An Electrical Motor Provides 0.50 W Of Mechanical Power
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
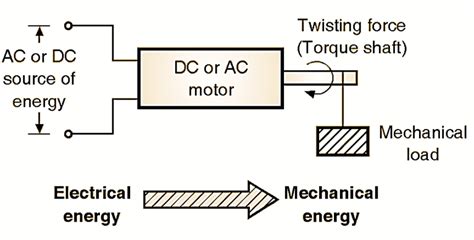
Table of Contents
An Electrical Motor Provides 0.50 W of Mechanical Power: A Deep Dive into Efficiency and Applications
An electrical motor delivering 0.50 watts of mechanical power might seem insignificant compared to the powerful motors driving industrial machinery. However, this seemingly small power output opens a vast world of applications in micro-robotics, sensor technology, and various low-power devices. Understanding the intricacies of such a low-power motor, its efficiency, and potential applications requires a detailed examination. This article delves into the specifics of a 0.50-watt motor, exploring its characteristics, limitations, and the technological advancements that make it a vital component in a wide range of modern applications.
Understanding Power and Efficiency in Small Motors
Mechanical power, measured in watts (W), represents the rate at which a motor performs work. 0.50 W signifies that the motor can perform 0.5 joules of work per second. This might seem minuscule, but it's crucial to remember that the context matters greatly. The efficiency of the motor is just as important as the power output. Efficiency, expressed as a percentage, indicates the ratio of useful mechanical power output to the electrical power input. A highly efficient motor minimizes energy loss as heat, maximizing the usable power.
Factors Affecting Efficiency:
- Internal Friction: Friction within the motor's components, such as bearings and brushes (in brushed DC motors), directly impacts efficiency. Minimizing these frictional losses is paramount in low-power motors.
- Magnetic Losses: Losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents in the motor's magnetic components contribute to reduced efficiency. Optimized magnetic materials and design can mitigate these losses.
- Electrical Losses: Resistance in the windings and other electrical components leads to heat generation and power loss. Using low-resistance materials and efficient winding techniques is essential.
- Motor Type: Different motor types (DC brushed, DC brushless, stepper, etc.) exhibit varying levels of inherent efficiency. The selection of an appropriate motor type is critical for optimal performance in a specific application.
Types of Motors Suitable for 0.50 W Output
Several motor types can achieve a 0.50 W power output, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
1. DC Brushed Motors:
These motors are relatively simple and inexpensive, making them suitable for low-power applications. However, their efficiency tends to be lower compared to brushless DC motors due to brush friction and arcing. A 0.50 W DC brushed motor would likely be found in simple toys, hobbyist projects, or very basic applications where cost is a primary factor.
2. DC Brushless Motors:
Brushless DC motors offer higher efficiency and longer lifespan than their brushed counterparts due to the absence of brushes. Their higher initial cost is often justified by their superior performance and reliability, especially in applications requiring longer operational periods. A 0.50 W brushless DC motor might be found in precision instruments or applications demanding higher efficiency and longevity.
3. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors provide precise rotational control in discrete steps. While they can achieve 0.50 W output, their efficiency might be lower than brushless DC motors, particularly at lower speeds. Their suitability for a 0.50 W application hinges on the need for precise positional control, which might outweigh the efficiency concerns. Micro-robotics and precision positioning systems could utilize such a motor.
4. Micro-Motors:
The term "micro-motor" encompasses a range of extremely small motors often designed for miniature applications. These motors are frequently tailored for specific needs, resulting in diverse efficiency levels and power outputs. A 0.50 W micro-motor would be commonly integrated into micro-devices and systems.
Applications of a 0.50 W Electrical Motor
The seemingly small power output of a 0.50 W motor doesn't diminish its importance. Its compact size and low power consumption make it ideal for various applications where large, power-hungry motors are impractical or undesirable. Here are some examples:
1. Micro-Robotics:
In the field of micro-robotics, where size and energy efficiency are paramount, a 0.50 W motor plays a crucial role. It can power the actuators in miniature robots used for tasks such as micro-manipulation, micro-assembly, or exploration in confined spaces. Examples include microsurgical tools or robots navigating tiny spaces.
2. Sensor Actuators:
Many sensors require small actuators for positioning, calibration, or adjustment. A 0.50 W motor is well-suited for these tasks, enabling precise movement without excessive power consumption. Examples include the fine adjustment of optical components in scientific instruments or the movement of probes in medical devices.
3. Consumer Electronics:
Low-power motors find their way into various consumer electronics, providing quiet and efficient operation. Examples might include small fans in portable electronics, automated mechanisms in toys, or the movement of internal components in compact devices.
4. Wearable Technology:
As wearable technology becomes increasingly sophisticated, the need for miniature power sources and motors grows. A 0.50 W motor could be integrated into smartwatches, fitness trackers, or other wearable devices to power small actuators or mechanisms. Think of a small mechanism adjusting the position of an element on a smartwatch face.
5. Medical Devices:
In the medical field, low-power motors are essential for various minimally invasive procedures and devices. They might be used in micro-surgical tools, drug delivery systems, or other medical instruments where precise control and minimal power consumption are critical.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
The development of increasingly efficient and compact low-power motors continues at a rapid pace. Technological advancements in materials science, manufacturing processes, and motor design lead to improved performance and reduced costs. Here are some key trends:
- Improved Magnetic Materials: The use of advanced magnetic materials reduces magnetic losses and improves motor efficiency. This allows for smaller motors with higher power density.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Techniques such as micro-machining and 3D printing enable the creation of highly precise and compact motors. This opens up possibilities for even smaller and more efficient designs.
- Optimized Motor Control Algorithms: Sophisticated control algorithms improve motor efficiency by optimizing the power delivery and reducing energy losses.
- Integration of Power Electronics: The integration of power electronics directly into the motor module minimizes power loss during energy conversion and reduces the overall size of the system.
Conclusion: The Significance of Small Power
While a 0.50 W electrical motor might seem insignificant in terms of sheer power, its importance in the context of micro-devices and low-power applications is undeniable. Its small size, low power consumption, and increasing efficiency make it an essential component in a wide range of technologies, from micro-robotics and sensor systems to consumer electronics and medical devices. Continued advancements in motor technology are poised to further enhance the capabilities and expand the applications of these powerful, yet miniature, machines. The seemingly small 0.50 W signifies a potent force in driving innovation across numerous technological sectors. The efficiency considerations detailed above are crucial for optimizing the performance and longevity of these small but vital components, ensuring their continued importance in the ever-evolving landscape of modern technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Christian High School Equivalency Exam Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Introduction To Health Assessment 3 0 Test
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lord Of The Flies Student Workbook Answers Pdf
Mar 17, 2025
-
In Time Of The Butterflies Quotes
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not Part Of Feminist Psychology
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about An Electrical Motor Provides 0.50 W Of Mechanical Power . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
