6.5.10 Create And Link A Gpo
Onlines
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
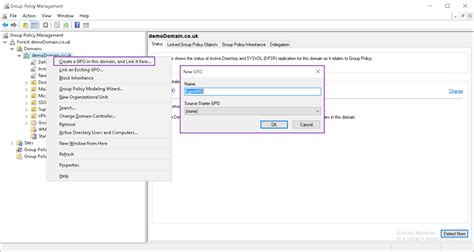
Table of Contents
6.5.10: Creating and Linking a GPO: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating and linking Group Policy Objects (GPOs) is a cornerstone of effective Windows domain administration. GPOs allow you to centrally manage settings for users and computers within your organization, ensuring consistency, security, and streamlined IT management. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of creating and linking a GPO, covering various scenarios and best practices. We'll delve into the intricacies of linking GPOs to different Organizational Units (OUs) and the impact of link order.
Understanding Group Policy Objects (GPOs)
Before we dive into the creation and linking process, let's establish a solid understanding of what GPOs are and why they are crucial for efficient domain management.
What is a GPO? A Group Policy Object is a collection of settings that determine how computers and users within a domain behave. These settings range from simple things like desktop wallpapers and screen savers to complex security configurations, software installations, and network settings. By centralizing these settings in GPOs, administrators can easily manage and enforce consistent configurations across their entire network.
Why Use GPOs? The benefits of utilizing GPOs are numerous:
- Centralized Management: Manage settings for hundreds or thousands of machines from a single point.
- Improved Security: Enforce security policies consistently, reducing vulnerabilities.
- Streamlined Software Deployment: Deploy and update software effortlessly across the organization.
- Enhanced User Experience: Customize the user environment for improved productivity.
- Reduced IT Overhead: Automate tasks and reduce the need for manual configuration.
- Version Control: Maintain a history of policy changes for easier troubleshooting and rollback.
Creating a GPO
The process of creating a new GPO is straightforward and can be accomplished through the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.MSC).
Step 1: Open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.msc)
Locate and run gpmc.msc either through the Run dialog (Win + R) or by searching for it in the Start Menu.
Step 2: Navigate to the Domain or OU
In the GPMC console, expand the domain and locate the Organizational Unit (OU) where you want to link the new GPO. Choosing the appropriate OU is critical for scope and efficiency. Linking a GPO to a higher-level OU applies the settings to all child OUs and their members. Linking to a lower-level OU provides more granular control but requires more GPOs.
Step 3: Create the GPO
Right-click on the selected OU and choose "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…".
Step 4: Name the GPO
Give your GPO a descriptive and meaningful name. This will help in identifying the GPO's purpose and managing multiple GPOs in the future. For example, "Software Deployment - Office 2019," or "Security Settings - Restricted Internet Access."
Step 5: Edit the GPO (Optional)
After creating the GPO, you can immediately edit its settings. Right-click the newly created GPO and select "Edit." This will open the Group Policy Management Editor, where you can configure various settings. This is where you'll define your specific policies, ranging from user configurations to computer configurations.
Linking a GPO
Linking a GPO is the process of associating the GPO with a specific OU. This determines which users and computers are affected by the policies defined within the GPO.
Step 1: Link Order Matters
Understanding Link Order is crucial. When multiple GPOs are linked to the same OU, their policies are applied in a specific order. The order is determined by the order they appear in the OU's GPO list. The GPO appearing first has precedence; its settings override those of any GPOs listed below.
Step 2: Linking a GPO to an OU (using the GPMC)
As we mentioned before, this step is essentially done during creation, but you can always link a pre-existing GPO to a different OU later:
- Find the GPO in the GPMC.msc console.
- Right-click the GPO and select "Link to."
- Navigate to the target OU and click "OK."
Step 3: Checking Link Order
After linking the GPO, you should check its order relative to other GPOs linked to the same OU. This is critical for resolving conflicts and ensuring intended settings are applied.
Advanced GPO Scenarios and Best Practices
Let's explore some advanced scenarios and best practices for efficient GPO management:
1. Nested OUs and GPO Inheritance:
When you link a GPO to a parent OU, its settings are inherited by all child OUs unless explicitly blocked. This inheritance allows for efficient management of large organizations. You can selectively block inheritance at any child OU to create exceptions to the parent OU's settings.
2. Delegation of Control:
You can delegate specific administrative rights over GPOs to other users or groups. This improves security and allows for more efficient task distribution within your IT team.
3. Filtering GPOs:
You can use Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filtering to apply GPOs only to specific computers or users that meet certain criteria. This is a powerful technique for granular control. For instance, you can apply a GPO only to computers running a specific operating system version or only to users in a specific department.
4. Group Policy Preferences:
Group Policy Preferences (GPP) provide a more flexible and granular approach to configuring settings compared to traditional Group Policy settings. GPP allows for more customization and better handling of conflicting settings.
5. Using the gpresult command:
The gpresult command-line tool is invaluable for troubleshooting GPO issues. It displays the applied GPOs and their settings for a particular computer or user, helping you determine which GPO is responsible for a specific setting.
6. Regularly Auditing and Reviewing GPOs:
Establish a regular schedule for auditing and reviewing your GPOs. This ensures that your policies remain up-to-date, relevant, and secure.
7. Testing GPOs in a Test Environment:
Before deploying GPOs to your production environment, thoroughly test them in a test environment that mirrors your production infrastructure. This mitigates the risk of unexpected issues and ensures that your policies work as intended.
8. Documenting Your GPOs:
Maintain comprehensive documentation for each GPO, including its purpose, settings, and any potential dependencies. This documentation will be invaluable for troubleshooting, maintenance, and future modifications.
9. Using Central Store:
Utilize the Central Store to centrally manage and store your GPOs. This aids in efficient backup and restoration of your policies.
10. Understanding GPO Replication:
GPOs are replicated throughout the domain via the Active Directory. Understanding this replication process is crucial for troubleshooting replication issues.
Troubleshooting Common GPO Issues
Several common issues can arise during GPO creation and deployment. Here are some troubleshooting steps:
- GP Result: Run
gpresult /h gpresult.htmlto generate a detailed report of the GPOs applied to a computer. This is invaluable in identifying which GPO is applying or overriding particular settings. - Event Viewer: Check the Event Viewer (Application and System logs) for any errors related to Group Policy processing. Error messages often pinpoint the cause of the problem.
- Active Directory Replication: Ensure Active Directory replication is functioning correctly. If replication fails, GPOs may not be applied correctly.
- Loopback Processing: Be mindful of Loopback Processing settings. This feature determines how Group Policy affects users when they log on to computers.
- Security Filtering: Incorrectly configured security filtering can prevent a GPO from being applied. Review the security settings associated with the GPO.
- Link Order: Incorrect GPO link order can lead to unexpected settings. Always verify the link order within the OUs to ensure the intended precedence.
- WMI Filtering: If using WMI filtering, ensure the filters are correctly configured and that the query returns the expected results.
By carefully following these steps and understanding the nuances of Group Policy Objects, you can effectively manage your Windows domain, ensuring consistent configurations, robust security, and a streamlined IT environment. Remember, thorough planning, testing, and documentation are essential for successful GPO implementation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Perfect Parties Inc Has Several Divisions
Apr 02, 2025
-
Data On Health Physical Activity And Sports Indicates That
Apr 02, 2025
-
Night Chapter 5 Questions And Answers Pdf
Apr 02, 2025
-
Carter Racing Case Study Solution Pdf
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Good Behavioral Definition Of A Behavior Involves
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 6.5.10 Create And Link A Gpo . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
