A Home Must Be ______ Green To Be Leed Qualified.
Onlines
Mar 06, 2025 · 7 min read
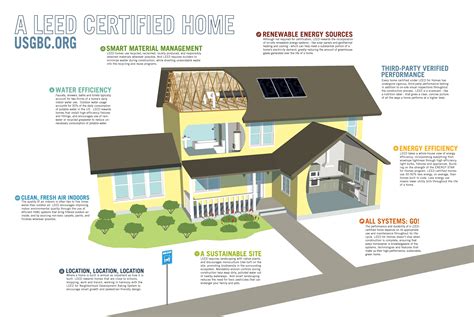
Table of Contents
A Home Must Be Remarkably Green to Be LEED Qualified
The pursuit of sustainable living has spurred a global movement towards eco-conscious construction and design. In this realm, LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification stands as a gold standard, signifying a building's commitment to environmental responsibility. But what exactly does it take for a home to achieve this prestigious certification? The answer is multifaceted, requiring a commitment to a remarkably green approach throughout the entire building process, from initial design to final construction and beyond. This article delves into the stringent requirements a home must meet to achieve LEED qualification, exploring the key areas where sustainability is paramount.
Understanding LEED Certification for Homes
LEED certification isn't a simple checklist; it's a holistic assessment of a building's environmental impact across various categories. The rating system awards points based on performance across these categories, and the total points earned determine the level of certification achieved: Certified, Silver, Gold, or Platinum. Higher levels of certification represent a greater commitment to sustainability. Achieving a Platinum rating demands an exceptionally high level of green building practices.
To understand the "remarkably green" nature required, let's examine the key areas that contribute to a home's LEED score:
1. Sustainable Sites: Minimizing Land Impact
This category focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of the building's location and construction on the surrounding land. Key considerations include:
- Reducing site disturbance: Minimizing land clearing and preserving existing vegetation are crucial. The goal is to leave the natural landscape largely undisturbed.
- Protecting water resources: Implementing strategies to manage stormwater runoff and reduce water consumption through efficient irrigation systems is essential. This might involve the use of rainwater harvesting or permeable paving.
- Improving the site's biodiversity: Incorporating native plants, creating habitats for wildlife, and reducing the impact on local ecosystems are all vital aspects.
- Location and transportation: Choosing a site with access to public transportation, reducing reliance on cars, and encouraging alternative commuting methods contributes significantly. Proximity to amenities also reduces the need for extensive travel.
2. Water Efficiency: Conserving a Precious Resource
Water conservation is a critical component of LEED certification. Homes must demonstrate a commitment to significantly reducing water consumption compared to conventional buildings. This involves:
- High-efficiency fixtures and appliances: Installing low-flow showerheads, toilets, faucets, and washing machines is essential. These fixtures are designed to reduce water usage without compromising performance.
- Water-wise landscaping: Using drought-tolerant plants that require less irrigation, implementing efficient irrigation techniques, and minimizing the overall size of the landscaping contribute to water conservation.
- Water harvesting and reuse: Collecting rainwater for irrigation or other non-potable uses can significantly reduce reliance on municipal water supplies. Greywater recycling systems also contribute to water efficiency.
- Leak detection and repair: Regularly monitoring and promptly repairing any leaks or malfunctions in plumbing systems prevent unnecessary water waste.
3. Energy and Atmosphere: Reducing Carbon Footprint
Reducing the building's energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions is central to LEED certification. This category requires a comprehensive approach to energy efficiency:
- Energy-efficient building envelope: Proper insulation, high-performance windows, and airtight construction are crucial for minimizing energy loss. This reduces reliance on heating and cooling systems.
- Renewable energy sources: Integrating solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy technologies can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Net-zero energy homes, which generate as much energy as they consume, are increasingly common in LEED-certified projects.
- High-efficiency HVAC systems: Installing energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems ensures optimal performance while minimizing energy consumption.
- Energy-efficient lighting and appliances: Using energy-star rated appliances and energy-efficient lighting contributes to overall energy savings.
- Smart building technologies: Integrating smart thermostats and other smart building technologies can optimize energy use based on occupancy and weather conditions.
