Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Lymph Node.
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
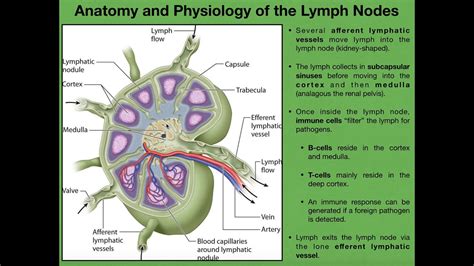
Table of Contents
Correctly Labeling the Anatomical Features of a Lymph Node: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the anatomy of a lymph node is crucial for anyone studying biology, medicine, or related fields. These small, bean-shaped organs play a vital role in the body's immune system, acting as filters for lymph fluid and housing immune cells that fight infection. This detailed guide provides a comprehensive overview of lymph node anatomy, focusing on accurately identifying and labeling its key features. We'll explore both macroscopic and microscopic structures, enhancing your understanding of this essential component of the lymphatic system.
Macroscopic Anatomy: The Big Picture
Before delving into the microscopic details, let's examine the lymph node's overall structure visible to the naked eye or with low magnification. A typical lymph node exhibits several easily identifiable features:
1. Hilum: The Gateway to the Node
The hilum is a crucial indentation on the concave side of the lymph node. This isn't just a random dip; it's the entry and exit point for several vital structures:
- Efferent lymphatic vessels: These vessels carry filtered lymph away from the lymph node, transporting it towards larger lymphatic ducts and ultimately back into the bloodstream. Think of these as the "output" channels of the node.
- Blood vessels: The hilum also provides access for blood vessels that supply the lymph node with oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products. These are essential for maintaining the node's functionality.
- Nerves: Nerve fibers enter and leave the lymph node through the hilum, regulating its activity and responding to immune signals.
The hilum's strategic location makes it a key landmark for identifying and orienting a lymph node.
2. Capsule: Protective Outer Layer
Encasing the entire lymph node is a tough, fibrous capsule. This capsule provides structural support and protection, shielding the delicate internal structures from external damage. The capsule isn't just a passive barrier; it also plays a role in the organization of the lymph node's internal architecture.
3. Trabeculae: Internal Support Structures
Extending inward from the capsule are fibrous strands called trabeculae. These septa act like internal scaffolding, dividing the lymph node into compartments and providing structural support for the lymphatic tissue within. They help organize the flow of lymph and the distribution of immune cells.
Microscopic Anatomy: Delving into the Details
Now, let's zoom in to the microscopic level to appreciate the intricate details of lymph node structure. This is where the real immune action happens.
1. Cortex: The Outer Region
The cortex is the outer region of the lymph node, characterized by densely packed lymphatic tissue. This area is primarily composed of:
a) Follicles: Sites of B Cell Activity
Within the cortex, you'll find numerous lymphoid follicles. These are spherical structures that are primarily composed of B lymphocytes (B cells). These B cells are crucial for humoral immunity—the antibody-mediated aspect of the immune response. Follicles can be categorized as:
- Primary follicles: These are relatively small and contain mostly resting B cells.
- Secondary follicles: These are larger and exhibit a germinal center, a region of rapid B cell proliferation and differentiation. The germinal center is where B cells undergo affinity maturation, improving their ability to recognize and bind to specific antigens.
b) Paracortex: T Cell Territory
Surrounding the follicles is the paracortex, a region rich in T lymphocytes (T cells). T cells are crucial for cell-mediated immunity, directly attacking infected or cancerous cells. The paracortex's population of T cells increases significantly during immune responses. This area is strategically positioned between the follicles (B cell zone) and the medulla (the area where lymphocytes exit the lymph node), facilitating interactions between B and T cells during immune responses.
2. Medulla: The Inner Region
The medulla is the innermost region of the lymph node, located deep within the cortex. It's characterized by:
a) Medullary Cords: Networks of Immune Cells
The medulla contains medullary cords, which are elongated strands of lymphatic tissue extending from the cortex into the medulla. These cords contain a mixture of B cells, T cells, plasma cells (antibody-producing cells), and macrophages (cells that engulf and digest cellular debris and pathogens).
b) Medullary Sinuses: Lymph Pathways
Running between the medullary cords are medullary sinuses. These are wide, irregular channels filled with lymph fluid. These sinuses are lined with specialized cells, including macrophages and reticular cells, which help to filter the lymph and remove pathogens or debris. The medullary sinuses ultimately converge at the hilum, allowing filtered lymph to exit the lymph node.
3. Subcapsular Sinus: Initial Filtering Stage
Located just beneath the capsule, the subcapsular sinus is the first encounter point for lymph entering the lymph node. This sinus is a large, irregular space that acts as an initial filter, trapping antigens and pathogens. Macrophages within this sinus play a critical role in eliminating these foreign invaders.
4. Trabecular Sinuses: Connecting the Subcapsular Sinus to the Medulla
Lymph flows from the subcapsular sinus into smaller trabecular sinuses, located within the trabeculae. These sinuses connect the subcapsular sinus to the medullary sinuses, facilitating the movement of lymph through the node. Like the subcapsular sinus, these also contain macrophages and other immune cells that help filter the lymph.
Clinical Significance: Why Accurate Labeling Matters
Accurate labeling of lymph node anatomy is not merely an academic exercise; it has significant clinical implications. Knowledge of lymph node structure is essential for:
- Diagnosing lymphomas and other lymph node cancers: Abnormal lymph node size, consistency, and cellular composition can be indicative of various malignancies. Precise identification of the affected areas is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Staging cancers: The presence and location of cancerous cells in lymph nodes are key factors in determining the stage and prognosis of various cancers. Lymph node involvement indicates metastasis, meaning the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Understanding immune responses: Studying the microscopic architecture of lymph nodes helps researchers understand how the immune system responds to infections and diseases. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective vaccines and immunotherapies.
- Surgical procedures: Surgeons need a detailed understanding of lymph node anatomy to perform lymph node biopsies and other surgical procedures accurately and safely.
Conclusion: Mastering Lymph Node Anatomy
This comprehensive guide has explored the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the lymph node, highlighting its key features and their functional significance. Accurate labeling of these anatomical features is paramount for understanding the intricacies of the lymphatic system and its crucial role in the body's immune defense mechanisms. By mastering the details presented here, you'll gain a solid foundation for further studies in immunology, oncology, and other related fields. Remember to practice labeling diagrams and referencing high-quality anatomical illustrations to solidify your understanding. The more you engage with this complex yet fascinating structure, the clearer the picture will become.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Borderlands La Frontera The New Mestiza
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Sun Also Rises Summary By Chapter
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Banner Requires 1 1 3
Mar 14, 2025
-
Secondary Math 3 Module 6 Modeling Periodic Behavior 6 1 Answers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Silvina Tuvo Un Accidente En Su Automovil
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Lymph Node. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
