Compare Types Of Savings Accounts Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 26, 2025 · 7 min read
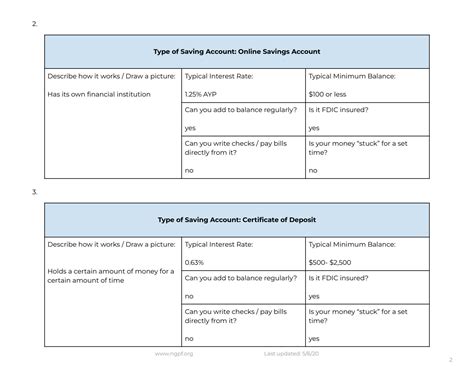
Table of Contents
Compare Types of Savings Accounts: Your Answer Key to Choosing the Best One
Saving money is a crucial part of building a secure financial future. However, simply putting money aside isn't enough; you need to choose the right savings vehicle to maximize your returns and reach your financial goals. This comprehensive guide compares different types of savings accounts, providing you with the answer key to selecting the best option for your specific needs.
Understanding Savings Accounts: The Fundamentals
Before diving into the different types, let's establish a common understanding of what a savings account is. Essentially, a savings account is a deposit account held at a bank or credit union that earns interest. This interest is the reward you receive for letting the financial institution use your money. The key difference between a savings account and a checking account is its purpose: savings accounts are designed for long-term savings and building wealth, while checking accounts facilitate everyday transactions.
Key Features to Consider:
- Interest Rate: The rate at which your savings grow. Higher rates mean faster growth, but they aren't always indicative of the best account.
- Minimum Deposit: The minimum amount required to open and maintain the account.
- Fees: Monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, or fees for falling below a minimum balance.
- Accessibility: How easily you can access your funds. Some accounts offer easier access than others.
- Insurance: Is your money insured by the FDIC (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) or a similar agency? This protection is crucial.
Types of Savings Accounts: A Detailed Comparison
Let's explore the most common types of savings accounts available, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you make an informed decision.
1. Regular Savings Accounts: The Foundation of Saving
Regular savings accounts are the most basic type. They offer a relatively low interest rate but provide easy access to your funds and typically have minimal fees. They are perfect for beginners or those who need easy access to their money while still earning some interest.
Pros:
- Easy Access: Funds are easily accessible via ATM, debit card, or online transfers.
- Low Minimums: Often require minimal initial deposits.
- FDIC Insured: Your deposits are typically insured up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
Cons:
- Low Interest Rates: Typically offer lower interest rates compared to other savings options.
- Potential Fees: Some banks may charge monthly maintenance fees if the balance falls below a certain threshold.
2. High-Yield Savings Accounts: Maximizing Your Returns
High-yield savings accounts offer significantly higher interest rates than regular savings accounts, making them ideal for building wealth more rapidly. While they still provide relatively easy access to funds, the higher returns come at the cost of potentially slightly higher minimum balance requirements.
Pros:
- Higher Interest Rates: Significantly higher returns compared to regular savings accounts.
- FDIC Insured: Your deposits are typically insured up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
Cons:
- Slightly Higher Minimums: May require a higher minimum balance to avoid fees.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Interest rates on these accounts can fluctuate based on market conditions.
3. Money Market Accounts (MMAs): A Blend of Savings and Checking
Money market accounts combine features of both savings and checking accounts. They typically offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts and often come with check-writing or debit card capabilities, offering more flexibility. However, they usually have higher minimum balance requirements.
Pros:
- Higher Interest Rates: Typically offer higher interest rates than regular savings accounts.
- Check-Writing Capabilities: May allow for a limited number of checks or debit card transactions.
- FDIC Insured: Your deposits are typically insured up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
Cons:
- Higher Minimum Balance Requirements: Usually require a significantly higher minimum balance than regular savings accounts.
- Potential Fees: May charge fees for falling below the minimum balance or for excessive transactions.
