_____ Brings Phosphorous Into Our Waterways.
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
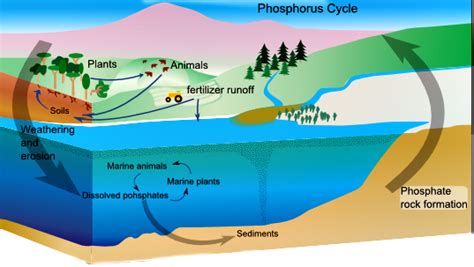
Table of Contents
Agricultural Runoff: The Silent Thief of Phosphorus and the Bane of Our Waterways
Phosphorus, a crucial nutrient for plant growth, plays a paradoxical role in our environment. While essential for healthy ecosystems, excessive phosphorus in our waterways triggers a cascade of devastating consequences. This article delves into the significant contribution of agricultural runoff as the primary culprit in this environmental crisis, exploring its mechanisms, impacts, and potential solutions.
Understanding the Phosphorus Problem: Eutrophication and its Ramifications
Phosphorus, unlike nitrogen which can be fixed from the atmosphere, is primarily found in rocks and soils. Its release into waterways, particularly in excessive amounts, fuels a process called eutrophication. This process initiates a chain reaction:
The Eutrophication Cascade: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Nutrient Overload: Excess phosphorus, primarily from agricultural runoff, enters lakes, rivers, and coastal waters.
- Algal Blooms: This surge of phosphorus triggers an explosive growth of algae and other aquatic plants. These blooms often appear as unsightly scums on the water's surface.
- Oxygen Depletion: As these massive algal blooms die and decompose, bacteria consume vast amounts of dissolved oxygen in the water. This process, known as hypoxia, creates "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive.
- Habitat Loss: The depletion of oxygen and the smothering effect of dense algal blooms destroy underwater habitats, threatening fish populations, shellfish, and other organisms.
- Water Quality Degradation: Eutrophication renders water unsuitable for drinking, recreation, and other human uses. The decaying algae can release toxins, further impacting water quality.
- Economic Impacts: The damage to fisheries, tourism, and recreational activities translates into significant economic losses for communities reliant on healthy waterways.
Agricultural Runoff: The Major Culprit
While various sources contribute to phosphorus pollution, agricultural runoff stands out as the dominant factor. The intensity of its impact is amplified by several intertwined mechanisms:
1. Fertilizers: The Phosphorus Powerhouse
Commercial fertilizers, essential for boosting crop yields, are a primary source of phosphorus entering waterways. These fertilizers contain significant amounts of phosphorus in readily soluble forms that are easily leached into the soil and subsequently transported via runoff.
Types of Fertilizers and their Phosphorus Content:
Different fertilizers vary in their phosphorus content. Understanding these differences is crucial for implementing effective management strategies. Diammonium phosphate (DAP) and monoammonium phosphate (MAP), for example, are high-phosphorus fertilizers frequently used in agriculture.
2. Manure Management: A Double-Edged Sword
Animal manure, a byproduct of livestock operations, is rich in phosphorus. Improper storage and management of manure can lead to significant phosphorus runoff. Rainwater can easily leach phosphorus from improperly managed manure piles, transporting it directly into adjacent waterways.
Effective Manure Management Practices:
Implementing best practices in manure management, such as using covered storage facilities, employing appropriate application rates, and incorporating manure into the soil, can significantly minimize phosphorus runoff.
3. Soil Erosion: Unmasking the Hidden Phosphorus
Soil erosion, often exacerbated by intensive agricultural practices, contributes significantly to phosphorus pollution. Eroded soil particles carry adsorbed phosphorus into waterways, further exacerbating the problem. The intensity of soil erosion is influenced by factors such as soil type, topography, and rainfall patterns.
Conservation Tillage and its Role:
Conservation tillage methods, such as no-till farming, minimize soil disturbance and thus reduce erosion rates, effectively preventing phosphorus loss from the soil.
4. Weather Patterns: A Force Multiplier
Rainfall and snowmelt play a crucial role in transporting phosphorus from agricultural fields into waterways. Heavy rainfall events can saturate soils, leading to increased surface runoff that carries phosphorus with it.
