Ap Macroeconomics Unit 1 Test Answers
Onlines
Apr 06, 2025 · 6 min read
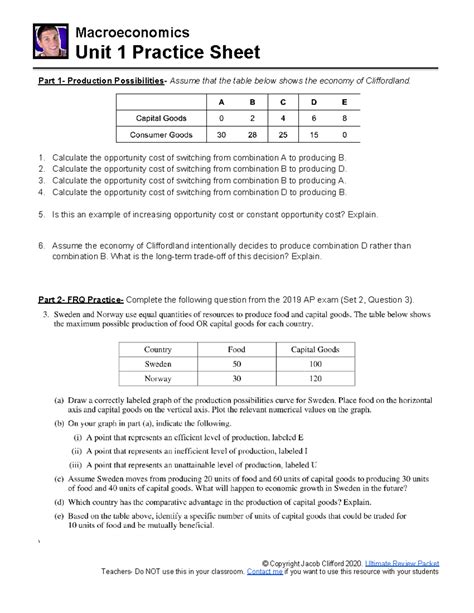
Table of Contents
AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 Test Answers: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Basic Economic Concepts
The first unit of AP Macroeconomics lays the groundwork for the entire course. Mastering these fundamental concepts is crucial for success in later units and on the AP exam. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of key topics covered in Unit 1, offering insights into common test questions and strategies for achieving a high score. We will explore essential concepts and provide example questions and answers to illustrate the principles. Remember, this is not a substitute for thorough study of your textbook and class notes; rather, it's designed to supplement your learning and solidify your understanding.
Unit 1: Fundamental Economic Concepts
Unit 1 typically covers several interconnected topics, including:
-
What is Economics? This introductory section defines economics, distinguishing between microeconomics and macroeconomics. It explores scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost – the core principles underpinning all economic decisions.
-
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): Understanding the PPF is critical. This model illustrates the trade-offs a society faces when allocating scarce resources between different goods or services. Questions often involve analyzing shifts in the PPF due to technological advancements, changes in resource availability, or increases in the workforce.
-
Economic Systems: This section examines various economic systems, including market economies, command economies, and mixed economies. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each system is crucial for answering comparative questions.
-
Circular Flow Diagram: The circular flow diagram visually represents the flow of goods, services, and money between households and firms in a market economy. Analyzing the interactions within this model is key to understanding macroeconomic activity.
-
Supply and Demand: This fundamental concept underpins much of macroeconomics. Understanding the factors that shift supply and demand curves, as well as how equilibrium price and quantity are determined, is vital for success. You should be able to analyze market changes due to various factors like consumer tastes, input prices, government regulations, and technological advancements.
-
Market Equilibrium and Disequilibrium: Understanding how markets reach equilibrium and how disruptions affect price and quantity is a major component of Unit 1. You should be prepared to analyze surplus and shortage situations and explain the market forces that lead to equilibrium restoration.
Example Questions and Answers
Let's explore some example questions that commonly appear on AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 tests, covering the key concepts discussed above.
Question 1: Opportunity Cost
Scenario: A farmer can produce either 100 bushels of wheat or 50 bushels of corn using all available resources.
Question: What is the opportunity cost of producing 50 bushels of corn?
Answer: The opportunity cost of producing 50 bushels of corn is 50 bushels of wheat (100 bushels of wheat / 50 bushels of corn = 2 bushels of wheat per bushel of corn). This is because producing 50 bushels of corn means forgoing the opportunity to produce 50 bushels of wheat.
Question 2: Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
Scenario: A country produces two goods: computers and automobiles. The PPF is shown as a bowed-out curve.
Question: Explain why the PPF is bowed outward, and what economic principle does this illustrate?
Answer: The bowed-out shape of the PPF illustrates the principle of increasing opportunity cost. As a country produces more of one good (say, computers), it must give up increasingly larger amounts of the other good (automobiles). This is because resources are not perfectly adaptable to the production of both goods. Some resources are better suited to computer production, while others are better suited to automobile production. To produce more computers, the country must shift resources from automobile production that are increasingly less efficient at producing computers, leading to a higher opportunity cost.
