Continuous Monitors Are Run For Systems That Could
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
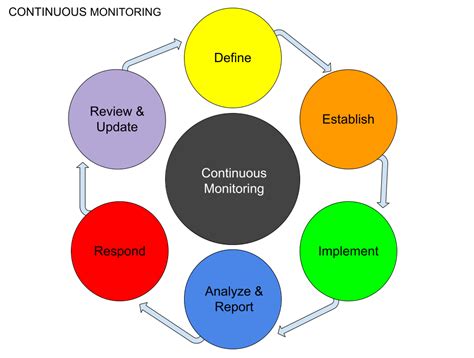
Table of Contents
- Continuous Monitors Are Run For Systems That Could
- Table of Contents
- Continuous Monitors: Keeping a Watchful Eye on Critical Systems
- Why Continuous Monitoring Matters: Protecting Your Vital Systems
- The Consequences of Inadequate Monitoring
- Key Components of a Robust Continuous Monitoring System
- Types of Continuous Monitoring
- Challenges in Implementing Continuous Monitoring
- Best Practices for Effective Continuous Monitoring
- The Future of Continuous Monitoring
- Conclusion: Continuous Vigilance, Continuous Improvement
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Continuous Monitors: Keeping a Watchful Eye on Critical Systems
Continuous monitoring is crucial for systems that could experience unexpected failures or performance degradation. These systems, often the backbone of businesses and critical infrastructure, demand constant vigilance to ensure uptime, security, and optimal performance. This article delves deep into the world of continuous monitoring, exploring its applications, benefits, challenges, and best practices.
Why Continuous Monitoring Matters: Protecting Your Vital Systems
The importance of continuous monitoring cannot be overstated, particularly for systems that:
- Support critical business operations: Downtime for e-commerce platforms, financial trading systems, or healthcare applications can have catastrophic consequences, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even loss of life.
- Handle sensitive data: Continuous monitoring is essential to detect and respond to security breaches, data leaks, and unauthorized access attempts.
- Require high availability: Systems with stringent uptime requirements, like cloud infrastructure or online gaming servers, necessitate round-the-clock monitoring to prevent disruptions and maintain user satisfaction.
- Operate in complex environments: Distributed systems, microservices architectures, and hybrid cloud deployments demand sophisticated monitoring solutions to track the performance and health of numerous interconnected components.
- Undergo frequent updates and deployments: Continuous monitoring provides insights into the impact of software updates and deployments, helping identify and mitigate potential issues early on.
The Consequences of Inadequate Monitoring
Ignoring the need for continuous monitoring can result in:
- Prolonged downtime: Unidentified problems can escalate, leading to extensive outages and significant business disruptions.
- Data breaches and security vulnerabilities: Unmonitored systems are more susceptible to cyberattacks, resulting in data loss, financial losses, and regulatory penalties.
- Poor performance and user dissatisfaction: Slow response times, application errors, and other performance issues can negatively impact user experience and brand reputation.
- Increased operational costs: Reactive problem-solving is more expensive and time-consuming than proactive monitoring and maintenance.
- Compliance violations: Industries with strict regulatory requirements (e.g., healthcare, finance) must ensure compliance through robust monitoring and auditing practices.
Key Components of a Robust Continuous Monitoring System
A comprehensive continuous monitoring system comprises several vital components:
-
Data Collection: This involves gathering data from various sources, including servers, applications, databases, networks, and user activity. Techniques used include metrics collection (CPU usage, memory consumption, network latency), log analysis, and synthetic transaction monitoring.
-
Data Processing and Analysis: Raw data needs processing to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends. This often involves techniques such as data aggregation, filtering, correlation, and machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection.
-
Alerting and Notification: The system should automatically alert administrators when critical thresholds are breached or anomalies are detected. This could involve email alerts, SMS messages, or integration with collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams. Effective alerting is crucial to ensure timely responses to problems.
-
Visualization and Reporting: Dashboards and reports provide a clear overview of system performance, allowing administrators to quickly identify and understand trends. These tools should provide visualizations of key metrics, trends, and alerts, facilitating informed decision-making.
-
Automation and Remediation: Automating responses to certain events, such as automatically restarting failed services or scaling resources, can significantly reduce downtime and improve efficiency.
-
Centralized Management: A centralized management console provides a single pane of glass for monitoring multiple systems and applications. This simplifies the management of complex environments and enhances operational efficiency.
