Advanced Hardware Lab 8-4: Terminate Twisted-pair Cables
Onlines
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
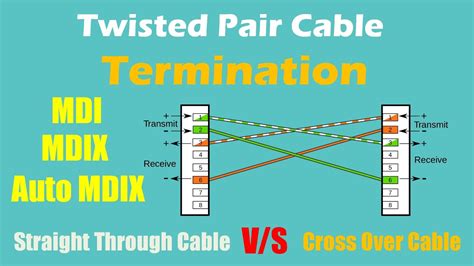
Table of Contents
Advanced Hardware Lab 8-4: Terminating Twisted-Pair Cables
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of terminating twisted-pair cables, a crucial skill in networking and telecommunications. We'll move beyond the basics, exploring advanced techniques, troubleshooting common issues, and emphasizing best practices for ensuring reliable and high-performance network connections. This lab guide is designed for students and professionals seeking a deep understanding of this fundamental aspect of cabling infrastructure.
Understanding Twisted-Pair Cable Fundamentals
Before diving into termination techniques, let's solidify our understanding of twisted-pair cables. These cables consist of multiple pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together. The twisting is a critical design element, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between pairs. Different categories of twisted-pair cables exist, each with varying specifications regarding bandwidth, distance limitations, and application suitability.
Common Twisted-Pair Cable Categories:
- Cat5e: A widely used standard, suitable for Gigabit Ethernet and other applications requiring speeds up to 1 Gigabit per second.
- Cat6: Offers improved performance over Cat5e, supporting speeds up to 10 Gigabit per second over shorter distances.
- Cat6a: An enhanced version of Cat6, capable of handling 10 Gigabit Ethernet over longer distances.
- Cat7: Provides even higher bandwidth and is designed for high-speed applications, including 10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond.
- Cat8: The latest standard, offering exceptional performance for 40 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond.
Understanding the cable category is paramount when selecting termination tools and techniques. Using inappropriate tools or methods can compromise signal integrity and lead to connectivity problems.
Preparing for Cable Termination
Successful cable termination demands meticulous preparation. This includes gathering the necessary tools and materials, understanding the cable's specifications, and preparing the workspace for efficient and error-free work.
Essential Tools and Materials:
- Wire Strippers/Cutters: Choose a quality tool specifically designed for twisted-pair cables. A poor-quality tool can nick the wires, causing signal degradation.
- Punch Down Tool: This tool is essential for securely connecting the wires to the connector. Different connectors require different punch-down tools, so ensure compatibility.
- Crimping Tool: Used for securely attaching the RJ45 connector to the cable. A high-quality crimping tool ensures a reliable connection.
- Cable Tester: Crucial for verifying the integrity of the terminated cable. This tool identifies shorts, opens, and incorrect wiring.
- RJ45 Connectors: Select connectors that match the cable category. Using inferior connectors can significantly impact performance.
- Safety Glasses: Always protect your eyes from potential flying debris.
- Scissors: For trimming excess cable jacket.
Workspace Preparation:
Maintain a clean and well-organized workspace. Sufficient lighting and a comfortable working posture are essential for accurate and safe work.
Advanced Termination Techniques: The 568A and 568B Standards
The most common termination standard is the RJ45 connector, adhering to either the 568A or 568B wiring scheme. The choice between these standards is arbitrary as long as both ends of the cable use the same scheme. Inconsistent wiring will result in connectivity failure.
568A Wiring Standard:
- Pin 1: Green/White
- Pin 2: Green
- Pin 3: Orange/White
- Pin 4: Blue
- Pin 5: Blue/White
- Pin 6: Orange
- Pin 7: Brown/White
- Pin 8: Brown
568B Wiring Standard:
- Pin 1: Orange/White
- Pin 2: Orange
- Pin 3: Green/White
- Pin 4: Blue
- Pin 5: Blue/White
- Pin 6: Green
- Pin 7: Brown/White
- Pin 8: Brown
Important Note: While both standards are functionally equivalent, maintaining consistency is crucial. Mixing 568A and 568B at either end will result in a non-functional cable.
