Drag Each Label To The Location Of Each Structure Described.
Onlines
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
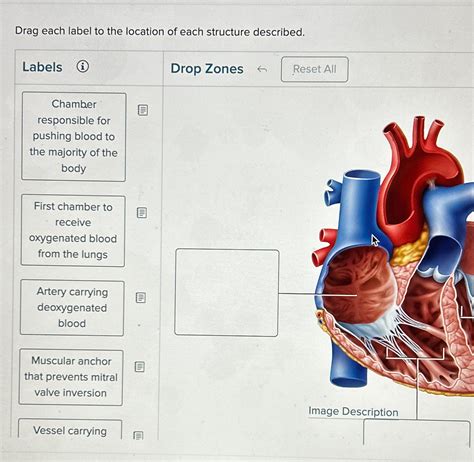
Table of Contents
- Drag Each Label To The Location Of Each Structure Described.
- Table of Contents
- Drag Each Label to the Location of Each Structure Described: A Comprehensive Guide to Anatomy Labeling
- Why Anatomical Labeling is Crucial
- Strategies for Mastering Anatomical Labeling
- Labeling Different Anatomical Regions and Systems
- The Skeletal System: Bones of the Human Body
- The Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles
- The Nervous System: Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves
- The Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels
- The Respiratory System: Lungs and Airways
- The Digestive System: Organs of Digestion
- The Urinary System: Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra
- The Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones
- Utilizing Online Resources and Tools
- Beyond Simple Labeling: Understanding Function and Relationships
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Drag Each Label to the Location of Each Structure Described: A Comprehensive Guide to Anatomy Labeling
Labeling anatomical structures is a fundamental skill for anyone studying biology, anatomy, or medicine. This interactive exercise, often presented as a "drag-and-drop" activity, tests your understanding of the body's intricate systems and the precise location of its various components. This guide goes beyond a simple answer key; it aims to provide a deep understanding of the structures involved, improving not only your labeling skills but also your broader anatomical knowledge. We'll explore effective strategies for mastering this task, focusing on various anatomical regions and systems.
Why Anatomical Labeling is Crucial
Before delving into specific structures, let's understand the importance of accurately labeling anatomical diagrams. This skill isn't merely an academic exercise; it's a cornerstone of:
- Medical Diagnosis: Accurate identification of structures is critical for diagnosing medical conditions and guiding treatment plans. Radiologists, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals rely on precise anatomical knowledge daily.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgeons must have a flawless understanding of anatomical relationships to perform procedures safely and effectively, minimizing the risk of complications.
- Research and Development: Researchers studying the human body, whether developing new treatments or advancing our understanding of physiology, rely heavily on accurate anatomical descriptions and models.
- Effective Communication: Clear and precise anatomical terminology ensures effective communication among healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators. Ambiguity can have serious consequences.
- Strengthening Knowledge Retention: The active process of labeling structures reinforces learning and improves long-term retention. It's far more effective than passively reading about them.
Strategies for Mastering Anatomical Labeling
Successfully labeling anatomical structures requires a multi-faceted approach:
1. Visual Learning: Begin by thoroughly studying high-quality anatomical diagrams and images. Use textbooks, online resources, and anatomical atlases to familiarize yourself with the shapes, sizes, and relative positions of different structures. Focus on:
- Multiple Views: Examine structures from different angles (anterior, posterior, lateral, medial, superior, inferior) to fully grasp their three-dimensional relationships.
- Cross-Sectional Images: Understanding how structures appear in cross-sections (e.g., MRI, CT scans) is essential for real-world applications.
- Color Coding: Many anatomical diagrams use color-coding to distinguish different tissues and systems. Leverage this visual cue.
2. Active Recall: Don't just passively look at diagrams. Test yourself frequently. Use flashcards, quizzes, or online interactive exercises to actively recall the names and locations of structures. This active recall strengthens neural connections and improves memory.
3. Mnemonic Devices: For challenging structures, create mnemonic devices (memory aids) to help you remember their names and locations. These can be acronyms, rhymes, or visual associations. For example, to remember the order of the cranial nerves, you might use a mnemonic like "Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet."
4. Systematic Approach: Don't try to memorize everything at once. Break down the task into smaller, manageable parts, focusing on specific regions or systems. Start with simpler structures and gradually progress to more complex ones.
5. Repetition and Practice: Consistent practice is crucial for mastering anatomical labeling. The more you practice, the better you'll become at quickly and accurately identifying structures. Regular review is key to retaining information.
Labeling Different Anatomical Regions and Systems
Let's explore specific anatomical regions and systems, highlighting key structures and offering tips for accurate labeling:
The Skeletal System: Bones of the Human Body
The skeletal system provides structural support, protects vital organs, and facilitates movement. Key areas to focus on include:
- Skull: Learn the names of the cranial bones (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid) and facial bones (maxilla, mandible, zygomatic, nasal).