Types of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring strategies vary depending on the specific needs of the system being monitored. Some common types include:
-
Application Performance Monitoring (APM): APM focuses on the performance of applications, tracking metrics such as response times, error rates, and resource utilization. It provides insights into the behavior of individual applications and their interactions within a larger system.
-
Infrastructure Monitoring: This type of monitoring focuses on the health and performance of underlying infrastructure components, including servers, networks, and storage systems. It monitors metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, and network latency.
-
Log Monitoring: Analyzing log files from applications and infrastructure components can uncover valuable information about system behavior, errors, and security events. Log monitoring solutions can aggregate, filter, and analyze large volumes of log data to identify patterns and anomalies.
-
Security Monitoring: This focuses on detecting and responding to security threats, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, and data breaches. Security monitoring solutions often use techniques like intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) and security information and event management (SIEM) to identify and respond to security events.
-
Synthetic Monitoring: This involves simulating user interactions with applications and systems to proactively detect performance issues. Synthetic monitoring can detect problems before they impact real users, allowing for proactive remediation.
Challenges in Implementing Continuous Monitoring
While the benefits of continuous monitoring are significant, implementing a robust system can present several challenges:
-
Data Volume and Velocity: Modern systems generate massive amounts of data, requiring powerful infrastructure and efficient data processing techniques.
-
Data Complexity: Correlating data from multiple sources and interpreting complex relationships requires advanced analytics capabilities.
-
Alert Fatigue: Excessive alerts can overwhelm administrators, leading to alert fatigue and delayed responses to critical issues.
-
Integration Complexity: Integrating monitoring tools with existing systems and applications can be challenging, requiring careful planning and execution.
-
Cost: Implementing and maintaining a comprehensive continuous monitoring system can be expensive, requiring investment in infrastructure, software, and skilled personnel.
Best Practices for Effective Continuous Monitoring
To maximize the effectiveness of your continuous monitoring strategy, consider these best practices:
-
Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define what you want to achieve with continuous monitoring, focusing on specific metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs).
-
Choose the Right Tools: Select monitoring tools that align with your specific needs and budget. Consider factors like scalability, integration capabilities, and ease of use.
-
Establish Baselines: Establish baseline performance metrics for your systems to provide a reference point for identifying anomalies.
-
Automate Alerting: Configure automated alerts for critical events to ensure timely responses.
-
Develop Response Plans: Develop clear procedures for responding to different types of alerts and incidents.
-
Regularly Review and Refine: Regularly review your monitoring strategy and make adjustments based on your evolving needs and learnings. The system should be adaptable to changing business needs and technological advancements.
-
Invest in Training: Train your staff on how to effectively use monitoring tools and interpret data.
The Future of Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is rapidly evolving, with emerging trends shaping its future:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being increasingly used to automate anomaly detection, predict potential problems, and optimize resource allocation.
-
Serverless Computing and Microservices: Monitoring serverless architectures and microservices requires new approaches to track performance and identify issues across distributed systems.
-
Observability: Observability focuses on understanding the internal state of a system based on its outputs. It goes beyond traditional monitoring by providing deeper insights into system behavior.
-
Automated Remediation: Automating responses to incidents is becoming increasingly important to reduce downtime and improve efficiency.
Conclusion: Continuous Vigilance, Continuous Improvement
Continuous monitoring is not just a best practice; it's a necessity for systems that are crucial to business operations and overall success. By implementing a robust, well-designed continuous monitoring system, organizations can protect their vital systems, enhance performance, improve security, and achieve business continuity. Regular evaluation, adaptation, and the adoption of emerging technologies will further ensure the ongoing effectiveness of this critical function, offering the ability to proactively address issues before they become catastrophic, and thus ensuring long-term stability and success. Continuous monitoring is about more than simply watching your systems; it's about ensuring their continuous improvement and unwavering reliability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Discovery Channel Body Story Breaking Down Answer Key
Mar 21, 2025
-
Rn Learning System Communication Final Quiz
Mar 21, 2025
-
Sedra Smith Microelectronic Circuits 8th Edition Solutions Pdf
Mar 21, 2025
-
Interactive Tutorial Forming Questions In Spanish
Mar 21, 2025
-
Tienes Tu Cuaderno No No 1 Of 1 Tengo
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Continuous Monitors Are Run For Systems That Could . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
