Correctly Label The Following Structures Of The Female Breast
Onlines
Mar 16, 2025 · 7 min read
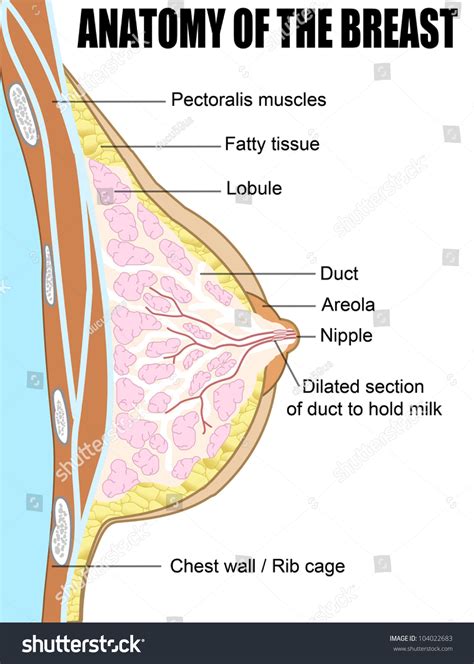
Table of Contents
Correctly Label the Following Structures of the Female Breast: A Comprehensive Guide
The female breast, a complex and fascinating organ, is far more than just a symbol of femininity. Understanding its intricate anatomy is crucial for healthcare professionals, students, and even those simply seeking a deeper appreciation of the human body. This comprehensive guide will delve into the detailed structures of the female breast, providing a clear and accurate labeling system to enhance your understanding. We will explore each component, its function, and its clinical significance, ensuring a thorough and informative exploration.
I. The Major Components of the Female Breast: A Layered Approach
The female breast isn't a single, monolithic structure. Instead, it's a layered arrangement of tissues and components, each playing a vital role in its overall function and appearance. Let's break down these layers and their constituent parts:
A. The Skin: The Outermost Layer
The skin overlying the breast is a delicate yet crucial component. Its characteristics vary depending on individual factors like age, genetics, and hormonal influences.
- Nipple: The highly pigmented, centrally located projection of the breast. It's characterized by its numerous tiny openings – the lactiferous duct openings – that allow for milk ejection during lactation. The nipple's sensitivity arises from a high concentration of nerve endings.
- Areola: The circular pigmented area surrounding the nipple. Its darker color is due to increased melanin concentration. The areola contains Montgomery's glands, small sebaceous glands that secrete a lubricating substance to protect the nipple during breastfeeding. These glands appear as tiny bumps on the areola's surface.
- Skin texture and color: The skin's texture and color can vary considerably. It is generally smooth, but can become uneven with age or pregnancy due to changes in connective tissue and fat distribution. Changes in skin color can indicate underlying medical conditions, emphasizing the importance of regular self-exams.
B. The Subcutaneous Tissue: A Layer of Support and Fat
Beneath the skin lies the subcutaneous tissue, a crucial layer composed primarily of adipose (fat) tissue. This layer contributes significantly to the breast's overall size and shape. The amount of fat varies widely depending on individual factors, genetics, and body weight.
- Cooper's ligaments (Suspensory ligaments): These fibrous bands of connective tissue extend from the skin to the underlying pectoral fascia, providing structural support to the breast. They help to maintain the breast's shape and prevent sagging (ptosis). The weakening of these ligaments is a contributing factor to breast sagging with age and changes in body weight.
- Blood vessels and lymphatic vessels: A rich network of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels runs through the subcutaneous tissue, supplying nutrients and oxygen to the breast tissue and draining waste products. These vessels are crucial for immune function and are relevant in the spread of breast cancer. The axillary lymph nodes are particularly important in this context.
C. The Glandular Tissue: The Milk-Producing Unit
The glandular tissue, located within the breast parenchyma, is the primary functional unit of the breast responsible for milk production.
- Lobules: These are the smallest functional units of the glandular tissue. Each lobule contains numerous alveoli, the actual milk-producing cells.
- Alveoli: These tiny, sac-like structures produce milk during lactation. They are clustered together to form lobules.
- Lactiferous ducts: These small tubes collect milk produced by the alveoli and transport it to the nipple. They converge to form larger ducts.
- Lactiferous sinuses: These are dilated portions of the lactiferous ducts located near the nipple. They act as reservoirs for milk storage prior to ejection.
D. The Retromammary Space: A Layer of Separation
The retromammary space is a layer of loose connective tissue that separates the breast tissue from the underlying pectoral muscles. This space allows for some movement of the breast tissue over the chest wall.