Predicting Runoff Events:
Understanding regional rainfall patterns and predicting high-intensity rainfall events are essential for developing targeted management strategies to minimize the impact of runoff.
The Ripple Effect: Environmental and Societal Consequences
The consequences of phosphorus pollution extend far beyond the immediate degradation of water quality. The impacts reverberate through entire ecosystems and affect human communities in significant ways:
1. Biodiversity Loss: A Silent Extinction
Eutrophication severely impacts aquatic biodiversity. The loss of oxygen in dead zones eliminates habitats for fish, shellfish, and other aquatic organisms, leading to population declines and even extinctions.
2. Human Health Risks: Toxins and Disease
Algal blooms can produce toxins that pose risks to human health. Exposure to these toxins through contaminated drinking water or recreational activities can cause various health problems.
3. Economic Strain: Beyond the Environmental Cost
The economic impacts of phosphorus pollution are substantial. Damage to fisheries, tourism, and recreation, coupled with the costs of water treatment and remediation efforts, places a heavy burden on communities and economies.
Mitigating the Phosphorus Problem: A Multifaceted Approach
Addressing phosphorus pollution requires a comprehensive and multifaceted strategy that targets various sources and pathways. The following measures are crucial in reducing phosphorus runoff from agricultural lands:
1. Best Management Practices (BMPs): A Holistic Approach
Implementing BMPs, which integrate various techniques, is essential in minimizing phosphorus loss from agricultural lands. These include:
- Nutrient Management Planning: Carefully planning fertilizer application based on soil testing and crop needs to avoid excessive phosphorus use.
- Cover Cropping: Planting cover crops during fallow periods helps prevent soil erosion and nutrient leaching.
- Buffer Strips: Establishing vegetated buffer strips along waterways helps filter out phosphorus and other pollutants from runoff.
- Riparian Buffers: Protecting and restoring riparian zones (areas adjacent to waterways) enhances natural filtration and reduces runoff.
- Precision Agriculture Techniques: Employing GPS-guided application of fertilizers and other inputs allows for targeted application and minimizes nutrient waste.
2. Policy and Regulation: A Driving Force for Change
Strong policies and regulations are needed to incentivize the adoption of BMPs and to hold agricultural producers accountable for phosphorus runoff. These regulations could include:
- Phosphorus Discharge Limits: Implementing strict limits on phosphorus discharge into waterways.
- Incentive Programs: Offering financial incentives for farmers who adopt BMPs.
- Education and Outreach: Educating farmers and stakeholders on the impacts of phosphorus pollution and the effectiveness of BMPs.
3. Technological Advancements: Innovation for a Sustainable Future
Technological advancements offer promising solutions for reducing phosphorus pollution. These innovations include:
- Phosphorus-efficient Fertilizers: Developing fertilizers that release phosphorus more slowly, reducing leaching losses.
- Advanced Water Treatment Technologies: Implementing advanced water treatment technologies to remove phosphorus from wastewater.
- Remote Sensing and Monitoring: Utilizing remote sensing techniques to monitor phosphorus levels in waterways and assess the effectiveness of BMPs.
Conclusion: A Collaborative Effort for Cleaner Waterways
Agricultural runoff is undeniably the primary driver of phosphorus pollution in our waterways. Addressing this challenge requires a collaborative effort involving farmers, policymakers, researchers, and the public. By implementing best management practices, strengthening regulations, and embracing technological advancements, we can significantly reduce phosphorus runoff and protect the health of our valuable water resources. The preservation of clean and healthy waterways is not just an environmental imperative; it is a cornerstone of sustainable communities and a thriving planet. The fight against phosphorus pollution demands sustained commitment and collective action – a concerted effort to secure a cleaner, healthier future for all.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match Each Characteristic With The Type Of Election It Describes
Mar 04, 2025
-
Geology Earth Systems 1340 Exam 4
Mar 04, 2025
-
Unit 1 Progress Check Frq Part A Ap Precalculus
Mar 04, 2025
-
Superfund Mini Webquest Answer Key Pdf
Mar 04, 2025
-
Dihybrid Genetics Practice Problems Answer Key
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about _____ Brings Phosphorous Into Our Waterways. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
