Earthquake P Wave And S Wave Travel Time Worksheet Answers
Onlines
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
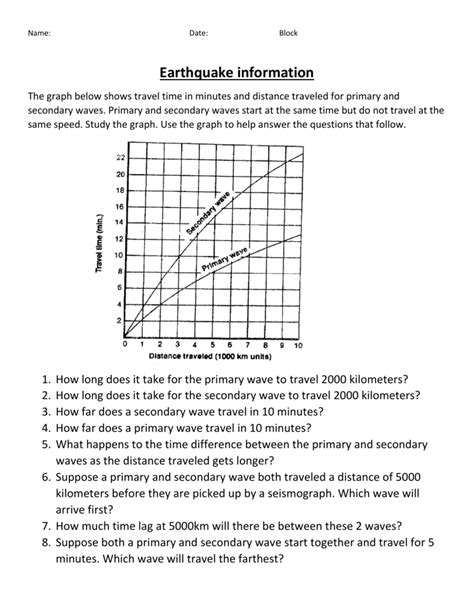
Table of Contents
Earthquake P-Wave and S-Wave Travel Time Worksheet Answers: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding seismic waves, specifically P-waves and S-waves, is crucial for comprehending earthquake occurrences and their effects. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to interpreting earthquake data, focusing on P-wave and S-wave travel times. We will explore the underlying principles, delve into practical worksheet examples, and offer tips for accurate analysis.
Understanding P-Waves and S-Waves
Earthquakes generate two primary types of body waves: P-waves (primary waves) and S-waves (secondary waves). These waves propagate through the Earth's interior, carrying energy away from the earthquake's hypocenter (focus). Their distinct properties influence their travel times and allow seismologists to locate earthquakes.
P-Waves: The Speed Demons
P-waves are compressional waves, meaning they travel by compressing and expanding the material they pass through. Think of it like a slinky being pushed and pulled. This compressional motion allows P-waves to travel faster than S-waves through solids, liquids, and gases. Their high velocity is why they are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph station following an earthquake.
- Key Characteristics:
- Fastest wave type: Arrives first at seismograph stations.
- Longitudinal waves: Particle motion is parallel to the wave direction.
- Travels through solids, liquids, and gases: This property is crucial for understanding Earth's internal structure.
S-Waves: The Shear Specialists
S-waves are shear waves, meaning they travel by shearing or shaking the material perpendicular to their direction of travel. Imagine shaking a rope up and down; the wave travels along the rope, but the rope itself moves perpendicularly. Because of this shearing motion, S-waves cannot travel through liquids or gases, only solids.
- Key Characteristics:
- Slower than P-waves: Arrives second at seismograph stations.
- Transverse waves: Particle motion is perpendicular to the wave direction.
- Travels only through solids: This property helps determine the boundaries between solid and liquid layers within the Earth.
Analyzing Travel Time Data: The Worksheet Approach
Seismic travel-time worksheets provide a practical way to understand the relationship between distance, time, and wave velocities. These worksheets typically present data showing the arrival times of P-waves and S-waves at different seismograph stations. The difference in arrival times provides crucial information for determining the earthquake's epicenter.
Interpreting Travel-Time Curves
Most worksheets utilize travel-time curves, graphs that plot the distance from the earthquake's epicenter against the arrival time of P-waves and S-waves. These curves are generally non-linear because wave velocity changes with depth within the Earth. The difference in arrival times between the P-wave and S-wave increases with distance from the epicenter.
Analyzing the curves involves:
- Identifying P-wave and S-wave arrival times: The worksheet will provide this data for various seismograph stations.
- Calculating the S-P time interval: Subtracting the P-wave arrival time from the S-wave arrival time gives the S-P interval, representing the time difference between the arrival of the two waves at a specific station.
- Determining the epicentral distance: Using the travel-time curve, locate the S-P time interval on the vertical axis and trace it horizontally to the curve. Then, trace vertically down to the horizontal axis to determine the corresponding distance from the earthquake's epicenter.