4. Certificates of Deposit (CDs): Locked-In Returns for a Specific Term
Certificates of deposit (CDs) are savings accounts with a fixed term and interest rate. You agree to keep your money in the CD for a specific period (e.g., 6 months, 1 year, 5 years), and in return, you receive a higher interest rate than you would with a regular savings account. However, withdrawing your money before the maturity date typically incurs a penalty.
Pros:
- Higher Interest Rates: Generally offer higher interest rates than regular savings or high-yield savings accounts.
- Predictable Returns: The interest rate is fixed for the term of the CD.
Cons:
- Limited Access: Withdrawing money early typically incurs penalties.
- Interest Rate Risk: If interest rates rise after you've locked in a CD rate, you may miss out on higher returns.
5. Savings Bonds: A Government-Backed Investment
Savings bonds are debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury. They offer a fixed interest rate, and the interest is compounded semi-annually. They are considered low-risk investments, backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
Pros:
- Government-Backed: Backed by the U.S. government, making them very low-risk.
- Tax Advantages: May offer tax advantages depending on how they are used.
Cons:
- Limited Liquidity: May be difficult to sell before maturity.
- Lower Interest Rates: Interest rates may be lower than other savings options.
6. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): Tax Advantages for Healthcare
A Health Savings Account (HSA) is a tax-advantaged savings account used to pay for eligible healthcare expenses. Contributions are tax-deductible, grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
Pros:
- Tax Advantages: Triple tax benefits: tax-deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
- Long-Term Savings: Funds can grow tax-free for future medical expenses.
Cons:
- Eligibility Requirements: You must be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) to be eligible.
- Limited Use: Funds can only be used for qualified medical expenses.
Choosing the Right Savings Account: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the best savings account depends on your individual circumstances and financial goals. Consider the following factors:
-
Your Financial Goals: What are you saving for? A short-term goal (like a down payment) might benefit from a high-yield savings account or money market account, while a long-term goal (like retirement) might be better suited to a CD or savings bonds.
-
Your Risk Tolerance: How comfortable are you with the risk of losing money? CDs and savings bonds are low-risk, while higher-yield accounts carry a slightly higher degree of risk (though still very low).
-
Your Time Horizon: How long do you plan to save your money? If you need access to your funds quickly, a regular savings account or high-yield savings account is preferable. If you can lock your money away for a longer period, a CD may offer better returns.
-
Your Liquidity Needs: How much access to your money do you need? Regular savings accounts offer the highest liquidity, while CDs and savings bonds offer the least.
-
Fees and Minimum Balance Requirements: Carefully review the fees associated with each account, including monthly maintenance fees and minimum balance requirements, to ensure they align with your financial situation.
-
Interest Rates: Compare the interest rates offered by different banks and credit unions to maximize your returns. Remember that higher interest rates aren't always the best indicator; consider the overall package of features and fees.
Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Your Savings Strategy
Once you've chosen the right savings account, consider these strategies to enhance your savings efforts:
- Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account each month. This makes saving consistent and effortless.
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish clear, achievable savings goals to stay motivated and track your progress.
- Review Your Accounts Regularly: Regularly review your savings accounts to monitor your progress and ensure your chosen account still meets your needs.
- Diversify Your Savings: Consider diversifying your savings across different account types to manage risk and potentially increase returns.
Conclusion: Your Savings Journey Starts Now
Choosing the right savings account is a crucial step in securing your financial future. By carefully considering the features and benefits of each type of account, and aligning your choice with your personal financial goals and risk tolerance, you can build a strong foundation for financial success. Remember to regularly review and adjust your savings strategy as your circumstances evolve. This comprehensive guide serves as your answer key to navigating the world of savings accounts and making informed decisions that will help you achieve your financial aspirations. Start saving today and watch your wealth grow!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Damage To The Circled Area May Cause What Symptoms
Mar 29, 2025
-
Ap Bio Unit 7 Progress Check Mcq Part B
Mar 29, 2025
-
Summary Of Chapter 17 Of The Giver
Mar 29, 2025
-
Which Evasion Aids Can Assist You With Making Contact
Mar 29, 2025
-
Analyze A High School Resume And Cover Letter
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Compare Types Of Savings Accounts Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
