Drag Each Definition To The Alliance Type It Describes.
Onlines
Mar 19, 2025 · 7 min read
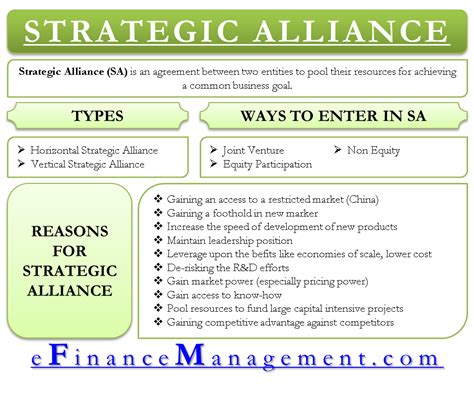
Table of Contents
Drag Each Definition to the Alliance Type It Describes: A Deep Dive into Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances are a cornerstone of modern business, offering companies a pathway to growth, innovation, and market expansion without the significant capital investment or risk associated with mergers or acquisitions. However, navigating the diverse landscape of alliance types requires a clear understanding of their defining characteristics. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of strategic alliances, providing detailed definitions and helping you effectively categorize them.
This article addresses the nuances of each alliance type, focusing on key distinguishing features to help you accurately classify any given alliance scenario. We'll be examining common alliance types, their advantages and disadvantages, and crucial success factors, ultimately equipping you with the knowledge to strategically leverage alliances for your organization's benefit.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Strategic Alliances
Before diving into the specific types, let's establish a solid foundation. A strategic alliance is a collaborative arrangement between two or more independent organizations to achieve common goals. These goals can range from expanding market share to developing new products or technologies. The core principle is mutual benefit – each partner contributes resources, expertise, or market access to create synergistic value. The degree of integration and commitment varies considerably depending on the type of alliance formed.
Key Types of Strategic Alliances: A Detailed Examination
Several frameworks exist for categorizing strategic alliances. While no single system is universally accepted, we'll explore some of the most common and widely recognized types, highlighting their distinct features:
1. Joint Ventures (JVs): A Shared Commitment
A joint venture represents a significant commitment, involving the creation of a new, independent legal entity owned and operated jointly by two or more parent companies. This is often the most complex and demanding type of alliance, requiring substantial investment and shared decision-making power.
Key Characteristics:
- New Legal Entity: A distinct legal entity is formed, separate from the parent companies.
- Shared Ownership and Control: Partners typically share ownership equity and management responsibilities.
- Significant Investment: Substantial resources are committed from each partner.
- Shared Risks and Rewards: Profits and losses are shared proportionally to ownership.
- Long-term Commitment: JVs often represent long-term strategic partnerships.
Example: Two car manufacturers could form a JV to develop and produce a new line of electric vehicles, combining their respective expertise in engineering and manufacturing.
2. Equity Strategic Alliances: A Stake in Success
Equity strategic alliances involve one partner acquiring an equity stake in the other. This demonstrates a stronger commitment than a non-equity alliance, providing the investing partner with more influence and a share in the profits.
Key Characteristics:
- Ownership Stake: One partner acquires ownership shares in the other.
- Financial Investment: Involves a direct financial investment in the partner company.
- Influence and Control: The equity holder gains a degree of influence over the partner's strategic direction.
- Potential for Synergies: Allows for shared knowledge, resources, and market access.
- Flexibility: Less complex than a joint venture, providing greater flexibility in terms of structure and management.
Example: A technology company might acquire a minority stake in a marketing firm to gain access to their expertise and client base.
3. Non-Equity Strategic Alliances: Collaboration Without Ownership
Non-equity strategic alliances involve a collaborative agreement between partners without any exchange of equity. These alliances are typically less formal and easier to establish than equity alliances or joint ventures, often involving contracts or licensing agreements.
Key Characteristics:
- No Ownership Stake: Partners retain full ownership and control of their respective companies.
- Contractual Agreements: The relationship is governed by formal contracts specifying roles, responsibilities, and deliverables.
- Flexibility and Ease of Formation: Generally simpler and faster to set up than equity alliances or JVs.
- Limited Commitment: Can be terminated more easily than equity alliances or JVs.
- Specific Scope: Often focused on specific projects or initiatives.