Question 3: Economic Systems
Question: Compare and contrast market economies and command economies. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
Answer:
| Feature | Market Economy | Command Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation | Determined by market forces (supply and demand) | Determined by central planning authority |
| Decision-Making | Decentralized; individuals and firms make decisions | Centralized; government makes decisions |
| Incentives | Primarily profit-motivated | Primarily fulfilling production quotas |
| Efficiency | Potentially high efficiency due to competition and price signals | Potentially low efficiency due to lack of competition and price signals |
| Innovation | High potential for innovation due to competition | Low potential for innovation due to lack of competition and price signals |
| Equity | Can lead to income inequality | Can lead to more equitable distribution of resources, but often inefficient |
| Examples | United States, Japan, most Western European countries | Cuba, North Korea (historically) |
Question 4: Circular Flow Diagram
Question: Explain the role of households and firms in the circular flow diagram, and describe the flow of goods and services and the flow of money.
Answer: In the circular flow diagram, households supply factors of production (labor, land, capital) to firms. In return, firms pay households wages, rent, interest, and profits. This is the flow of money from firms to households. Firms then use these factors of production to produce goods and services. These goods and services are sold to households in the market for goods and services. This is the flow of goods and services from firms to households. Households then use their income to purchase these goods and services, completing the circular flow.
Question 5: Supply and Demand
Scenario: The price of coffee beans increases significantly due to a poor harvest.
Question: Using supply and demand analysis, explain the impact of this increase on the equilibrium price and quantity of coffee.
Answer: An increase in the price of coffee beans represents an increase in the cost of production for coffee. This causes a leftward shift in the supply curve for coffee. With a decrease in supply and constant demand, the equilibrium price of coffee will rise, and the equilibrium quantity of coffee will fall. Consumers will pay a higher price for less coffee.
Advanced Topics and Test Strategies
While the examples above focus on basic concepts, AP Macroeconomics Unit 1 tests may also include more advanced questions. These might involve:
-
Analyzing changes in the PPF: Understanding how technological advancements or changes in resource availability affect the PPF curve and its implications for economic growth.
-
Comparative advantage and trade: Analyzing gains from trade based on comparative advantage and its impact on the PPF.
-
Market interventions: Analyzing the effects of government policies such as price floors, price ceilings, taxes, and subsidies on market equilibrium.
-
Elasticity of supply and demand: Understanding how price elasticity of demand and supply affects market responses to changes in price or quantity.
To prepare effectively for the Unit 1 test:
-
Review your class notes and textbook thoroughly. Pay close attention to key definitions, graphs, and diagrams.
-
Practice solving problems. Use practice tests and online resources to familiarize yourself with different question types.
-
Understand the underlying economic principles. Don't just memorize formulas; focus on understanding the logic behind them.
-
Draw graphs and diagrams. Visually representing economic concepts can enhance your understanding and help you solve problems more effectively.
-
Seek clarification from your teacher. If you are struggling with any concepts, don't hesitate to ask for help.
By diligently studying the key concepts in Unit 1 and practicing with example questions, you'll be well-prepared to achieve a strong score on the test. Remember to focus on a deep understanding of the underlying principles, rather than rote memorization, to succeed in AP Macroeconomics and beyond. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation, but remember to actively engage with your course materials and seek additional resources for further enrichment. Good luck!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit 6 Similar Triangles Homework 2 Similar Figures
Apr 07, 2025
-
The Ordinary And Commonplace Events Of Life Are Classified As
Apr 07, 2025
-
Pal Histology Epithelial Tissue Lab Practical
Apr 07, 2025
-
Combination Strategies Likely Provide Value Through
Apr 07, 2025
-
All Ncic Records Have The Same Level Of Restriction
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ap Macroeconomics Unit 1 Test Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
