Exercise 29 Us Geological Survey Topographic Maps
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
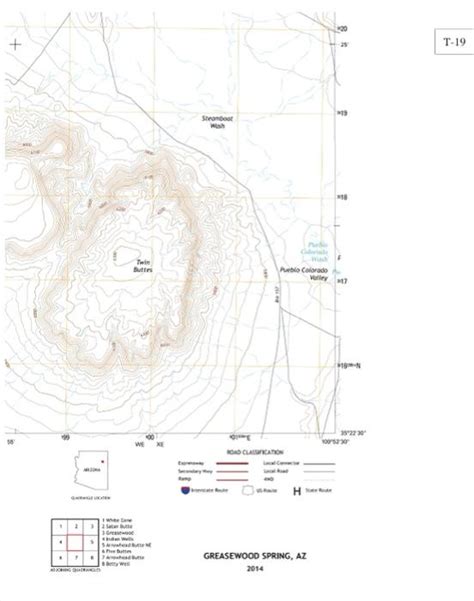
Table of Contents
Exercise 29: Mastering USGS Topographic Maps
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) topographic maps are invaluable tools for hikers, researchers, land managers, and anyone needing detailed information about the Earth's surface. Exercise 29, often found in introductory geography or outdoor recreation courses, focuses on developing proficiency in reading and interpreting these maps. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key elements of USGS topographic maps, providing practical exercises and tips to enhance your map-reading skills.
Understanding the Fundamentals of USGS Topographic Maps
Before diving into Exercise 29, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental components of a USGS topographic map. These maps represent the three-dimensional landscape on a two-dimensional surface using contour lines, symbols, and a scale.
Contour Lines: The Key to Elevation
Contour lines are the most distinctive feature of topographic maps. Each line connects points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope. Widely spaced contour lines indicate a gentler slope. Index contours, usually thicker and labeled with elevation, help quickly identify elevation changes. Understanding contour line spacing is critical for judging terrain difficulty and planning routes.
Map Symbols: Deciphering the Landscape
USGS topographic maps use a standardized system of symbols to represent various features. These symbols depict everything from roads and buildings to rivers, forests, and even man-made structures like power lines and pipelines. Familiarizing yourself with these symbols is essential for accurately interpreting the map’s information. A map legend is included to aid in this process.
Map Scale: Relating Map Distance to Real-World Distance
The map scale is a crucial element that establishes the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. It is typically represented as a ratio (e.g., 1:24,000) or a bar scale. Understanding the map scale allows you to accurately measure distances and plan routes based on the map's information.
Exercise 29: A Deep Dive into Map Interpretation
Exercise 29 typically involves a series of tasks designed to test your understanding of USGS topographic maps. These tasks might include:
1. Determining Elevation and Relief
This involves identifying the highest and lowest points on the map using contour lines and calculating the relief, which is the difference between the highest and lowest elevations. This exercise helps you understand the relationship between contour lines and elevation changes. Practice identifying index contours to speed up this process.
2. Identifying Landforms
Topographic maps reveal various landforms such as hills, valleys, ridges, and saddles. Exercise 29 may require you to locate and identify these landforms based on the pattern of contour lines. Understanding how contour lines bend and converge allows you to identify specific landforms.
3. Measuring Distance and Slope
Using the map scale, you'll measure distances between points on the map and translate them to real-world distances. You’ll also calculate the slope between two points using the elevation difference and the horizontal distance. This combines scale interpretation with elevation data to assess terrain challenges.
4. Interpreting Map Symbols
This task focuses on identifying and interpreting various symbols on the map. You'll need to correctly identify roads, trails, rivers, buildings, and other features. A thorough understanding of the map legend is crucial for this component of Exercise 29. Pay special attention to symbols indicating potential hazards like cliffs or swamps.
5. Route Planning and Navigation
A critical application of topographic map skills is route planning. Exercise 29 may require you to plan a route between two points, considering terrain features, elevation changes, and potential obstacles. This task integrates your understanding of elevation, distance, and map symbols to create a practical, safe route.
6. Profile Development
This involves creating an elevation profile, a graph showing the elevation changes along a specific route. This requires measuring elevations at regular intervals along your chosen route and plotting them on a graph. An elevation profile provides a visual representation of the terrain’s ups and downs along your planned route.
Advanced Applications and Beyond Exercise 29
The skills you develop through Exercise 29 are transferable to various real-world situations. Beyond basic map reading, these skills become crucial in:
- Hiking and Backpacking: Planning routes, identifying potential hazards, and estimating travel time.
- Search and Rescue Operations: Locating individuals in distress using topographic maps and GPS coordinates.
- Land Management and Planning: Assessing land suitability for different uses, identifying potential environmental impacts, and planning infrastructure projects.
- Engineering and Construction: Surveying land, planning road construction, and designing drainage systems.
- Environmental Studies: Mapping ecosystems, monitoring changes in land cover, and studying geological features.
Tips for Success in Exercise 29 and Beyond
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is key to mastering topographic map reading. Start with simpler maps and gradually progress to more complex ones.
- Use Multiple Resources: Consult online tutorials, textbooks, and other resources to enhance your understanding.
- Work with a Partner: Collaborating with a classmate or friend can make learning more engaging and efficient.
- Focus on Accuracy: Pay meticulous attention to detail when measuring distances, calculating slopes, and identifying features.
- Relate it to Real-World Scenarios: Imagine yourself in the environment depicted on the map to better understand the terrain and the implications of various features.
- Utilize Online Tools: Several online resources provide interactive topographic maps and tools for practicing map-reading skills.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Map Reading
Exercise 29 serves as an excellent introduction to the world of USGS topographic maps. By mastering the skills outlined in this guide, you’ll gain a valuable tool for navigating the outdoors, understanding the landscape, and addressing various real-world challenges. Remember that consistent practice and attention to detail are crucial for effectively interpreting these essential maps. The ability to read and interpret USGS topographic maps is a skill that will serve you well in numerous academic, professional, and recreational settings. Embrace the challenge, hone your skills, and discover the rich information these maps reveal about our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match Each Characteristic With The Type Of Election It Describes
Mar 04, 2025
-
Geology Earth Systems 1340 Exam 4
Mar 04, 2025
-
Unit 1 Progress Check Frq Part A Ap Precalculus
Mar 04, 2025
-
Superfund Mini Webquest Answer Key Pdf
Mar 04, 2025
-
Dihybrid Genetics Practice Problems Answer Key
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Exercise 29 Us Geological Survey Topographic Maps . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
