Assessing Elephant Populations Using Population Census Numbers
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
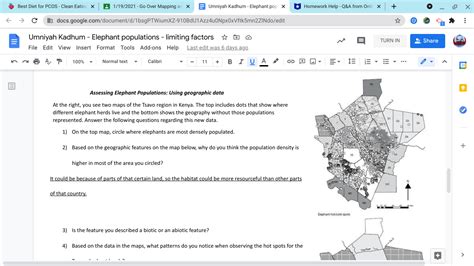
Table of Contents
Assessing Elephant Populations Using Population Census Numbers: A Comprehensive Guide
Elephant populations face numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Accurate assessment of their numbers is crucial for effective conservation strategies. While various methods exist, population census numbers remain a cornerstone of understanding elephant demographics and informing management decisions. This article delves into the intricacies of using population census numbers to assess elephant populations, covering methodologies, challenges, and the importance of data analysis and interpretation.
The Importance of Accurate Elephant Population Census Data
Accurate data on elephant populations is not merely a scientific curiosity; it's fundamental to effective conservation. Understanding population size, distribution, and trends allows conservationists to:
- Identify population declines: Early detection of declining populations is crucial for prompt intervention and the implementation of effective conservation measures.
- Target conservation efforts: Knowing where elephants are concentrated allows for focused protection efforts, such as anti-poaching patrols or habitat restoration projects.
- Assess the impact of conservation interventions: Population census data, collected over time, provides a benchmark to measure the effectiveness of conservation initiatives. Are populations increasing, stabilizing, or continuing to decline after implementing new strategies?
- Inform policy decisions: Reliable population data is essential for advocating for policy changes that protect elephant habitats and combat poaching. This might include lobbying for stricter anti-poaching laws, creating protected areas, or promoting sustainable land use practices.
- Monitor the impact of human activities: Census data can help assess the impact of human activities, such as infrastructure development or agricultural expansion, on elephant populations and their habitats.
Methodologies for Conducting Elephant Population Censuses
Several methodologies are employed for conducting elephant population censuses, each with its strengths and limitations. The choice of method depends on factors like the study area's size, terrain, elephant density, and available resources.
1. Complete Counts (Complete Censuses):
- Description: This involves attempting to count every single elephant within a defined area. This is usually only feasible for smaller, isolated populations.
- Method: Often involves ground surveys, potentially aided by aerial surveys for larger areas. Teams systematically traverse the study area, recording sightings and employing techniques to minimize double-counting (such as mapping individual elephant locations).
- Advantages: Provides the most accurate estimate of population size when successfully conducted.
- Disadvantages: Extremely time-consuming, labor-intensive, and expensive; impractical for large populations or extensive geographic areas. It also presents logistical and safety challenges.
2. Sampling Methods:
- Description: These methods involve counting elephants in a representative sample of the total area and extrapolating the findings to estimate the entire population.
- Methods: Common sampling techniques include:
- Line Transects: Observers walk or drive along predetermined lines, recording elephant sightings and the perpendicular distance from the line. Statistical models then estimate population density based on these sightings.
- Quadrats: The study area is divided into smaller, square quadrats, and elephants are counted in a randomly selected subset of quadrats.
- Distance Sampling: Similar to line transects, but also incorporates information about the distance to each elephant sighting to improve estimation accuracy.
- Advantages: Less time-consuming and expensive than complete counts; feasible for large populations and extensive areas.
- Disadvantages: Accuracy depends on the representativeness of the sample; requires careful design and statistical analysis to minimize bias and obtain reliable estimates.
3. Aerial Surveys:
- Description: Employing aircraft or drones to count elephants from the air. This is particularly useful in areas with dense vegetation or difficult terrain.
- Methods: Aerial surveys can be combined with ground surveys for improved accuracy. Sophisticated image analysis techniques, including machine learning algorithms, are increasingly used to analyze aerial imagery and count elephants more efficiently.
- Advantages: Covers large areas efficiently, minimizing the impact on elephant behavior.
- Disadvantages: Expensive, requires specialized equipment and expertise; accuracy can be affected by factors such as weather conditions, vegetation density, and observer bias. Distinguishing individual elephants can be challenging, particularly in dense herds.