4. Materials and Resources: Embracing Sustainable Materials
The selection of building materials is crucial for LEED certification. Sustainable material choices have a substantial impact on the environmental footprint of the home:
- Recycled content: Prioritizing materials with recycled content reduces the demand for virgin materials, minimizing environmental impact.
- Locally sourced materials: Using materials sourced from nearby locations reduces transportation costs and emissions associated with material transport.
- Sustainable forestry practices: Ensuring that wood products originate from sustainably managed forests prevents deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Rapidly renewable materials: Utilizing rapidly renewable materials like bamboo or straw bale construction further reduces the environmental impact.
- Material reuse and reclamation: Reusing or reclaiming existing materials whenever possible minimizes waste and resource consumption.
- Reducing construction waste: Implementing strategies to minimize waste during construction, such as careful material planning and efficient waste management, is critical.
5. Indoor Environmental Quality: Promoting Health and Wellbeing
This category focuses on creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment for occupants. Key considerations include:
- Improving indoor air quality: Using low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints, adhesives, and other building materials helps maintain healthy indoor air quality. Proper ventilation is also crucial.
- Daylighting and views: Maximizing natural light and providing access to outdoor views have been shown to improve occupant well-being and productivity.
- Thermal comfort: Ensuring comfortable temperatures throughout the year through efficient insulation and HVAC systems is vital.
- Acoustic comfort: Controlling noise levels through appropriate building design and construction methods minimizes noise pollution.
- Controllability: Providing occupants with control over their indoor environment, including temperature, lighting, and ventilation, is critical for enhancing comfort and well-being.
6. Innovation in Design: Pushing the Boundaries of Sustainability
This category rewards innovative approaches to sustainable building design that go beyond the standard requirements. Examples include:
- Innovative energy efficiency measures: Implementing advanced energy efficiency technologies that exceed standard requirements.
- Sustainable site development strategies: Employing innovative site design strategies that significantly reduce the environmental impact.
- Sustainable material innovations: Using cutting-edge sustainable materials with exceptional environmental benefits.
- Community engagement: Involving the community in the design and construction process to foster a sense of ownership and sustainability.
7. Regional Priority Credits: Addressing Local Environmental Concerns
LEED also allows for regional credits that address specific environmental challenges in the local area. These credits can vary depending on the region and reflect local priorities.
The Remarkably Green Home: Beyond Compliance
Achieving LEED certification isn't just about meeting minimum requirements; it's about striving for excellence in sustainability. A truly "remarkably green" home goes above and beyond the minimum requirements, incorporating innovative strategies and embracing a holistic approach to environmental responsibility. This often includes:
- Net-zero energy performance: Generating as much energy as the home consumes, reducing its reliance on the grid.
- Passive design strategies: Utilizing natural elements like sunlight and wind to minimize energy consumption.
- Water self-sufficiency: Minimizing or eliminating the need for municipal water supplies.
- Zero waste construction: Minimizing or eliminating waste generation during the construction process.
- Sustainable landscaping with biodiversity: Creating a vibrant ecosystem that supports local flora and fauna.
- Integration with smart home technology: Monitoring and optimizing energy, water, and other resource consumption in real-time.
- Health-focused interior design: Prioritizing materials and finishes that promote occupant health and well-being.
Conclusion: The Path to LEED Certification
Achieving LEED certification requires a comprehensive and committed approach to sustainable building practices. A home must be remarkably green, demonstrating a significant reduction in its environmental footprint across all aspects of its design, construction, and operation. While the specific requirements may vary depending on the project's location and other factors, the core principles of sustainability remain consistent: reducing energy consumption, conserving water, minimizing waste, using sustainable materials, and promoting occupant health and wellbeing. By adhering to these principles and striving for excellence, homeowners and builders can contribute to a more sustainable future while creating homes that are not only environmentally responsible but also comfortable, healthy, and aesthetically pleasing. The journey to LEED certification is a testament to the commitment to a remarkably green future for the built environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
All Eucom Personnel Must Know The Difference Between
Mar 06, 2025
-
Amazon And Orbitz Are Both Part Of
Mar 06, 2025
-
Quotes From Perks Of Being A Wallflower
Mar 06, 2025
-
The Rime Of The Ancient Mariner Plot Summary
Mar 06, 2025
-
Course Hero Vocabulary Worksheet Cold War Vocabulary Answer Key
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Home Must Be ______ Green To Be Leed Qualified. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
