Anticipating Potential Provider Prescriptions System Disorder
Onlines
Mar 26, 2025 · 6 min read
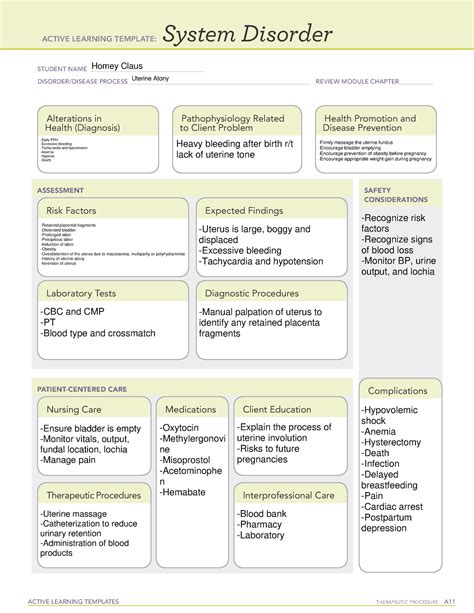
Table of Contents
Anticipating Potential Provider Prescription System Disorders
The healthcare system relies heavily on prescription systems. These systems, whether electronic health records (EHRs) or paper-based, are critical for patient safety and efficient healthcare delivery. However, these systems are susceptible to various disorders that can lead to significant consequences, from medication errors to significant financial losses. Anticipating and mitigating these potential disorders is crucial for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. This comprehensive article delves into the potential disorders of provider prescription systems, exploring their causes, consequences, and strategies for prevention and mitigation.
Understanding Provider Prescription System Disorders
"Provider prescription system disorders" encompasses a broad range of issues affecting the processes and technologies involved in prescribing and dispensing medications. These disorders can be broadly categorized into:
1. System-Related Disorders:
- Software Glitches and Bugs: EHRs and pharmacy management systems are complex software applications prone to bugs, glitches, and unexpected errors. These can manifest as incorrect dosage calculations, inaccurate drug interactions warnings, or complete system failures.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Server crashes, network outages, and printer malfunctions can disrupt the entire prescription workflow, delaying medication delivery and causing significant inconvenience.
- Data Integrity Issues: Incorrect data entry, incomplete patient information, and outdated drug databases can lead to prescribing errors and medication mismanagement.
- Security Breaches: Unauthorized access to prescription data can lead to identity theft, fraud, and the potential diversion of controlled substances. This includes both internal and external breaches.
- Integration Problems: Seamless communication between different healthcare systems (e.g., EHRs, pharmacy systems, insurance databases) is crucial. Integration problems can result in fragmented data, delays, and errors.
- Lack of System Updates and Maintenance: Outdated software and hardware increase the risk of vulnerabilities and malfunctions. Regular updates and maintenance are essential for optimal system performance and security.
2. Process-Related Disorders:
- Workflow Inefficiencies: Poorly designed workflows can lead to delays, errors, and increased workload for healthcare providers and pharmacy staff. This includes inefficient prescription writing processes, medication reconciliation procedures, and communication between providers and pharmacies.
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistent practices across different healthcare organizations can lead to communication breakdowns and medication errors. Standardization of prescribing practices, medication reconciliation procedures, and data entry protocols can mitigate this risk.
- Human Error: Even with the most advanced systems, human error remains a significant contributor to prescription system disorders. This includes typos, incorrect dosage calculations, and failure to properly document patient information.
- Insufficient Training: Inadequate training of healthcare professionals and pharmacy staff on the use of prescription systems can lead to errors and inefficient workflows.
- Poor Communication: Inadequate communication between providers, pharmacists, and patients can result in medication errors and adverse events. Clear, concise, and effective communication channels are essential.
- Lack of Oversight and Monitoring: Insufficient oversight and monitoring of prescription practices can allow errors to go undetected and uncorrected. Regular audits and quality control measures are crucial.
3. Data-Related Disorders:
- Incomplete or Inaccurate Patient Information: Missing or incorrect patient data can lead to prescribing errors and adverse drug events. This includes allergies, current medications, and medical history.
- Outdated Drug Information: Relying on outdated drug databases can result in prescribing medications with known interactions or contraindications.
- Lack of Data Standardization: Inconsistent data formats and terminology across different healthcare systems can hamper data exchange and analysis.
- Data Silos: Isolated data repositories within healthcare organizations can prevent a comprehensive view of patient medication history and increase the risk of errors.
