Circuit Training Using The Unit Circle
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
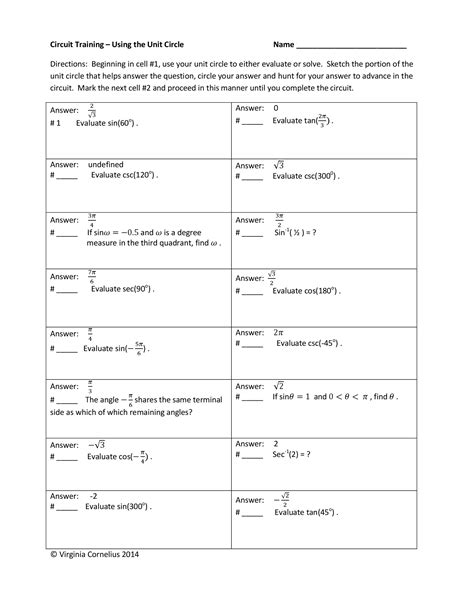
Table of Contents
Circuit Training Using the Unit Circle: A Trigonometric Workout for Your Brain
The unit circle. That seemingly simple circle with a radius of one, nestled within the Cartesian plane. It's a cornerstone of trigonometry, a gateway to understanding angles, radians, and the cyclical nature of sine, cosine, and tangent functions. But it's more than just a diagram in a textbook; it's a powerful tool for building a strong foundation in trigonometry, a foundation that can be strengthened through a rigorous program of "circuit training." This isn't your typical gym workout, though. This is a mental workout designed to boost your understanding and problem-solving abilities related to the unit circle.
Level 1: Warming Up with the Basics
Before we jump into the intensive circuit, we need to warm up our trigonometric muscles. This level focuses on the fundamental concepts and relationships within the unit circle.
1.1: Identifying Key Angles and Coordinates
The unit circle's beauty lies in its simplicity and its ability to represent all angles. Remember, the x-coordinate represents the cosine of the angle, and the y-coordinate represents the sine of the angle. Start by memorizing the coordinates for the key angles: 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, and their corresponding radians (0, π/6, π/4, π/3, π/2). Then, extend your knowledge to the other quadrants, remembering the signs of sine and cosine in each quadrant (All Students Take Calculus – ASTC is a handy mnemonic).
1.2: Mastering Radians and Degrees
This is crucial. You need to be comfortable converting between radians and degrees. Practice converting key angles back and forth. For instance, quickly determine the radian measure of 135° or the degree measure of 5π/6. Fluency in both systems is essential for efficient problem-solving.
1.3: Understanding the Unit Circle's Symmetry
The unit circle is symmetrical. Understanding this symmetry allows you to quickly determine the sine and cosine of angles based on their relationship to the key angles. For example, knowing the coordinates for 30° allows you to easily determine the coordinates for 150°, 210°, and 330° by considering the symmetry and the sign changes in different quadrants.
Level 2: Intermediate Circuits: Sine, Cosine, and Tangent
Now that we've warmed up, it's time to increase the intensity. This level focuses on applying the knowledge of the unit circle to calculate sine, cosine, and tangent values.
2.1: Calculating Trigonometric Ratios
Practice calculating the sine, cosine, and tangent of angles using the unit circle. Start with the key angles, then move on to angles derived from those angles using symmetry. Don't just rely on your calculator; try to calculate them mentally. This will reinforce your understanding of the relationships between angles and their trigonometric ratios. For instance, challenge yourself with questions like: What is sin(2π/3)? What is cos(7π/6)? What is tan(5π/4)?
2.2: Solving Trigonometric Equations
This step takes things a notch higher. You will now start solving equations involving sine, cosine, and tangent. For example: Find all angles θ such that sin(θ) = 1/2. Or, find all angles θ in the interval [0, 2π) such that cos(θ) = -√3/2. These exercises require a deeper understanding of the unit circle and its cyclical nature. Remember to consider all possible solutions within the specified range.
