Biological Classification Model 4 Dichotomous Key
Onlines
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
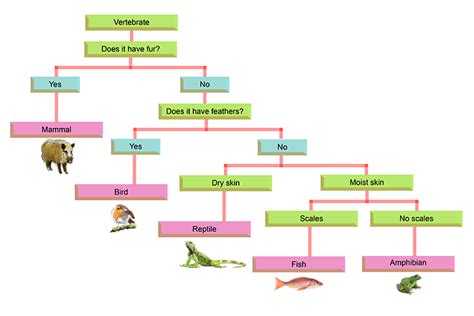
Table of Contents
Biological Classification and the Dichotomous Key: A Deep Dive into Model 4
Biological classification, also known as taxonomy, is the science of organizing and classifying living organisms. It provides a framework for understanding the relationships between different species and helps us make sense of the incredible biodiversity on Earth. One crucial tool used in biological classification is the dichotomous key, a hierarchical system that uses a series of paired statements (couplets) to identify an unknown organism. This article delves deep into Model 4 of dichotomous keys, exploring its structure, applications, and advantages, while also touching upon the limitations and alternatives.
Understanding Dichotomous Keys: The Foundation of Biological Identification
A dichotomous key is a structured identification tool that employs a series of paired, mutually exclusive choices to lead the user to the correct identification of an organism. Each choice presents two contrasting characteristics, and based on the observation of the organism, the user progresses down the key, narrowing down the possibilities until a final identification is reached. Several models of dichotomous keys exist, with Model 4 representing a sophisticated and widely-used approach.
The Structure of a Dichotomous Key
Dichotomous keys are characterized by their branching, tree-like structure. The structure is crucial for its functionality. It starts with a broad, encompassing statement and branches into increasingly specific statements with each choice. This progressive narrowing-down process effectively filters out species until only one possibility remains. The choices are generally based on easily observable morphological characteristics, such as leaf shape, flower structure, or animal body plan.
Key Components:
- Couplets: Pairs of mutually exclusive statements that describe contrasting characteristics of organisms.
- Numbers/Letters: Each couplet is numbered or lettered for easy navigation.
- Indentation: Indentation is used to show the hierarchical structure and the branching of the key.
- Terminal taxa: The end points of the key, representing the identified organism.
Model 4 Dichotomous Key: A Detailed Exploration
Model 4, often referred to as the indented key, is a particularly effective method for constructing and using dichotomous keys. Its structure focuses on clarity and ease of use, making it a popular choice for various applications.
Characteristics of Model 4:
- Indented Format: Uses indentation to visually represent the hierarchical structure. This improves readability and aids in following the correct path.
- Clear and Concise Language: Employs simple, unambiguous language that is easily understandable by users, regardless of their expertise level.
- Focus on Observable Characteristics: Relies primarily on readily observable characteristics, minimizing the need for specialized equipment or expertise.
- Hierarchical Structure: Organizes choices hierarchically, starting with broad characteristics and progressively narrowing down to specific ones.
Example of Model 4:
Let's consider a simplified example for identifying common tree types:
-
a. Leaves needle-like ...................................... go to 2 b. Leaves broad, flat ................................... go to 3
-
a. Needles in clusters ................................... Pine b. Needles single ....................................... Spruce
-
a. Leaves with lobed edges ............................. Oak b. Leaves with serrated edges .......................... Maple
In this example, the user starts at statement 1. Based on the observation of the tree's leaves, they follow either 1a or 1b. This process continues until they reach a terminal taxon (Pine, Spruce, Oak, or Maple).
Applications of Model 4 Dichotomous Keys
Model 4 dichotomous keys find widespread use across various fields, including:
- Biology Education: A fundamental tool for teaching students about biological classification and identification. It fosters critical thinking and observational skills.
- Field Biology: Essential for identifying organisms in their natural habitats. Portable and easy-to-use, they are invaluable tools for ecologists, botanists, and zoologists.
- Environmental Monitoring: Used to assess biodiversity and track changes in ecosystems over time. Accurate identification is crucial for conservation efforts.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Helps identify plant pests and diseases, enabling timely intervention and preventing significant losses.
- Medical Diagnosis: While not as common as other diagnostic methods, simplified dichotomous keys can be used in preliminary diagnoses based on observable symptoms.
Advantages of Using Model 4
Model 4’s popularity stems from several key advantages:
- Ease of Use: The indented format and clear language make it exceptionally easy to navigate and use. Even novice users can easily follow the key.
- Improved Accuracy: The hierarchical structure minimizes the chances of errors in identification. By systematically eliminating possibilities, it increases the accuracy of the identification process.
- Efficiency: Model 4 efficiently guides the user to the correct identification without unnecessary steps. The structured approach saves time and effort compared to other methods.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various levels of taxonomic detail. Keys can be constructed for identifying species, genera, families, or even higher taxonomic levels.
- Portability: Can be easily printed and carried into the field, making it ideal for fieldwork and outdoor applications.
Limitations of Dichotomous Keys and Alternative Approaches
While Model 4 dichotomous keys are incredibly useful, they do possess some limitations:
- Ambiguity in Characteristics: Sometimes organisms may exhibit characteristics that don't neatly fit into the dichotomies. This can lead to misidentification.
- Oversimplification: Dichotomous keys often simplify complex biological features, potentially overlooking subtle variations within a species.
- Lack of Evolutionary Context: Traditional dichotomous keys primarily focus on morphological characteristics, not necessarily reflecting evolutionary relationships.
- Not Suitable for All Organisms: Some organisms may have highly variable characteristics, making it difficult to construct a reliable dichotomous key. Microscopic organisms or those with highly similar features present particular challenges.
Alternatives to Dichotomous Keys:
In light of these limitations, alternative identification methods are frequently employed:
- Phylogenetic Trees: Illustrate evolutionary relationships between organisms, providing a more robust framework for classification.
- DNA Barcoding: Uses DNA sequencing to identify species, offering a more precise and objective approach compared to morphological characteristics.
- Expert Systems and Artificial Intelligence: Computer-based identification systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, capable of integrating various data types (morphological, molecular, ecological) for accurate identification.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Model 4 Dichotomous Keys
Despite the emergence of advanced identification techniques, Model 4 dichotomous keys retain significant value in biological classification. Their simplicity, ease of use, and portability make them indispensable tools for many applications, especially in field biology and educational settings. While limitations exist, understanding these constraints and employing supplementary methods where necessary allows for a more comprehensive and accurate approach to biological identification. By combining the strengths of Model 4 with other techniques, researchers and educators can harness the power of various methods to unlock the intricacies of the biological world and further our understanding of biodiversity. The future of biological classification likely involves a synergistic approach, integrating traditional techniques with cutting-edge technologies to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Capitulo 3a Pasando Por El Centro Answer Key
Mar 09, 2025
-
Three Candidates Showed Up For An Interview
Mar 09, 2025
-
Domain 4 Lesson 2 Fill In The Blanks
Mar 09, 2025
-
Frankenstein Volume 3 Chapter 5 Summary
Mar 09, 2025
-
Modeling Population Growth Rabbits Answer Key
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Biological Classification Model 4 Dichotomous Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
