Ati Nursing Skill Template Medication Administration
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
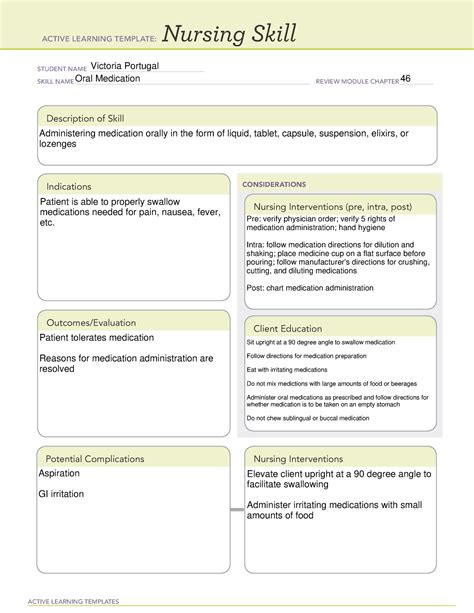
Table of Contents
ATI Nursing Skill Template: Medication Administration – A Comprehensive Guide
Medication administration is a fundamental skill for any registered nurse (RN). Accuracy and precision are paramount, as errors can have severe consequences for patients. This article provides a comprehensive guide to medication administration, utilizing the ATI nursing skill template as a framework. We'll explore each step in detail, offering practical tips and best practices to ensure safe and effective medication delivery.
Understanding the ATI Nursing Skill Template
The ATI (Assessment Technologies Institute) nursing skill templates offer a standardized approach to documenting nursing procedures. This structured format ensures consistency, clarity, and completeness, minimizing the risk of omission and improving overall patient safety. While the exact template may vary slightly depending on the version and institution, the core components remain consistent. These generally include:
- Assessment: Pre-administration assessment of the patient.
- Planning: Defining the goals and expected outcomes of medication administration.
- Implementation: The steps involved in administering the medication.
- Evaluation: Assessing the effectiveness of the medication and monitoring for adverse effects.
- Documentation: Detailed and accurate recording of the entire process.
Pre-Administration Assessment: The Crucial First Step
Before administering any medication, a thorough assessment is critical. This involves several key steps:
1. Verify the Patient's Identity: Two Identifiers are Essential
This is arguably the most crucial step. Never administer medication without confirming the patient's identity using two identifiers, such as:
- Name: Check the patient's name against the medication administration record (MAR).
- Date of Birth: Verify the date of birth on the patient's identification band and MAR.
- Medical Record Number: Compare the medical record number on the patient's wristband with the MAR.
Never rely on room number or visual identification alone.
2. Assess Allergies and Medication History: Preventing Adverse Reactions
Review the patient's medical record and allergy bracelet (if applicable) for any known drug allergies or adverse reactions. Inquire directly with the patient about any allergies or previous negative experiences with medications. Document all allergies and reactions clearly.
3. Review the Medication Order: Accuracy is Non-Negotiable
Scrutinize the medication order carefully for the following:
- Patient's Name: Ensure it matches the patient's identification.
- Medication Name: Verify the correct medication is prescribed.
- Dosage: Confirm the correct dose and frequency.
- Route of Administration: Check the specified route (oral, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, topical, etc.).
- Time of Administration: Note the scheduled administration time.
- Physician's Signature: Ensure the order is signed by a licensed physician.
Any discrepancy requires immediate clarification with the prescribing physician.
4. Assess the Patient's Condition: Tailoring Care to Individual Needs
Conduct a relevant physical assessment related to the medication being administered. For example, before administering cardiac medications, check the patient's heart rate and blood pressure. Before administering insulin, assess blood glucose levels. This helps to determine if the medication is appropriate at that time and to monitor for potential adverse effects.
5. Educate the Patient: Empowering Informed Consent
Educate the patient about the medication, including its purpose, dosage, potential side effects, and any necessary precautions. Obtain informed consent, ensuring the patient understands the medication and its administration. Answer any questions the patient may have. This step demonstrates respect for patient autonomy and promotes medication adherence.
Planning: Defining Goals and Expected Outcomes
Based on the assessment, formulate specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for medication administration. This typically involves:
- Goal: Administer the medication safely and effectively.
- Expected Outcomes: The patient will receive the correct medication, at the correct dose, via the correct route, at the correct time, without experiencing any adverse reactions. The patient will demonstrate understanding of the medication's purpose and potential side effects.
