12.4.6 Check Your Understanding - Capwap Operation
Onlines
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
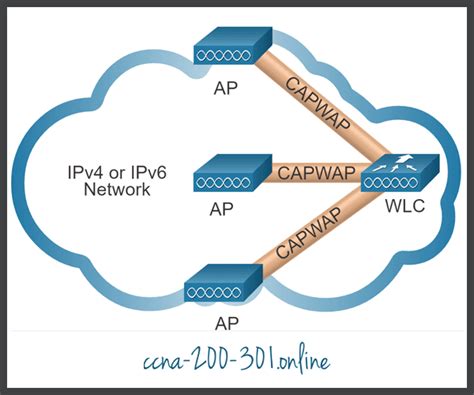
Table of Contents
12.4.6 Check Your Understanding: CAPWAP Operation – A Deep Dive
Understanding the intricacies of CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) is crucial for anyone managing a wireless network. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key aspects of CAPWAP operation, addressing common questions and misconceptions. We'll explore the protocol's architecture, its role in managing wireless access points (APs), and the various mechanisms it employs to ensure seamless network connectivity and efficient management. By the end of this article, you will possess a solid grasp of CAPWAP and its significance in modern wireless networks.
CAPWAP Architecture: A Foundation for Understanding
CAPWAP isn't just a single protocol; it's a layered architecture designed for robust wireless management. This architecture allows for scalability, flexibility, and resilience in even the largest wireless deployments. Key components include:
1. Wireless Access Point (AP): The Edge of the Network
The AP is the fundamental building block, responsible for communicating with client devices and forwarding data to the wired network. In a CAPWAP environment, the AP operates as a lightweight client, offloading complex tasks to the Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). This allows for simpler, less resource-intensive AP designs.
2. Wireless LAN Controller (WLC): The Central Brain
The WLC is the central management unit, responsible for configuration, monitoring, and control of all APs within its domain. It acts as the "brain" of the wireless network, handling tasks such as authentication, security, radio resource management, and roaming. The WLC communicates with the APs using CAPWAP.
3. Network Infrastructure: The Backbone
The underlying network infrastructure, typically Ethernet, connects the WLC to the APs and the rest of the network. This infrastructure needs to be reliable and robust to ensure consistent communication between the WLC and the APs. Network performance directly impacts the efficiency of CAPWAP operations.
CAPWAP Tunneling: Secure and Efficient Communication
CAPWAP utilizes a secure tunneling mechanism to encapsulate management and data traffic between the AP and the WLC. This tunneling ensures confidentiality and integrity of the communication. Key aspects of CAPWAP tunneling include:
1. Encapsulation: Protecting the Data
CAPWAP encapsulates management traffic and client data into secure tunnels. This encapsulation protects sensitive information from eavesdropping and tampering. The precise method of encapsulation depends on the underlying network infrastructure but often leverages established technologies like UDP or DTLS.
2. Security Mechanisms: Ensuring Confidentiality and Integrity
Various security protocols work in conjunction with CAPWAP to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of the communication. This typically includes methods like encryption and authentication to prevent unauthorized access and data manipulation. Proper security configuration is crucial for a secure wireless network.
3. Multiplexing: Efficient Use of Bandwidth
CAPWAP effectively multiplexes both management and data traffic over the same tunnel, optimizing bandwidth utilization. This multiplexing allows for efficient communication between the AP and the WLC without requiring separate channels for management and data.
CAPWAP Management Capabilities: Streamlining Wireless Network Management
CAPWAP's strength lies in its sophisticated management capabilities. These capabilities significantly simplify the administration of large and complex wireless networks:
1. Centralized Configuration: Simplifying Deployment and Maintenance
The WLC allows for centralized configuration of all APs under its control. This means administrators can apply configurations to multiple APs simultaneously, saving time and effort. This centralized approach streamlines the process of deploying and maintaining the wireless network.
2. Remote Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Proactive Network Management
The WLC provides real-time monitoring capabilities, enabling administrators to track the status of individual APs and the entire wireless network. This enables proactive troubleshooting and preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime and improving overall network reliability.