4. Dung-Pile Counts:
- Description: This indirect method involves counting elephant dung piles within a defined area. The rate of dung deposition is estimated, and this is used to extrapolate the population size.
- Methods: Requires establishing a relationship between dung pile density and elephant density through additional methods, such as direct observation. This method is particularly useful in areas with dense vegetation where direct sighting is difficult.
- Advantages: Relatively inexpensive and less labor-intensive than direct counts; can provide insights into elephant distribution and movement patterns.
- Disadvantages: Accuracy depends on several assumptions, such as consistent dung decomposition rates and uniform dung distribution. Environmental factors like rainfall and temperature can affect dung pile persistence.
Challenges in Assessing Elephant Populations
Several challenges complicate accurate assessment of elephant populations:
- Difficult terrain and dense vegetation: Makes it difficult to observe elephants directly, especially in tropical forests and dense savannas.
- Elephant behavior: Elephants are highly mobile and often travel in large herds, making it difficult to count them without double-counting or missing individuals. Nocturnal behavior further complicates the process.
- Large geographic range: Many elephant populations span vast areas, making complete counts logistically challenging and expensive.
- Poaching and human-wildlife conflict: These factors can impact elephant populations, leading to population declines that need to be quantified.
- Limited resources: Conducting accurate and comprehensive elephant censuses requires significant financial and human resources.
- Data analysis and interpretation: Correct statistical analysis is essential to account for biases and uncertainties associated with various census methodologies. Expertise in ecological statistics is often needed.
Data Analysis and Interpretation of Census Data
Once population census data has been collected, rigorous analysis is crucial for accurate interpretation. This involves:
- Estimating population size: Employing appropriate statistical techniques to estimate the total population size from the collected data. This includes accounting for biases, such as detection probability and incomplete coverage.
- Assessing population trends: Analyzing population census data collected over time to identify trends, such as population increases, decreases, or stability. Statistical models can help predict future population trends.
- Mapping elephant distribution: Using geographic information systems (GIS) to map the location of elephant sightings and create spatial models of elephant distribution. This informs conservation strategies by identifying areas of high elephant density.
- Identifying critical habitats: Determining which habitats are most important for elephant survival and reproduction. This requires correlating elephant distribution data with environmental variables such as vegetation type, water availability, and human presence.
- Evaluating conservation effectiveness: Comparing population trends before and after implementing conservation interventions to assess their effectiveness.
Integrating Population Census Data with Other Information
Elephant population census numbers should not be considered in isolation. Integrating these data with other sources of information significantly enhances the understanding of elephant populations and informs more effective conservation strategies. These other data sources include:
- Genetic data: Assessing genetic diversity and population structure using DNA analysis can provide insights into the health and connectivity of elephant populations.
- Demographic data: Collecting data on age structure, sex ratio, and reproductive rates can provide valuable insights into elephant population dynamics.
- Ecological data: Data on habitat quality, food availability, and water resources can help explain variations in elephant distribution and abundance.
- Human-wildlife conflict data: Tracking instances of human-elephant conflict provides valuable information on areas requiring mitigation strategies.
Conclusion
Accurate assessment of elephant populations is essential for implementing effective conservation strategies. While challenges exist, advances in methodology, data analysis, and technology provide valuable tools. By integrating population census data with other sources of information and applying rigorous analytical techniques, conservationists can gain a deeper understanding of elephant populations, their threats, and opportunities for long-term conservation. The ongoing collection and analysis of population census numbers remain a crucial pillar in the fight to safeguard these magnificent animals for future generations. Further research into improved methodologies, the integration of novel technologies, and enhanced data analysis techniques will continue to refine our ability to monitor and protect elephant populations globally. Collaborative efforts among researchers, conservationists, and local communities are essential for the success of these endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Under Dodd 5240 06 Reportable Foreign Intelligence
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Sata Devices Did You Find
Mar 20, 2025
-
End Of Semester Test English 11a
Mar 20, 2025
-
Where Is An Integrated Microphone Normally Located On A Laptop
Mar 20, 2025
-
Pogil Electron Configuration And Orbitals Answer Key Model 2
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Assessing Elephant Populations Using Population Census Numbers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