Implementation: The Steps of Medication Administration
The implementation phase outlines the procedural steps involved in administering the medication. This section varies considerably depending on the route of administration. Let’s consider some common routes:
Oral Medication Administration
- Verify the "Five Rights": Right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, right time.
- Assess for Swallowing Ability: Ensure the patient can swallow safely.
- Administer the Medication: Follow any specific instructions (e.g., with or without food).
- Offer Water: Unless contraindicated.
- Observe the Patient: Monitor for any adverse reactions or difficulties swallowing.
Intramuscular (IM) Injection
- Verify the "Six Rights": Including the right site.
- Prepare the Injection: Draw up the medication using sterile technique.
- Select the Injection Site: Use appropriate anatomical landmarks (e.g., vastus lateralis, deltoid).
- Cleanse the Site: Use an antiseptic swab.
- Administer the Injection: Insert the needle at the correct angle, aspirate (if required by policy), and inject the medication slowly.
- Withdraw the Needle: Apply gentle pressure to the site.
- Dispose of the Needle and Syringe: Follow proper safety procedures.
Subcutaneous (SubQ) Injection
Similar to IM injection, but with a shallower angle and smaller needle size. Common sites include the abdomen, outer thighs, and upper arms.
Intravenous (IV) Medication Administration
This requires advanced training and should only be performed by qualified nurses. It involves inserting an IV catheter into a vein and administering medication directly into the bloodstream. Strict adherence to aseptic technique is essential to prevent infection.
Topical Medication Administration
This involves applying medication to the skin or mucous membranes. Follow specific instructions for each medication, including dosage and application techniques.
Evaluation: Assessing Effectiveness and Monitoring for Adverse Effects
After medication administration, evaluate the effectiveness of the medication and monitor for any adverse reactions. This includes:
- Monitoring Vital Signs: Observe for changes in heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and temperature.
- Assessing for Side Effects: Look for signs and symptoms of adverse effects listed in the medication information.
- Evaluating Patient Response: Note any improvements or changes in the patient's condition related to the medication.
- Documenting Findings: Record all observations and evaluations accurately.
Documentation: A Critical Component of Patient Safety
Accurate and complete documentation is crucial for legal and clinical reasons. Record the following information:
- Date and Time of Administration: Include the exact time the medication was given.
- Medication Name and Dose: Specify the exact medication and dose administered.
- Route of Administration: Indicate the route used (oral, IM, IV, etc.).
- Site of Injection (if applicable): Note the specific location of the injection.
- Patient's Response: Record any observed effects, both positive and negative.
- Any Problems Encountered: Document any difficulties or unexpected events during the administration.
- Nurse's Signature: Sign and date the entry to ensure accountability.
Following the ATI template provides a structured approach to documenting this information accurately and comprehensively.
Additional Considerations: Best Practices and Safety Measures
- Medication Reconciliation: Ensure a thorough medication reconciliation process is in place at admission, transfer, and discharge to avoid medication errors.
- Six Rights of Medication Administration: Always adhere to the six rights: right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, right time, and right documentation.
- High-Alert Medications: Exercise extra caution when administering high-alert medications (e.g., insulin, heparin) due to their potential for causing significant harm if administered incorrectly.
- Medication Safety Protocols: Follow all hospital or institutional medication safety protocols and procedures.
- Policy and Procedure Adherence: Ensure strict adherence to policies and procedures related to medication administration.
- Continuing Education: Stay up-to-date on the latest medication safety guidelines and best practices through continuing education.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Collaborate with other healthcare professionals, including pharmacists and physicians, to ensure safe and effective medication administration.
Conclusion: Mastering Medication Administration for Optimal Patient Care
Mastering medication administration is a vital skill for every registered nurse. By following the ATI nursing skill template and employing best practices, nurses can significantly improve patient safety and achieve optimal treatment outcomes. Remember, accuracy, precision, and meticulous attention to detail are paramount in this critical aspect of nursing care. Consistent application of the knowledge presented here, alongside ongoing professional development, will contribute to a successful and safe nursing practice. Thorough understanding of each step, from pre-administration assessment to thorough documentation, is key to preventing medication errors and ensuring the best possible patient care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Annotations For A Raisin In The Sun
Mar 19, 2025
-
Lighting Fixtures In A Cooler Must Have Bulbs That Are
Mar 19, 2025
-
P O W E R Learning Online Success Free Pdf
Mar 19, 2025
-
Summary Of Brave New World Chapter 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Symbols In Their Eyes Were Watching God
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ati Nursing Skill Template Medication Administration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