3. Firmware Updates and Upgrades: Ensuring Network Consistency and Security
CAPWAP facilitates seamless firmware updates and upgrades for APs, ensuring that all APs run the latest software versions. This maintains network consistency, improves performance, and enhances security by addressing vulnerabilities promptly.
4. Dynamic Spectrum Management: Optimizing Radio Resource Utilization
CAPWAP empowers the WLC to dynamically manage radio resources, optimizing the use of available radio frequencies. This improves network performance and ensures efficient handling of increased client demands. This dynamic management is crucial in high-density environments.
CAPWAP Data Forwarding: Efficient Client Connectivity
CAPWAP efficiently handles data forwarding to ensure seamless client connectivity:
1. Data Plane: Handling Client Traffic
CAPWAP utilizes a dedicated data plane to forward client traffic between the AP and the WLC. This efficient data plane ensures minimal latency and maximum throughput for client devices.
2. Seamless Roaming: Maintaining Client Connectivity
CAPWAP supports seamless roaming, allowing clients to seamlessly move between APs without losing connectivity. This is achieved through coordination between the APs and the WLC, ensuring a smooth transition for the client.
3. Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizing Critical Traffic
CAPWAP enables the implementation of QoS mechanisms, allowing administrators to prioritize critical traffic, such as VoIP or video streaming. This prioritization ensures optimal performance for these demanding applications.
CAPWAP vs. Lightweight Access Points (LWAPP): Understanding the Differences
While both CAPWAP and LWAPP (Lightweight Access Point Protocol) serve similar purposes, there are key differences:
1. Security: Enhanced Security in CAPWAP
CAPWAP offers enhanced security features compared to LWAPP, utilizing secure tunneling protocols to protect communication between the AP and the WLC.
2. Scalability: Improved Scalability in CAPWAP
CAPWAP typically scales better than LWAPP, supporting larger and more complex wireless deployments. This enhanced scalability is a critical advantage in large enterprise environments.
3. Interoperability: Greater Flexibility in CAPWAP
CAPWAP exhibits greater interoperability with various vendors' equipment compared to LWAPP, offering greater flexibility in network deployments.
Troubleshooting CAPWAP Issues: Common Problems and Solutions
Despite its robustness, CAPWAP deployments can encounter issues. Understanding common problems and their solutions is essential for efficient network management:
1. Connectivity Issues: Addressing AP-WLC Communication Problems
Connectivity issues between APs and the WLC are common. Troubleshooting steps include verifying network cabling, checking IP addressing, and ensuring that firewalls are properly configured.
2. Authentication Problems: Ensuring Secure Access
Authentication problems can prevent APs from connecting to the WLC. Checking authentication credentials, verifying certificates, and ensuring proper configuration are crucial steps.
3. Performance Issues: Optimizing Network Efficiency
Performance issues may result from various factors, such as radio interference, insufficient bandwidth, or improper configuration. Optimizing radio settings, adjusting bandwidth allocation, and refining network configurations are essential for addressing performance bottlenecks.
Conclusion: CAPWAP as a Cornerstone of Modern Wireless Networking
CAPWAP remains a critical component of modern wireless networking, offering robust management, secure communication, and efficient data forwarding. Understanding its architecture, functionalities, and troubleshooting techniques is essential for anyone involved in deploying and managing wireless networks. By mastering CAPWAP, network administrators can ensure efficient, secure, and reliable wireless connectivity for their users. This deep dive has provided a thorough understanding of CAPWAP operation, enabling you to confidently navigate the complexities of wireless network management and troubleshooting. Remember that continuous learning and adapting to evolving wireless technologies are key to maintaining a robust and efficient wireless network.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Topic 2 Assessment Form B Answer Key
Mar 15, 2025
-
Characters The Catcher In The Rye
Mar 15, 2025
-
Tdx Arena Hack N Seek Solution Reddit
Mar 15, 2025
-
Tuesdays With Morrie Summary Of Each Chapter
Mar 15, 2025
-
Practice Putting It All Together Answer Key
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 12.4.6 Check Your Understanding - Capwap Operation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