- Vertebral Column: Identify the different vertebrae (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal) and their distinguishing features.
- Thoracic Cage: Learn the names and locations of the ribs, sternum, and costal cartilages.
- Appendicular Skeleton: Focus on the bones of the upper and lower limbs, including the humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, and fibula. Pay attention to the carpals, metacarpals, phalanges, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
The Muscular System: Skeletal Muscles
The muscular system is responsible for movement, posture, and heat production. Key muscle groups to focus on include:
- Head and Neck: Learn the muscles of facial expression, mastication (chewing), and neck movement.
- Trunk: Identify the muscles of the abdomen, back, and thorax, paying attention to their layers and actions.
- Upper Limb: Focus on the muscles of the shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand, understanding their roles in movement.
- Lower Limb: Learn the muscles of the hip, thigh, leg, and foot, focusing on their roles in locomotion and posture.
The Nervous System: Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves
The nervous system controls and coordinates bodily functions. Key structures to label include:
- Brain: Identify the major lobes of the cerebrum (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital), the cerebellum, brainstem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata), and diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus).
- Spinal Cord: Understand the segments of the spinal cord and their corresponding nerve roots.
- Cranial Nerves: Learn the names and functions of the twelve cranial nerves.
- Peripheral Nerves: Familiarize yourself with the major peripheral nerves and their distribution.
The Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels
The cardiovascular system transports blood throughout the body. Key structures to label include:
- Heart: Identify the four chambers (right and left atria, right and left ventricles), valves (tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, aortic), and major blood vessels connected to the heart (aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins).
- Blood Vessels: Distinguish between arteries, veins, and capillaries, understanding their roles in blood flow. Learn the names of major arteries and veins in different regions of the body.
The Respiratory System: Lungs and Airways
The respiratory system facilitates gas exchange. Key structures to label include:
- Lungs: Identify the lobes of the lungs (right and left) and their relationship to the thoracic cage.
- Airways: Trace the pathway of air from the nostrils/mouth to the alveoli, labeling the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
The Digestive System: Organs of Digestion
The digestive system breaks down food for absorption. Key structures to label include:
- Oral Cavity: Identify the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands.
- Esophagus: Trace the path of food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Understand its regions (cardia, fundus, body, pylorus).
- Small Intestine: Identify the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- Large Intestine: Learn the cecum, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid), rectum, and anus.
- Accessory Organs: Label the liver, gallbladder, pancreas.
The Urinary System: Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder, and Urethra
The urinary system filters waste from the blood. Key structures to label include:
- Kidneys: Identify the cortex, medulla, and renal pelvis.
- Ureters: Trace the path of urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Understand its structure and function.
- Urethra: Identify the pathway for urine elimination.
The Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones
The endocrine system regulates bodily functions through hormones. Key structures to label include:
- Hypothalamus: Understand its role in hormone production and regulation.
- Pituitary Gland: Identify its anterior and posterior lobes.
- Thyroid Gland: Understand its location and function.
- Parathyroid Glands: Know their location relative to the thyroid.
- Adrenal Glands: Identify their cortex and medulla.
- Pancreas (endocrine function): Label the islets of Langerhans and their role in insulin and glucagon production.
- Ovaries and Testes: Understand their role in hormone production and reproduction.
Utilizing Online Resources and Tools
Many online resources and tools can assist you in mastering anatomical labeling. Interactive anatomy websites and apps offer drag-and-drop exercises, quizzes, and 3D models that allow for exploration from various angles. These resources provide valuable practice and feedback, helping you identify areas where you need improvement.
Beyond Simple Labeling: Understanding Function and Relationships
While accurate labeling is essential, it's equally important to understand the function of each structure and how they interact with each other within a system and across systems. This deeper understanding will improve your overall comprehension of anatomy and its application in various fields.
For example, don't just label the "femur"; understand its role in weight-bearing, its articulation with the hip and knee joints, and the muscles that act upon it. This holistic approach transforms simple labeling into a comprehensive understanding of the human body.
By combining visual learning, active recall, mnemonic devices, a systematic approach, and consistent practice, you can master anatomical labeling and develop a robust understanding of the human body's intricate structure and function. Remember, this is a skill that improves with dedication and persistent effort. The rewards of achieving proficiency are substantial, extending beyond academic achievements to practical applications in various fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Catcher In The Rye Character Descriptions
Mar 22, 2025
-
In The Time Of The Butterflies Chapter 7 Summary
Mar 22, 2025
-
Unit 9 Progress Check Mcq Ap Chemistry Answers
Mar 22, 2025
-
Sequences And Series Unit Test Part 1
Mar 22, 2025
-
An Introduction To Cladograms And Trees Worksheet Answer Key
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Drag Each Label To The Location Of Each Structure Described. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