Example: A food distributor might partner with a local farmer to secure a reliable supply of produce, with the agreement outlining quantities, pricing, and delivery schedules.
4. Franchising: A Proven Business Model
Franchising represents a specific type of non-equity alliance where a franchisor grants a franchisee the right to use its brand, trademarks, and business model in exchange for fees and royalties.
Key Characteristics:
- Brand Licensing: The franchisor grants the franchisee the right to use its brand and intellectual property.
- Operational System: The franchisor provides a proven business model and operational support.
- Ongoing Fees and Royalties: The franchisee pays ongoing fees and royalties to the franchisor.
- Standardized Operations: Maintains consistent branding, quality, and service across franchise locations.
- Growth Potential: Allows for rapid expansion with lower risk for the franchisor.
Example: A fast-food chain grants a franchisee the right to operate a restaurant under its brand, following established operational procedures and utilizing its marketing materials.
5. Licensing Agreements: Access to Intellectual Property
Licensing agreements allow one party (licensor) to grant another party (licensee) the right to use its intellectual property (IP), such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, for a specified period and in exchange for royalties or other fees.
Key Characteristics:
- IP Rights Granted: The licensor grants specific rights to use its IP.
- Royalties or Fees: The licensee pays the licensor for the right to use the IP.
- Defined Scope: The agreement clearly defines the scope of the license, including geographical limitations and permitted uses.
- Risk Mitigation: Allows companies to leverage IP without significant investment or risk.
- Revenue Generation: Provides a revenue stream for the licensor while allowing the licensee to access valuable IP.
Example: A pharmaceutical company licenses its patented drug formulation to another company for manufacturing and distribution in a specific region.
6. Cross-Functional Alliances: Combining Diverse Expertise
Cross-functional alliances involve collaboration between companies from different industries or sectors, bringing together complementary expertise and resources.
Key Characteristics:
- Diverse Expertise: Partners possess unique skills and capabilities in different areas.
- Innovation and Growth: Enables innovation and market expansion through collaboration.
- Synergistic Value: Creates value beyond what each partner could achieve individually.
- Complex Coordination: Requires careful coordination and management due to the diverse nature of partners.
- Potential for Conflict: Differences in organizational cultures and operating styles can pose challenges.
Example: A technology company partners with a healthcare provider to develop innovative medical devices, combining the technology company's expertise in software development with the healthcare provider's knowledge of medical applications.
Choosing the Right Alliance Type: A Strategic Approach
Selecting the appropriate alliance type is crucial for success. The optimal choice depends on several factors, including:
- Strategic Goals: Clearly define the objectives the alliance aims to achieve.
- Resource Requirements: Assess the resources each partner can contribute.
- Risk Tolerance: Evaluate the level of risk each partner is willing to assume.
- Level of Commitment: Determine the desired level of integration and control.
- Long-term Vision: Consider the long-term implications of the alliance.
Success Factors for Strategic Alliances
Regardless of the chosen type, several factors contribute to the success of strategic alliances:
- Clear Goals and Objectives: Establishing shared, measurable goals is paramount.
- Strong Communication and Trust: Open and transparent communication is essential for building trust and maintaining a healthy relationship.
- Complementary Capabilities: Partners should possess complementary strengths and resources.
- Shared Vision and Culture: Alignment on strategic direction and organizational culture enhances cooperation.
- Effective Governance Mechanisms: Establishing clear decision-making processes and dispute resolution mechanisms is crucial.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly assess the alliance's performance and adapt as needed.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances offer a powerful tool for businesses seeking growth, innovation, and market expansion. By carefully considering the various types of alliances and aligning them with specific organizational goals, companies can effectively harness the collaborative potential of partnerships to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. Understanding the nuances of each type, from the highly committed joint ventures to the flexible non-equity arrangements, empowers businesses to make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of these strategic collaborations. Remember, thorough planning, effective communication, and continuous monitoring are key to maximizing the potential of any strategic alliance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Under Dodd 5240 06 Reportable Foreign Intelligence
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Sata Devices Did You Find
Mar 20, 2025
-
End Of Semester Test English 11a
Mar 20, 2025
-
Where Is An Integrated Microphone Normally Located On A Laptop
Mar 20, 2025
-
Pogil Electron Configuration And Orbitals Answer Key Model 2
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Drag Each Definition To The Alliance Type It Describes. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