- Pectoralis major and minor muscles: These underlying muscles provide the structural base for the breast. Their position and attachment points influence the overall shape and support of the breast.
E. The Deep Fascia: A Protective Covering
The deep fascia is a tough, fibrous layer that covers the underlying pectoral muscles. It provides additional support and protection for the breast.
II. Clinical Significance: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Labeling
Accurate labeling of the breast's structures is not merely an academic exercise; it's paramount in various clinical settings. Precise anatomical understanding is critical for:
- Breast Self-Examination (BSE): Recognizing changes in breast tissue requires a clear understanding of normal breast anatomy. The ability to identify irregularities, such as lumps, changes in skin texture, or nipple discharge, is crucial for early detection of potential breast abnormalities.
- Mammography and Ultrasound Interpretation: Radiologists rely on their knowledge of breast anatomy to interpret mammograms and ultrasounds accurately. Correct labeling helps in identifying and characterizing lesions or masses, guiding further investigations and treatment strategies.
- Breast Biopsy Procedures: Precise identification of the targeted area during a breast biopsy is essential to obtain a representative sample for pathology analysis. The accurate labeling of the location of the lesion relative to the surrounding structures is crucial for effective surgical planning and treatment.
- Breast Surgery: Surgical procedures, such as lumpectomy or mastectomy, require a meticulous understanding of breast anatomy to minimize damage to surrounding structures and ensure successful outcomes. Knowledge of the location and relationship between the glandular tissue, blood vessels, and nerves is essential for precision surgery.
- Breast Reconstruction: Following breast surgery, reconstruction techniques depend on a thorough understanding of the remaining tissue and surrounding structures. Accurate labeling of these structures aids in the planning and execution of reconstructive procedures.
III. Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further Anatomical Details
This section delves into more nuanced aspects of the female breast anatomy often overlooked in simplified descriptions:
- Lymphatic Drainage: Understanding the complex lymphatic drainage pathways of the breast is crucial in managing and understanding breast cancer. Lymphatic vessels drain fluid from the breast to the axillary lymph nodes, internal mammary lymph nodes, and supraclavicular lymph nodes. The involvement of these nodes in cancer metastasis has significant prognostic implications.
- Nerve Supply: The breast's sensory innervation is provided by branches of the intercostal nerves. This innervation explains the sensitivity of the breast tissue and its importance in pain perception and sensation.
- Blood Supply: The breast receives its blood supply from branches of the internal thoracic artery, axillary artery, and intercostal arteries. This vascular network is important for maintaining the health and viability of the breast tissue and plays a role in the surgical planning and treatment of breast cancer.
- Variations in Breast Anatomy: It's crucial to remember that breast anatomy can vary significantly between individuals. Factors like age, genetics, pregnancy, and lactation influence the breast's shape, size, and composition. Understanding these variations is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
IV. Practical Applications: Using this Knowledge in Real-world Scenarios
Let's consider a few practical examples to demonstrate the importance of correctly labeling breast structures:
-
Scenario 1: A patient presents with a palpable lump in the upper outer quadrant of her right breast. Knowing the anatomical location (upper outer quadrant) helps to guide further investigations, such as mammography or ultrasound, and increases the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis.
-
Scenario 2: A surgeon is planning a lumpectomy to remove a cancerous tumor. Accurate labeling of the tumor's location, relative to the surrounding glandular tissue, blood vessels, and nerves, is crucial for minimizing surgical damage and maximizing the chances of successful tumor removal while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
-
Scenario 3: A radiologist is interpreting a mammogram. A detailed understanding of breast anatomy allows the radiologist to differentiate between normal tissue variations and potentially cancerous lesions. The accurate labeling of findings allows for clear communication with the patient and referring physician.
V. Conclusion: The Importance of Continuous Learning
The female breast's anatomy is a subject that demands continuous learning and exploration. This guide provides a foundation for a deeper understanding, but further research and study are encouraged. Mastering the correct labeling of breast structures is not just a matter of memorization but a vital skill that underpins effective patient care and medical practice. By continually refining your knowledge and staying updated on advancements in breast imaging and surgical techniques, you can improve your diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and overall patient outcomes. The importance of correct labeling cannot be overstated, acting as a cornerstone of comprehensive breast health care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Correct Negation Of A Or Not B Is
Mar 17, 2025
-
Excerpts From Romeo And Juliet Commonlit Answers
Mar 17, 2025
-
Tuesdays With Morrie Summary Per Chapter
Mar 17, 2025
-
Esta Manana Comi Frutas En El
Mar 17, 2025
-
10 2 3 Select And Configure Dual Monitors
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Correctly Label The Following Structures Of The Female Breast . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
