Algebra Ii 5.2 Vertex Form Worksheet
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
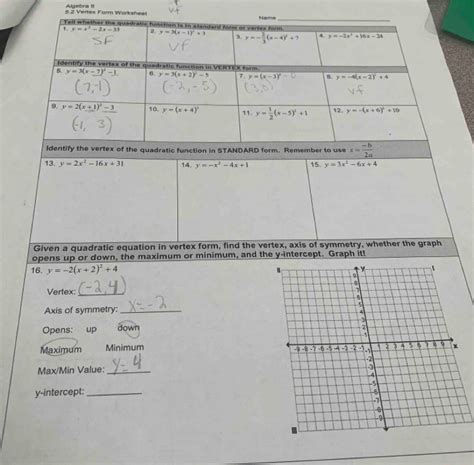
Table of Contents
Algebra II 5.2: Mastering the Vertex Form Worksheet
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Algebra II's 5.2 section, focusing on the vertex form of quadratic functions. We'll unpack the worksheet exercises, provide detailed explanations, and offer strategies to master this crucial concept. Understanding the vertex form is fundamental to graphing parabolas, solving quadratic equations, and comprehending the behavior of quadratic models in various real-world applications.
Understanding the Vertex Form of a Quadratic Function
The standard form of a quadratic function is given by: f(x) = ax² + bx + c. While useful, it doesn't directly reveal key features like the vertex (the parabola's turning point). This is where the vertex form shines.
The vertex form of a quadratic function is expressed as:
f(x) = a(x - h)² + k
Where:
- 'a' determines the parabola's vertical stretch or compression and its direction (opens upwards if a > 0, downwards if a < 0). A larger absolute value of 'a' indicates a narrower parabola; a smaller absolute value indicates a wider parabola.
- '(h, k)' represents the coordinates of the vertex of the parabola. 'h' is the x-coordinate, and 'k' is the y-coordinate.
- '(x - h)² indicates a horizontal shift. If 'h' is positive, the parabola shifts to the right; if 'h' is negative, it shifts to the left.
Decoding the 5.2 Worksheet: Common Problem Types
Algebra II 5.2 worksheets typically present a variety of problems designed to reinforce your understanding of the vertex form. Let's break down the common exercise types:
1. Identifying the Vertex and Axis of Symmetry
Many problems will ask you to identify the vertex and the axis of symmetry directly from the vertex form equation. Remember:
- Vertex: The vertex is simply the point (h, k).
- Axis of Symmetry: The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex. Its equation is always x = h.
Example:
Given f(x) = 2(x + 3)² - 5, the vertex is (-3, -5), and the axis of symmetry is x = -3. Note that the 'h' value is the opposite sign of what appears in the parentheses.
2. Converting from Standard Form to Vertex Form
This is a more challenging but crucial skill. The most common method is completing the square. Let's illustrate the process step-by-step:
Example: Convert f(x) = x² + 6x + 5 to vertex form.
- Group the x terms:
f(x) = (x² + 6x) + 5 - Complete the square: To complete the square for x² + 6x, take half of the coefficient of x (which is 6/2 = 3), square it (3² = 9), and add and subtract it inside the parentheses:
f(x) = (x² + 6x + 9 - 9) + 5 - Factor the perfect square trinomial:
f(x) = (x + 3)² - 9 + 5 - Simplify:
f(x) = (x + 3)² - 4
Now the equation is in vertex form, revealing the vertex as (-3, -4).
3. Graphing Quadratic Functions in Vertex Form
Once you have the equation in vertex form, graphing becomes significantly easier.
- Plot the vertex: Locate the point (h, k) on the coordinate plane.
- Determine the direction and width: The sign of 'a' tells you whether the parabola opens upwards or downwards. The absolute value of 'a' indicates the parabola's width.
- Find additional points: Choose x-values on either side of the vertex and substitute them into the equation to find their corresponding y-values. Plot these points.
- Draw the parabola: Sketch a smooth curve through the plotted points, ensuring it's symmetric around the axis of symmetry.
4. Writing the Equation in Vertex Form Given the Vertex and a Point
If you're given the vertex (h, k) and another point (x, y) on the parabola, you can determine the value of 'a' and write the equation in vertex form.
Example: The vertex is (2, -1), and the point (4, 3) is on the parabola.
- Substitute the vertex and point into the vertex form:
3 = a(4 - 2)² - 1 - Solve for 'a':
4 = 4a, soa = 1 - Write the equation:
f(x) = (x - 2)² - 1
5. Real-World Applications
Many worksheet problems involve applying the vertex form to real-world scenarios, such as projectile motion or optimization problems. Understanding the vertex's significance (maximum or minimum point) is crucial in these applications. For example, the vertex of a parabola representing the trajectory of a projectile indicates its maximum height.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The 5.2 worksheet might also include more advanced problems:
- Transformations of Parabolas: Understanding how changes in 'a', 'h', and 'k' affect the graph is essential.
- Solving Quadratic Equations using Vertex Form: Finding the x-intercepts (roots) by setting f(x) = 0 and solving for x.
- Comparing Quadratic Functions: Analyzing and contrasting multiple quadratic functions in vertex form to understand their relative positions and characteristics.
- Finding the minimum or maximum value: Identifying the y-coordinate of the vertex as the minimum or maximum value of the function.
Strategies for Mastering the Worksheet
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering the concepts. Work through numerous examples from the textbook and online resources.
- Understand the Concepts: Don't just memorize formulas; make sure you thoroughly understand the underlying principles.
- Seek Help When Needed: Don't hesitate to ask your teacher, classmates, or tutors for help if you're struggling with any concepts.
- Use Online Resources: Numerous websites and videos offer explanations and practice problems on vertex form.
- Break Down Complex Problems: Tackle complex problems step by step. Don't get overwhelmed by the entire problem at once.
- Review Your Mistakes: Analyze your mistakes carefully to identify areas where you need improvement.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Vertex Form
The Algebra II 5.2 worksheet on vertex form is a cornerstone of understanding quadratic functions. By mastering the concepts discussed above and practicing diligently, you'll not only ace the worksheet but also develop a solid foundation for more advanced topics in algebra and beyond. Remember that the vertex form provides a powerful tool for analyzing and manipulating quadratic functions, offering insights into their behavior and applications in various fields. The ability to seamlessly convert between standard and vertex forms, along with the skill of interpreting the meaning of each parameter (a, h, k), is essential for success in this area. Consistent practice and a focused approach will lead you to a thorough understanding of this crucial algebraic concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
When A Counselor Communicates With A Client Using E Mail
Mar 19, 2025
-
Biology Exam Review Webquest Study Guide Answer Key
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Curtail Corrupt Officials Brutus 1
Mar 19, 2025
-
Marcos Has Multiple Duties At Work
Mar 19, 2025
-
Live Virtual Machine Lab 18 1 Mobile Security Solutions
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Algebra Ii 5.2 Vertex Form Worksheet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
