: Mastering Your DSL Connection
Setting up a DSL internet connection and troubleshooting minor issues might seem challenging initially. However, by understanding the components involved, following the step-by-step configuration instructions, and utilizing the troubleshooting tips provided in this comprehensive guide, you can confidently establish and maintain a reliable and high-performing DSL internet connection in your home. Remember to always refer to your modem and router's documentation for specific instructions and contact your ISP's technical support for assistance if you encounter persistent problems. This guide provides a thorough overview, but individual situations may require additional problem-solving and research.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
While Reviewing Clinical Notes With Replacement Nurses
Mar 06, 2025
-
Advance Study Assignment Densities Of Solids And Liquids
Mar 06, 2025
-
Your New Material May Aggregate Or Bring Together
Mar 06, 2025
-
Why Doe Papa Pray Chapter 10
Mar 06, 2025
-
How To Get Coursehero For Free
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 11.7 8 Configure A Dsl Internet Connection . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
