A __________ Specimen Usually Is Collected To Determine Glucose Levels.
Onlines
May 09, 2025 · 6 min read
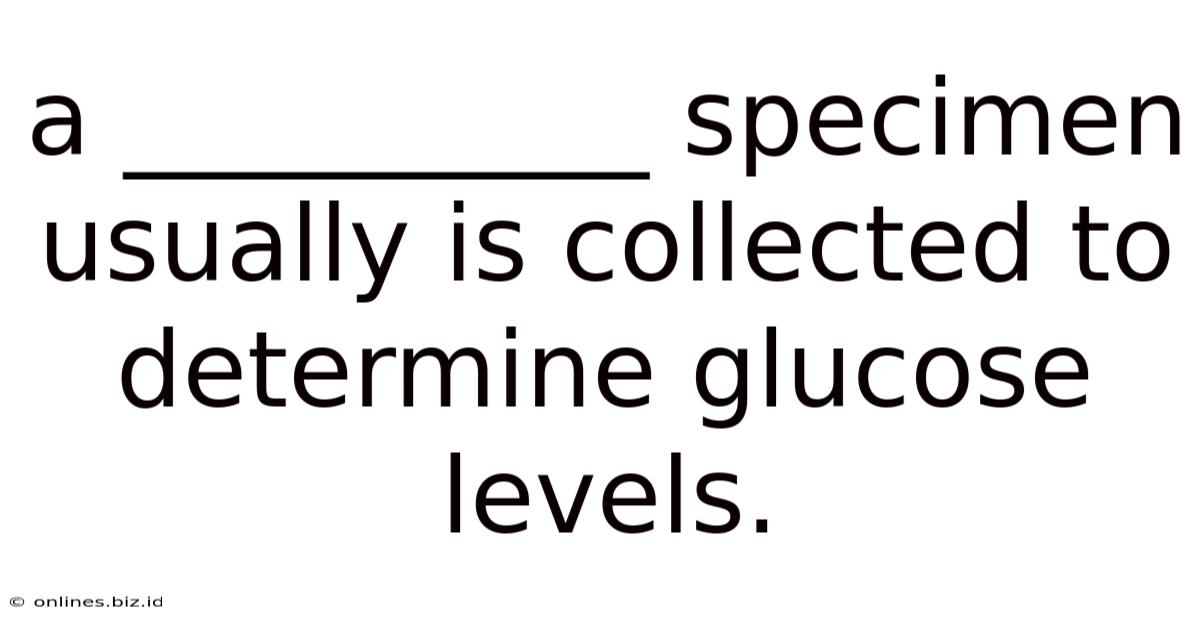
Table of Contents
A Blood Specimen: Your Key to Understanding Glucose Levels
Determining glucose levels is crucial for managing and diagnosing various health conditions, most notably diabetes. Understanding how glucose levels are measured, the specimen required, and the process involved is key to effective healthcare. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of glucose level testing, emphasizing the critical role of a blood specimen in this process.
Why Blood is the Gold Standard for Glucose Measurement
While other bodily fluids might contain glucose, blood remains the preferred specimen for several compelling reasons:
1. Accessibility and Ease of Collection:
Venipuncture (drawing blood from a vein) and capillary puncture (pricking a fingertip) are relatively straightforward procedures, requiring minimal equipment and easily performed by trained medical professionals. This ease of access significantly contributes to the widespread use of blood glucose testing. The process is minimally invasive and generally well-tolerated by patients.
2. Reflects Systemic Glucose Levels:
Glucose circulates throughout the bloodstream, providing a representative snapshot of the body's overall glucose concentration. This contrasts with other bodily fluids which might reflect glucose levels only in a specific region or organ. A blood specimen offers a comprehensive and accurate picture of your blood sugar.
3. Standardized Measurement Techniques:
Established and validated laboratory methods exist for accurately quantifying glucose levels in blood. These techniques ensure consistency and reliability across different testing environments, ensuring accurate diagnosis and monitoring. This standardized approach reduces variability and increases the dependability of results.
4. Wide Range of Testing Options:
Blood specimens allow for a range of glucose testing methods, from simple point-of-care tests (like those using glucose meters) to more sophisticated laboratory analyses. This flexibility allows healthcare providers to choose the most appropriate method based on individual needs and clinical context. This means that whether you need a quick check at home or a comprehensive analysis in a lab, blood offers the versatility needed.