2.3: Graphing Trigonometric Functions
Understanding the unit circle is key to understanding the graphs of sine, cosine, and tangent functions. By visualizing the coordinates on the unit circle as the angle changes, you can better understand the periodic nature, amplitude, and phase shift of these functions. Try sketching the graphs of these functions without relying on a graphing calculator. Focus on key points like intercepts, maxima, and minima.
Level 3: Advanced Circuit Training: Identities and Applications
This is where the real challenge begins. We'll move beyond basic calculations and explore the more intricate aspects of trigonometry.
3.1: Mastering Trigonometric Identities
Trigonometric identities are powerful tools. They allow you to simplify complex expressions and solve equations that would otherwise be intractable. Familiarize yourself with fundamental identities such as Pythagorean identities (sin²θ + cos²θ = 1), quotient identities (tanθ = sinθ/cosθ), and reciprocal identities (cscθ = 1/sinθ, secθ = 1/cosθ). Practice using these identities to simplify expressions and solve equations. For example, simplify (1 - cos²θ)/sin²θ, or solve the equation 2sin²θ + sinθ - 1 = 0.
3.2: Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Understanding inverse trigonometric functions (arcsin, arccos, arctan) requires a deep grasp of the unit circle. These functions "undo" the trigonometric functions, giving you the angle corresponding to a specific trigonometric ratio. Practice finding the principal values of inverse trigonometric functions, remembering the restricted domains and ranges of these functions. This involves careful consideration of which quadrant the angle lies in based on the sign of the trigonometric ratio.
3.3: Applications in Other Fields
The unit circle is not just a theoretical concept. It has practical applications in various fields. Explore some of these applications:
- Physics: The unit circle is frequently used in analyzing oscillatory motion (like a pendulum) and wave phenomena.
- Engineering: Understanding trigonometric functions and the unit circle is essential in many engineering disciplines, from calculating forces and stresses to designing circuits.
- Computer Graphics: The unit circle plays a vital role in computer graphics and animation, specifically in representing rotations and transformations.
- Navigation: Trigonometry, including the unit circle, is used in calculating distances, bearings, and positions.
Level 4: The Marathon: Problem-Solving and Application
This final level tests your endurance and ability to apply all the knowledge you've gained.
4.1: Complex Trigonometric Problems
Practice solving complex problems that combine multiple concepts from the previous levels. These problems might involve a combination of trigonometric identities, equations, and applications. This is where you can truly assess your understanding and problem-solving skills.
4.2: Word Problems and Real-World Applications
Translate real-world situations into mathematical models using trigonometry. This could involve problems related to height, distance, angles of elevation or depression, or other applications that rely on understanding trigonometric ratios and the unit circle.
4.3: Advanced Trigonometric Identities and Proofs
Dive into more advanced identities and try proving them using the unit circle as a visual aid. This further solidifies your understanding of the intricate relationships between trigonometric functions. Proofs involving sum and difference identities, double-angle identities, and half-angle identities are excellent examples.
Cooling Down: Review and Reflection
After completing this circuit training, take time to review the concepts you've covered. Identify your strengths and weaknesses. Review any areas where you struggled and seek further clarification. The unit circle is a powerful tool, but mastering it requires consistent effort and practice. Remember, this is a marathon, not a sprint. Regular review and practice will solidify your understanding and improve your ability to solve trigonometric problems efficiently and effectively. The unit circle, once mastered, becomes an intuitive tool, a mental map guiding you through the intricate world of trigonometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is Not True About Mobile Health
Mar 19, 2025
-
Disulfiram Is Taken By A Client Daily For Abstinence Maintenance
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Title Of This Work Of Art
Mar 19, 2025
-
Advanced Hardware Lab 3 3 Identify Memory Technologies
Mar 19, 2025
-
Intuit Academy Tax Level 1 Study Guide Pdf Free Download
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Circuit Training Using The Unit Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
