2-3 Practice Rate Of Change And Slope
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 7 min read
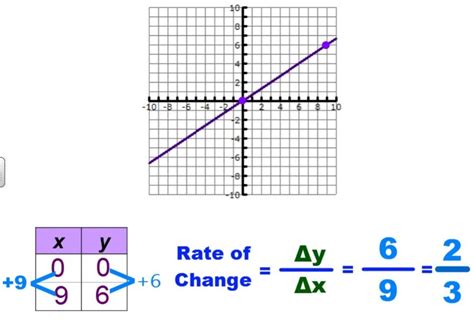
Table of Contents
Understanding Rate of Change and Slope: A Deep Dive with Practice Problems
The concepts of rate of change and slope are fundamental in mathematics, particularly in algebra, calculus, and data analysis. While seemingly simple, a thorough grasp of these concepts is crucial for understanding more complex mathematical ideas and their applications in various fields. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of rate of change and slope, including detailed explanations, practical examples, and numerous practice problems to solidify your understanding.
What is Rate of Change?
Rate of change describes how one quantity changes in relation to another. It quantifies the relationship between a dependent variable and an independent variable. In simpler terms, it answers the question: "How much does one thing change when another thing changes?"
Key characteristics of rate of change:
- It's a ratio: Rate of change is always expressed as a ratio, comparing the change in the dependent variable to the change in the independent variable.
- It can be positive, negative, or zero: A positive rate of change indicates an increase in the dependent variable as the independent variable increases. A negative rate indicates a decrease, while a zero rate means no change.
- It's context-dependent: The interpretation of a rate of change depends heavily on the specific variables involved. For example, a rate of change of 5 miles per hour has a different meaning than a rate of change of 5 dollars per item.
Examples of Rate of Change in Real-World Scenarios:
- Speed: The rate of change of distance with respect to time (e.g., miles per hour, kilometers per second).
- Growth Rate: The rate of change of a population over time (e.g., individuals per year).
- Inflation Rate: The rate of change of prices over time (e.g., percentage per year).
- Fuel Efficiency: The rate of change of distance traveled with respect to fuel consumed (e.g., miles per gallon).
What is Slope?
In mathematics, slope is a measure of the steepness and direction of a line. It represents the rate of change of the vertical distance (rise) with respect to the horizontal distance (run) between any two points on the line. The slope of a line is constant throughout its length.
Formula for calculating slope:
The slope (m) of a line passing through two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) is calculated using the following formula:
m = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
Where:
(y₂ - y₁)represents the vertical change (rise).(x₂ - x₁)represents the horizontal change (run).
Interpreting Slope:
- Positive Slope: A positive slope indicates a line that rises from left to right. The larger the positive slope, the steeper the line.
- Negative Slope: A negative slope indicates a line that falls from left to right. The larger the absolute value of the negative slope, the steeper the line.
- Zero Slope: A zero slope indicates a horizontal line. There is no change in the y-value as the x-value changes.
- Undefined Slope: An undefined slope indicates a vertical line. The formula for slope becomes undefined because the denominator (x₂ - x₁) is zero.
The Relationship Between Rate of Change and Slope
Rate of change and slope are intrinsically linked. The slope of a line represents the rate of change of the dependent variable with respect to the independent variable. When dealing with linear relationships (represented by straight lines), the slope is the constant rate of change.
For example, if a line represents the relationship between distance and time, its slope is equal to the speed (rate of change of distance with respect to time). If the slope is 60 mph, it means the distance changes by 60 miles for every 1 hour increase in time.
Practice Problems: Rate of Change and Slope
Let's delve into some practice problems to solidify your understanding of rate of change and slope. We'll work through various scenarios, highlighting different aspects of these concepts.
Problem 1: A car travels 240 miles in 4 hours. What is the average rate of change of the car's distance with respect to time?
Solution:
The rate of change (speed) is calculated as:
Rate of change = (Change in distance) / (Change in time) = 240 miles / 4 hours = 60 miles per hour
Problem 2: Find the slope of the line passing through points A(2, 3) and B(6, 9).
Solution:
Using the slope formula:
m = (9 - 3) / (6 - 2) = 6 / 4 = 3/2 = 1.5
The slope of the line is 1.5.
Problem 3: The population of a city increased from 10,000 to 12,500 in 5 years. What is the average rate of change of the population?
Solution:
Rate of change = (12,500 - 10,000) / 5 years = 2,500 / 5 years = 500 people per year
Problem 4: A graph shows the relationship between the number of hours worked and the amount of money earned. The points (2, 20) and (5, 50) are on the line. Find the slope and interpret its meaning.
Solution:
m = (50 - 20) / (5 - 2) = 30 / 3 = 10
The slope is 10. This means that for every 1 hour worked, the amount of money earned increases by $10. The slope represents the hourly wage.
Problem 5: The table shows the height of a plant over time.
| Time (weeks) | Height (cm) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 4 | 14 |
| 6 | 20 |
Find the average rate of change of the plant's height over the entire 6-week period.
Solution:
Rate of change = (20 - 2) / (6 - 0) = 18 / 6 = 3 cm/week
The average rate of change of the plant's height is 3 cm per week.
Problem 6: A line has a slope of -2 and passes through the point (1, 4). Find the equation of the line in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b).
Solution:
We know the slope (m) is -2 and a point (x₁, y₁) = (1, 4). The slope-intercept form is y = mx + b. Substitute the known values:
4 = -2(1) + b
Solving for b:
b = 6
Therefore, the equation of the line is y = -2x + 6
Problem 7: Explain why a vertical line has an undefined slope.
Solution:
A vertical line has an undefined slope because the change in x (the run) is always zero. The slope formula involves dividing by the change in x, and division by zero is undefined in mathematics.
Problem 8: Two points are given: (-3, 5) and (1, -1). Calculate the slope and determine if the line is increasing or decreasing.
Solution:
m = (-1 - 5) / (1 - (-3)) = -6 / 4 = -3/2 = -1.5
The slope is -1.5, which is negative. Therefore, the line is decreasing.
Problem 9 (Challenge): The cost of producing x units of a product is given by the function C(x) = 500 + 10x. What is the rate of change of the cost with respect to the number of units produced? Interpret your answer in the context of the problem.
Solution:
The function C(x) = 500 + 10x is a linear function. The slope of this linear function is 10. This means that for every additional unit produced, the cost increases by $10. The rate of change of the cost is $10 per unit. This represents the marginal cost of production—the cost of producing one more unit.
These practice problems demonstrate the application of rate of change and slope in various contexts. Remember that understanding the underlying principles and practicing regularly is key to mastering these fundamental mathematical concepts. Continue exploring different types of problems and applying the concepts to real-world scenarios to further strengthen your understanding. The more you practice, the more intuitive these concepts will become. Remember to always check your work and ensure your answers make sense within the context of the problem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Baby In The Photo Required Chest Compressions
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Left Hand Of Darkness Notes
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Turn Of The Screw Chapter Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
Cat On A Hot Tin Roof Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
Serendipity Love In The Time Of Cholera
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2-3 Practice Rate Of Change And Slope . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