Step-by-Step Termination Process:
-
Measure and Cut: Measure the required cable length, adding extra for flexibility. Use wire cutters to cleanly cut the cable.
-
Strip the Outer Jacket: Carefully strip the outer jacket, exposing approximately 1 inch of the wire pairs. Avoid nicking the individual wires.
-
Untwist and Straighten: Untwist the wire pairs, being careful not to pull or stretch them. Straighten the individual wires, ensuring they are neatly aligned.
-
Arrange Wires According to Standard: Arrange the wires according to the chosen wiring standard (568A or 568B). Maintain consistent order.
-
Insert into Connector: Insert the wires into the RJ45 connector, ensuring they reach the bottom and are correctly aligned with the corresponding pins.
-
Punch Down: Use the punch-down tool to firmly and securely connect the wires to the connector's pins. This step requires precision and even pressure to ensure a strong connection.
-
Crimp the Connector: Using the crimping tool, firmly crimp the connector onto the cable. This creates a secure mechanical connection.
-
Test the Cable: Use a cable tester to verify the continuity and wiring accuracy. The tester should indicate a successful connection according to the chosen standard.
Troubleshooting Common Termination Problems
Even with careful technique, problems can arise during termination. Here's how to address common issues:
-
No Connection: Check for correct wiring, proper crimping, and continuity using a cable tester.
-
Intermittent Connection: Examine the crimped connector for any signs of damage or loose wires. Re-crimping or replacing the connector may be necessary.
-
Slow Data Transfer Speeds: Verify cable category compatibility with the network equipment. Check for any damage or signal attenuation along the cable length.
-
Cross-talk or EMI: Ensure proper cable management and shielding to minimize interference. Consider using a higher cable category for better performance.
Advanced Considerations for High-Speed Networks:
For high-speed networks (10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond), additional considerations are necessary:
-
Cable Category: Using the appropriate cable category (Cat6a, Cat7, Cat8) is essential to support the required bandwidth.
-
Channel Testing: Specialized channel testing equipment is required to ensure that the entire cable channel, including connectors and patch panels, meets the specifications for high-speed networks.
-
Bend Radius: Maintaining proper bend radius is critical, as excessive bending can damage the cable and affect signal integrity.
-
Grounding: Proper grounding techniques are crucial to minimize EMI and ensure signal stability in high-speed networks.
Maintaining Cable Integrity: Best Practices
Regular maintenance and inspection are vital to ensuring the long-term reliability of twisted-pair cabling.
-
Proper Cable Management: Utilize cable ties, straps, and other management solutions to keep cables organized and prevent damage.
-
Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect cables for any signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or excessive bending.
-
Environmental Considerations: Protect cables from extreme temperatures, moisture, and direct sunlight.
-
Proper Labeling: Clearly label cables to facilitate troubleshooting and maintenance.
Conclusion: Mastering Twisted-Pair Cable Termination
Mastering the art of terminating twisted-pair cables is a foundational skill for anyone involved in networking or telecommunications. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of the process, from selecting the correct tools and materials to troubleshooting potential issues. By adhering to best practices and employing advanced techniques, you can ensure reliable and high-performance network connections, supporting the demands of today's high-speed data applications. Remember, meticulousness and attention to detail are crucial for successful and long-lasting cable terminations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Speaker Indicates That The Play Will Include
Mar 10, 2025
-
Physical Education 1 Word Search Volleyball Answer Key
Mar 10, 2025
-
Tattoos On The Heart Chapter 1 Summary
Mar 10, 2025
-
Identify The True And False Statements About Color Blind Racism
Mar 10, 2025
-
A Wrinkle In Time Chapter Synopsis
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Advanced Hardware Lab 8-4: Terminate Twisted-pair Cables . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