Consequences of Provider Prescription System Disorders
The consequences of provider prescription system disorders can be severe and far-reaching, impacting patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems as a whole:
- Medication Errors: Incorrect dosages, wrong medications, or missed doses can lead to adverse drug events, hospitalization, and even death.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Medication errors, hospital readmissions, and legal liabilities associated with prescription system failures contribute significantly to rising healthcare costs.
- Patient Harm: Medication errors and system failures can cause serious harm to patients, leading to decreased quality of life and reduced trust in the healthcare system.
- Reputational Damage: System failures and medication errors can damage the reputation of healthcare providers and organizations.
- Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Failure to comply with prescribing regulations and maintain secure systems can lead to legal action and regulatory penalties.
- Loss of Productivity: System downtime and inefficient workflows can disrupt healthcare operations and reduce the productivity of healthcare professionals.
- Financial Losses: System failures and medication errors can result in significant financial losses for healthcare organizations.
Strategies for Prevention and Mitigation
Preventing and mitigating potential provider prescription system disorders requires a multi-faceted approach that involves technological solutions, process improvements, and human resource development:
1. Technological Solutions:
- Invest in Robust and Secure EHRs and Pharmacy Management Systems: Choosing reliable, well-maintained systems with strong security features is critical.
- Implement Data Validation and Error Checking Mechanisms: Automated checks can help prevent data entry errors and ensure data integrity.
- Regular System Updates and Maintenance: Keeping software and hardware up-to-date reduces vulnerabilities and improves system performance.
- Utilize Advanced Analytics and Reporting Tools: Monitoring system performance, identifying trends, and detecting potential issues can help prevent future problems.
- Implement Secure Data Backup and Recovery Procedures: Protecting against data loss is crucial in the event of system failures or security breaches.
- Invest in Redundancy and Failover Systems: Having backup systems in place ensures continued operation in the event of system failures.
2. Process Improvements:
- Optimize Workflows: Streamlining prescription processes, improving communication channels, and implementing standardized protocols can reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- Implement Medication Reconciliation Procedures: Ensuring accurate and complete medication information at each stage of care is crucial for preventing medication errors.
- Establish Clear Communication Protocols: Develop clear and effective communication channels between providers, pharmacists, and patients.
- Implement Robust Training Programs: Providing comprehensive training on the use of prescription systems and best practices can improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Conduct Regular Audits and Quality Control Measures: Monitoring prescribing practices and system performance can help identify potential problems and prevent future errors.
- Utilize Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS can provide real-time alerts and recommendations to prevent medication errors.
3. Human Resource Development:
- Invest in Staff Training and Education: Providing comprehensive training on the use of prescription systems, medication safety, and best practices is essential.
- Promote a Culture of Safety: Creating a culture where reporting errors and near misses is encouraged can help identify and address potential problems.
- Empower Healthcare Professionals: Giving healthcare professionals the authority and resources to prevent errors is critical.
- Improve Communication Skills: Training healthcare professionals in effective communication techniques can improve collaboration and reduce errors.
- Foster Teamwork and Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between healthcare professionals and pharmacists can improve patient care and reduce errors.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Oversight:
- Adherence to Relevant Regulations and Guidelines: Staying updated on and complying with all relevant regulations and guidelines related to prescribing practices and data security is crucial.
- Regular Inspections and Audits: Regular inspections and audits by regulatory bodies can help ensure compliance and identify potential problems.
- Data Security and Privacy Measures: Implementing strict security protocols to protect patient data is paramount.
Conclusion
Anticipating and mitigating potential provider prescription system disorders is a crucial aspect of ensuring patient safety and the efficient delivery of healthcare services. By proactively addressing system-related, process-related, and data-related vulnerabilities through technological upgrades, process improvements, robust human resource development, and adherence to regulatory guidelines, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce the risk of medication errors, improve patient outcomes, and enhance the overall quality of healthcare. Continuous monitoring, adaptation, and investment in these areas are vital to maintaining the integrity and reliability of prescription systems for years to come. The proactive approach detailed above is not merely a cost; it is an investment in a safer, more effective, and more sustainable healthcare system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Using Figurative Or Non Literal Phrases Can Sometimes Be Seen As
Mar 29, 2025
-
Chapter 1 Summary Of Animal Farm
Mar 29, 2025
-
You Downloaded Several Of Your Favorite Songs
Mar 29, 2025
-
Summary Of To Kill A Mockingbird Chapter 18
Mar 29, 2025
-
For The Three Solutes Tested In B
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Anticipating Potential Provider Prescriptions System Disorder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