- Triangulation: By repeating steps 2 and 3 for at least three seismograph stations, you can create three circles with radii equal to the epicentral distances. The point where these circles intersect is the approximate location of the earthquake's epicenter.
Sample Worksheet Problems and Solutions
Let's analyze some hypothetical scenarios to solidify your understanding.
Example 1:
Three seismograph stations (A, B, and C) record the following arrival times (in seconds) for P-waves and S-waves from an earthquake:
| Station | P-wave Arrival Time (s) | S-wave Arrival Time (s) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 20 |
| B | 25 | 45 |
| C | 15 | 30 |
Solution:
-
Calculate S-P intervals:
- Station A: 20s - 10s = 10s
- Station B: 45s - 25s = 20s
- Station C: 30s - 15s = 15s
-
Determine epicentral distances (assuming you have a travel-time graph): Consult your provided travel-time curve. Let's assume the following distances (these would be read from the graph, not calculated):
- Station A: 200 km
- Station B: 400 km
- Station C: 300 km
-
Triangulation: Draw three circles on a map, centered on stations A, B, and C, with radii of 200 km, 400 km, and 300 km respectively. The intersection of these circles approximates the earthquake's epicenter.
Example 2: Determining Wave Velocities
A seismograph station records a P-wave arrival at 10 seconds and an S-wave arrival at 20 seconds. The distance to the earthquake's epicenter is 1000 km. Calculate the average velocities of the P-wave and S-wave.
Solution:
-
Calculate time difference: S-wave travel time = 20 seconds; P-wave travel time = 10 seconds.
-
Calculate P-wave velocity: Velocity = Distance / Time = 1000 km / 10 s = 100 km/s
-
Calculate S-wave velocity: Velocity = Distance / Time = 1000 km / 20 s = 50 km/s
Example 3: Understanding Limitations
Why might the intersection of circles in the triangulation method not be precise?
Solution:
The triangulation method relies on several assumptions which might not always hold true:
- Simplified Earth model: Travel-time curves often simplify the Earth's complex structure.
- Wave propagation variations: Seismic waves can be affected by local geological variations, causing travel time discrepancies.
- Measurement errors: Inaccurate arrival time readings can significantly affect the triangulation results.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The analysis of P-wave and S-wave travel times extends beyond simple worksheet exercises. More advanced applications include:
- Earthquake location refinement: Sophisticated algorithms incorporate data from numerous stations to pinpoint earthquake locations with high accuracy.
- Earth structure modelling: Analyzing the variations in P-wave and S-wave velocities at different depths helps scientists understand the composition and physical properties of Earth's layers.
- Tsunami warning systems: Rapid detection of P-waves can provide crucial time for tsunami warnings, as tsunamis are often associated with large underwater earthquakes.
Tips for Success with Travel Time Worksheets
- Carefully read the instructions: Understanding the specific format and requirements of your worksheet is crucial.
- Use a ruler and compass: Accurate measurements are essential for triangulation.
- Double-check your calculations: Simple errors can lead to inaccurate results.
- Consult reference materials: Don't hesitate to use textbooks or online resources for clarification.
- Practice regularly: The more you practice analyzing travel time data, the more proficient you will become.
This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of P-wave and S-wave travel times, their applications in earthquake analysis, and strategies for successfully completing travel-time worksheets. By grasping these concepts, you can contribute to a deeper appreciation of seismology and its importance in understanding our planet. Remember, consistent practice and attention to detail are key to mastering this essential skill.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Estimate The Number Of Heartbeats In A Pound Of Butter
Mar 18, 2025
-
Art Labeling Activity Summary Of Epithelial Tissues
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Martian Chronicles The Martian Summary
Mar 18, 2025
-
Examples Of Questions That Focus On Process Include
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Statement Is True About First Aid Measures And Hazardous Chemicals
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Earthquake P Wave And S Wave Travel Time Worksheet Answers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
