Effective Controls Protect ______ From Workplace Hazards.
Onlines
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
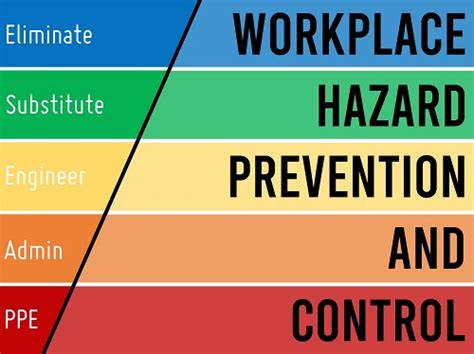
Table of Contents
Effective Controls Protect Workers from Workplace Hazards
Workplace hazards are a significant concern for businesses of all sizes and across all industries. From slips and falls to exposure to hazardous chemicals, the potential for injury or illness is ever-present. However, a proactive approach to safety management, focusing on effective hazard controls, can significantly reduce these risks and create a safer, healthier work environment. This article delves into the various types of hazard controls, their implementation, and the crucial role they play in protecting workers.
Understanding Workplace Hazards
Before exploring control measures, it's vital to understand the diverse nature of workplace hazards. These can be broadly categorized as:
-
Physical Hazards: These include factors like noise, vibration, temperature extremes (heat or cold), radiation (ionizing and non-ionizing), and ergonomic issues (poor posture, repetitive movements). Examples: prolonged exposure to loud machinery, working in extremely cold storage facilities, or repetitive typing leading to carpal tunnel syndrome.
-
Chemical Hazards: These encompass exposure to harmful substances, including gases, liquids, solids, and dusts. Examples: working with solvents, handling pesticides, or exposure to asbestos fibers. The risks range from minor irritation to severe health problems, including cancer.
-
Biological Hazards: These hazards involve exposure to infectious agents like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Examples: healthcare workers, agricultural workers, and laboratory technicians are at increased risk. Proper hygiene and protective equipment are paramount.
-
Ergonomic Hazards: These are related to the design of the workplace, tools, and tasks that can lead to musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). Examples: improper workstation setup, repetitive movements, and awkward postures can all contribute to MSDs like back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and tendonitis.
-
Psychosocial Hazards: These relate to the mental and emotional well-being of workers. Examples: stress, harassment, bullying, and violence. These can significantly impact productivity, mental health, and overall workplace safety.
The Hierarchy of Hazard Controls
The hierarchy of hazard controls provides a structured approach to managing workplace hazards, prioritizing the most effective methods. The hierarchy, from most to least effective, is:
-
Elimination: This involves completely removing the hazard from the workplace. It's the most effective control measure but often the most difficult to implement. Example: Replacing a hazardous chemical with a safer alternative.
-
Substitution: This involves replacing the hazard with a less hazardous alternative. Example: Replacing a solvent-based cleaning agent with a water-based one.
-
Engineering Controls: These involve modifying the workplace or equipment to reduce or eliminate the hazard. Example: Installing machine guards to prevent contact with moving parts, implementing ventilation systems to reduce airborne contaminants, or using ergonomic workstations. These controls are often preferred as they're inherently safer and don't rely on worker behavior.
-
Administrative Controls: These involve changing work practices or procedures to reduce exposure to hazards. Example: Implementing job rotation to reduce repetitive movements, providing adequate training and supervision, establishing safe work procedures, and implementing a permit-to-work system for high-risk tasks.
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This involves providing workers with equipment to protect them from hazards. Example: Safety glasses, hearing protection, respirators, gloves, and safety footwear. While essential, PPE should be considered a last resort, as it only protects the individual wearing it and doesn’t address the underlying hazard.
Implementing Effective Hazard Controls
Implementing effective hazard controls requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating the following steps:
-
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: This involves systematically identifying all potential hazards in the workplace and assessing the associated risks. This process should involve workers, as they are often the most aware of the hazards they face.
-
Control Selection: Once hazards are identified and risks assessed, appropriate control measures should be selected based on the hierarchy of controls. The goal is to select the most effective control measure that is also feasible and practical.
-
Implementation and Monitoring: The selected control measures must be implemented effectively. This involves providing necessary training to workers, ensuring that equipment is properly maintained, and establishing procedures for monitoring the effectiveness of the controls.
-
Regular Review and Updates: Hazard controls should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain effective. This should include periodic risk assessments, inspections, and employee feedback. Changes in technology, work processes, or regulations may necessitate updates to existing controls.
Specific Examples of Effective Controls:
-
Noise Reduction: Engineering controls, such as installing noise barriers, using quieter machinery, and implementing noise-dampening materials, are highly effective. Administrative controls include limiting exposure time, providing hearing protection, and implementing regular hearing tests.
-
Chemical Exposure Control: Substitution of hazardous chemicals with safer alternatives is ideal. Engineering controls like ventilation systems and enclosed processes minimize exposure. Administrative controls include proper labeling, handling procedures, and training on safe chemical handling. PPE, such as respirators and gloves, is crucial, but only as a last resort.
-
Ergonomic Improvements: Engineering controls like adjustable workstations, ergonomic tools, and proper lighting are highly effective. Administrative controls involve job rotation, regular breaks, and training on proper posture and lifting techniques.
-
Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls: Engineering controls such as improved flooring, adequate lighting, and non-slip surfaces are key. Administrative controls include regular cleaning, removal of obstructions, and employee training on safe walking practices.
The Importance of Worker Participation
Worker participation is crucial for the success of any safety management program. Workers are often the first to notice hazards and can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of control measures. Engaging workers in hazard identification, risk assessment, and the selection and implementation of controls ensures buy-in and improves the overall effectiveness of the program. Regular communication, feedback mechanisms, and safety committees can foster this participation and create a culture of safety.
Conclusion
Effective hazard controls are essential for protecting workers from workplace hazards. By following the hierarchy of controls, implementing comprehensive safety programs, and involving workers in the process, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of injuries and illnesses, creating a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment. Remember, a proactive approach to safety is not just a legal requirement; it's a moral obligation and a key ingredient to a successful and thriving business. Investing in safety is investing in your workforce, your productivity, and your bottom line. The cost of inaction far outweighs the investment in effective hazard control.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Summarize Christian Beliefs About The Origins Of The Universe
Mar 31, 2025
-
Their Eyes Were Watching God Chapter 11
Mar 31, 2025
-
Which Of These Technological Advances Improved Flu
Mar 31, 2025
-
Plato The Republic Summary Book 2
Mar 31, 2025
-
Characters From The Importance Of Being Earnest
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Effective Controls Protect ______ From Workplace Hazards. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
