All Things Algebra Answer Key 2015
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
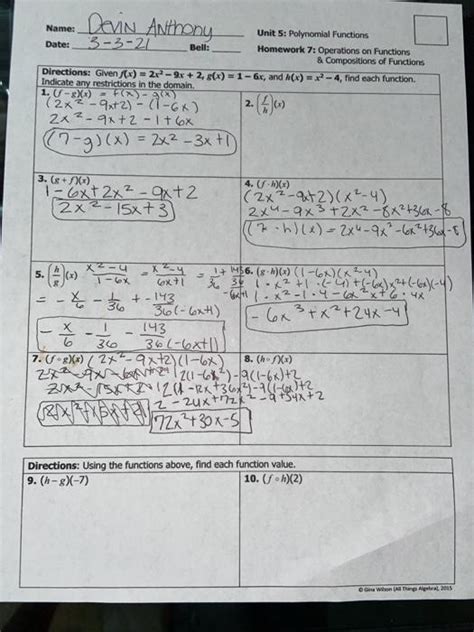
Table of Contents
All Things Algebra Answer Key 2015: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the answer key for the 2015 edition of "All Things Algebra" can be challenging. However, this comprehensive guide aims to provide assistance in understanding the concepts covered in the book, regardless of the specific edition. We'll delve into key algebraic topics, providing explanations and examples to help you master the subject. While we can't provide a direct copy of the answer key due to copyright restrictions, this resource will help you verify your work and solidify your understanding.
Note: This article covers general algebraic principles and concepts likely found within the "All Things Algebra 2015" textbook. Specific problem solutions will depend on the exact questions in your edition.
I. Core Algebraic Concepts: Building Your Foundation
Before tackling problem sets, it’s essential to solidify your understanding of fundamental algebraic concepts. This section serves as a refresher for those concepts likely covered in the "All Things Algebra 2015" book.
A. Variables and Expressions
Algebra introduces variables, which are symbols (usually letters) representing unknown quantities. Algebraic expressions combine variables, numbers, and operations (+, -, ×, ÷).
- Example: 3x + 5 is an algebraic expression where 'x' is the variable.
B. Equations and Inequalities
Equations show the equality between two expressions. The goal is to find the value(s) of the variable that make the equation true. Inequalities show the relationship between two expressions where one is greater than, less than, greater than or equal to, or less than or equal to the other.
- Example: 2x + 4 = 10 (equation) and 3x - 2 > 5 (inequality).
C. Solving Linear Equations
Linear equations involve variables raised to the power of 1. Solving them involves isolating the variable using inverse operations (addition/subtraction, multiplication/division).
- Example: Solve for x: 2x + 5 = 9. Subtract 5 from both sides: 2x = 4. Divide both sides by 2: x = 2.
D. Solving Linear Inequalities
Solving linear inequalities is similar to solving equations, but with a crucial difference: when multiplying or dividing by a negative number, you must reverse the inequality sign.
- Example: Solve for x: -2x + 3 > 7. Subtract 3: -2x > 4. Divide by -2 and reverse the sign: x < -2.
E. Systems of Linear Equations
Systems of linear equations involve two or more equations with the same variables. Solutions represent values that satisfy all equations simultaneously. Methods for solving include substitution and elimination.
-
Example: Solve: x + y = 5 x - y = 1
Using elimination, add the two equations: 2x = 6, so x = 3. Substitute x = 3 into either equation to find y = 2.
F. Graphing Linear Equations
Linear equations can be graphed on a coordinate plane. The graph is a straight line. The slope (m) represents the steepness of the line and the y-intercept (b) is the point where the line crosses the y-axis. The equation is often written in slope-intercept form: y = mx + b.
- Example: Graph y = 2x + 1. The slope is 2 and the y-intercept is 1.
II. Advanced Algebraic Concepts: Expanding Your Skills
Once you've mastered the basics, you'll likely encounter more advanced concepts in the "All Things Algebra 2015" book.
A. Polynomials
Polynomials are expressions with multiple terms, each containing variables raised to non-negative integer powers. Operations on polynomials include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Example: 3x² + 2x - 5 is a polynomial.
B. Factoring Polynomials
Factoring is the reverse of multiplication. It involves breaking down a polynomial into simpler expressions. Common techniques include factoring out the greatest common factor (GCF), difference of squares, and trinomial factoring.
- Example: Factoring x² - 9 gives (x + 3)(x - 3).
C. Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations have the form ax² + bx + c = 0, where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants. Solving methods include factoring, the quadratic formula, and completing the square.
- Example: Solve x² + 5x + 6 = 0. Factoring gives (x + 2)(x + 3) = 0, so x = -2 or x = -3.
D. Rational Expressions
Rational expressions are fractions containing polynomials. Operations on rational expressions involve simplifying, adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing.
- Example: (x² + 2x) / (x + 2) can be simplified to x.
E. Radical Expressions and Equations
Radical expressions involve square roots, cube roots, and other roots. Solving radical equations often requires squaring or cubing both sides.
- Example: Solve √x = 3. Squaring both sides gives x = 9.
F. Exponents and Logarithms
Exponents represent repeated multiplication. Logarithms are the inverse of exponents. Understanding their properties is crucial for solving exponential and logarithmic equations.
- Example: 2³ = 8 (exponent) and log₂8 = 3 (logarithm).
III. Strategies for Success and Problem-Solving Techniques
This section focuses on effective strategies to tackle algebra problems and improve your understanding. These techniques are beneficial regardless of which edition of "All Things Algebra" you're using.
A. Understanding the Problem
Before attempting to solve a problem, carefully read and understand the question. Identify the key information, variables, and what is being asked.
B. Breaking Down Complex Problems
Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable steps. This makes the overall problem less daunting and easier to tackle.
C. Working Through Examples
The textbook likely contains numerous solved examples. Study these examples closely, paying attention to the steps and reasoning involved. Try to solve similar problems independently, then compare your work to the solutions.
D. Practicing Regularly
Regular practice is key to mastering algebra. Solve a variety of problems to reinforce your understanding and identify areas where you need further practice.
E. Utilizing Online Resources
While we cannot directly link to external resources, many free online resources, such as educational websites and videos, can provide supplementary explanations and practice problems. Search for specific topics you're struggling with to find helpful tutorials.
F. Seeking Help When Needed
Don't hesitate to seek help when you get stuck. Ask your teacher, classmates, or tutor for assistance. Explaining your thought process to someone else can often help identify the source of your confusion.
IV. Conclusion: Mastering Algebra Through Consistent Effort
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of algebraic concepts likely covered in "All Things Algebra 2015," including fundamental and more advanced topics. While a direct answer key is unavailable for copyright reasons, the detailed explanations and strategies presented here should significantly aid in understanding the material. Remember, consistent effort, practice, and seeking help when needed are crucial to mastering algebra. By diligently applying these strategies and focusing on a solid understanding of the underlying principles, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any algebra problem, regardless of the textbook edition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of Feminist Psychology
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Puritan Value Most Influenced The Emerging Neoclassical Style
Mar 17, 2025
-
Things Fall Apart Chapter 4 Summary
Mar 17, 2025
-
One Issue Dual Language Programs Face Is
Mar 17, 2025
-
Quotes From Where The Red Fern Grows
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about All Things Algebra Answer Key 2015 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