Different Types of Blood Specimens and Their Applications
Several types of blood specimens can be used to measure glucose levels, each suited to specific testing needs:
1. Venous Blood:
Venous blood, drawn from a vein typically in the arm, is the most common sample used for glucose testing. It provides a larger volume of blood, allowing for a variety of tests to be performed simultaneously, not just glucose measurements. The larger volume is particularly beneficial for laboratory-based analyses requiring more material.
2. Capillary Blood:
Capillary blood, obtained by pricking a fingertip (or heel for infants), is often used for point-of-care testing with glucose meters. This method is less invasive and faster, making it ideal for self-monitoring blood glucose levels at home or in a quick clinical setting. However, the smaller sample size limits the number of tests that can be performed simultaneously.
3. Arterial Blood:
Arterial blood, collected from an artery, is generally reserved for specific clinical situations where precise blood gas analysis is required. While it can be used to measure glucose, it is more invasive and requires specialized training. It's rarely used for routine glucose monitoring.
The Glucose Testing Process: From Specimen Collection to Result Interpretation
The process of measuring glucose levels using a blood specimen involves several key steps:
1. Specimen Collection:
The method of collection (venipuncture or capillary puncture) depends on the type of testing and the clinical setting. Proper techniques are crucial to ensure the accuracy of the results. For instance, proper aseptic techniques must be adhered to in venipuncture to avoid contamination.
2. Specimen Handling and Transportation:
After collection, the blood specimen needs careful handling to prevent changes in glucose levels. This includes factors like storage temperature and the speed of transportation to the laboratory, if applicable. Delays can lead to inaccurate readings due to changes in glucose in the sample.
3. Laboratory Analysis (if applicable):
For laboratory-based testing, various methods are used to quantify glucose levels, including enzymatic methods (such as the hexokinase method, considered the gold standard) which measure glucose concentration based on enzymatic reactions.
4. Result Interpretation:
The results are interpreted in the context of the individual's medical history, symptoms, and other relevant clinical information. Normal glucose ranges vary slightly depending on the laboratory and testing method. Abnormally high or low glucose levels can indicate various health conditions, requiring further investigation and medical management.
Conditions Diagnosed and Monitored Using Glucose Levels:
The measurement of glucose levels in a blood specimen is essential in the diagnosis and management of several critical health conditions:
1. Diabetes Mellitus:
Diabetes is characterized by impaired glucose metabolism, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. Regular glucose monitoring using blood tests is vital for managing diabetes and preventing complications. This includes diagnosing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
2. Hypoglycemia:
Hypoglycemia, or low blood glucose, can occur in individuals with diabetes who take insulin or certain medications. Regular blood glucose testing helps identify and prevent episodes of hypoglycemia, which can be life-threatening.
3. Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and can affect both the mother and the developing fetus. Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial to manage gestational diabetes and ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
4. Other Metabolic Disorders:
Glucose levels can also be indicative of other metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance. Monitoring glucose levels can help in the early detection and management of these conditions.
Factors Affecting Glucose Levels:
Several factors can influence glucose levels in a blood specimen, impacting the accuracy and interpretation of results:
1. Food Intake:
Glucose levels fluctuate naturally after meals. Timing of blood sampling relative to meals is crucial for accurate interpretation. This is why fasting blood glucose tests are often recommended.
2. Physical Activity:
Exercise can influence glucose levels, so the level of physical activity before testing should be considered.
3. Medications:
Certain medications, including some steroids and diuretics, can impact glucose levels. This must be factored into the interpretation of results.
4. Stress:
Stress hormones can affect glucose metabolism and therefore blood glucose levels.
5. Illness:
Illnesses such as infections can also alter glucose levels.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Blood Specimens in Glucose Measurement
In conclusion, the blood specimen is undeniably the cornerstone of accurate and reliable glucose level determination. Its accessibility, representative nature, and compatibility with a wide range of testing methodologies make it the gold standard for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions associated with glucose metabolism. From simple home testing to sophisticated laboratory analyses, understanding the importance and proper handling of a blood specimen is crucial for effective healthcare and the well-being of individuals managing conditions related to glucose levels. The accurate measurement of blood glucose, obtained from a blood specimen, remains a fundamental tool in the fight against diabetes and other related conditions, ensuring timely diagnosis and effective management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Three Lines In The Poem Are Examples Of Alliteration
May 10, 2025
-
Which Aarp Entity Manages Provider Relationships And Performs Quality Control
May 10, 2025
-
The United States Is Not Truly Pluralistic Because
May 10, 2025
-
Determine Ix In The Circuit Of Fig P2 15
May 10, 2025
-
The Heart Of The Orchestra Is The
May 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A __________ Specimen Usually Is Collected To Determine Glucose Levels. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.