For External Reporting Income Statements Are Generally Prepared Using
Onlines
Apr 07, 2025 · 7 min read
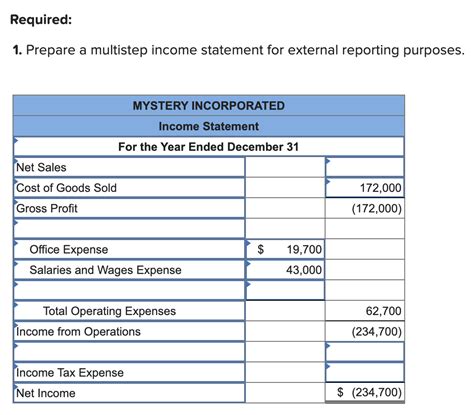
Table of Contents
For External Reporting, Income Statements Are Generally Prepared Using Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
The income statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, is a crucial financial statement that reports a company's financial performance over a specific period. For external reporting purposes, the preparation of income statements adheres to strict accounting standards, primarily Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the United States and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) internationally. This article delves into the intricacies of preparing income statements for external reporting, emphasizing the principles and practices that ensure transparency, consistency, and reliability for stakeholders.
The Significance of GAAP and IFRS in External Reporting
The preparation of financial statements for external dissemination is governed by a robust framework of accounting standards. This framework aims to establish consistency and comparability across different companies, facilitating informed decision-making by investors, creditors, and other external stakeholders.
GAAP and IFRS, while having some similarities, differ in certain aspects. Understanding these differences is crucial for preparing income statements for international audiences or comparing the financial performance of companies operating under different accounting standards. Both, however, share the fundamental principle of fair presentation, requiring that the income statement accurately reflects the company's financial performance. This requires adherence to specific principles regarding:
-
Revenue Recognition: Both GAAP and IFRS emphasize the importance of accurate revenue recognition. Revenue should only be recognized when it is earned, meaning when goods or services have been delivered and payment is reasonably assured. The specifics of how this is achieved can differ slightly, but the underlying principle remains consistent.
-
Expense Recognition: Similarly, expenses should be matched with the revenues they generate. This principle of matching ensures that the income statement accurately reflects the profitability of a given period. For example, the cost of goods sold should be deducted from revenue in the period when the sales are recognized.
-
Conservatism: Both frameworks emphasize a degree of conservatism. This means that in situations of uncertainty, the accounting treatment should err on the side of caution. For example, potential losses should be recognized sooner rather than later, while potential gains should be recognized only when they are reasonably certain.
-
Materiality: Information is deemed material if its omission or misstatement could influence the decisions of users of the financial statements. This principle allows for some flexibility in accounting treatment for items that are immaterial in the overall context of the company's financial position.
Key Components of an Income Statement Prepared Under GAAP/IFRS
A typical income statement prepared under GAAP or IFRS includes the following key components:
1. Revenues
This section reports the total sales generated by the company during the reporting period. It includes all sales of goods and services, net of any sales returns and allowances. Different revenue streams (e.g., sales from different product lines, service revenues) might be presented separately for better understanding. The detailed breakdown of revenues often enhances transparency and allows for a more in-depth analysis of the company's performance.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
For companies that sell goods, the cost of goods sold represents the direct costs associated with producing those goods. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. COGS is subtracted from revenue to arrive at the gross profit.
3. Gross Profit
Gross profit is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold. It represents the profit earned before considering operating expenses. A high gross profit margin (gross profit as a percentage of revenue) indicates that the company is efficiently managing its production costs.
4. Operating Expenses
These are the expenses incurred in the ordinary course of business. Examples include:
- Selling expenses: Costs associated with marketing, sales, and distribution.
- General and administrative expenses: Costs related to running the business, such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Research and development expenses: Costs incurred in developing new products or services.
- Depreciation and amortization: Allocation of the cost of long-term assets over their useful lives.
Operating expenses are deducted from gross profit to arrive at operating income.
5. Operating Income (EBIT)
Operating income, also known as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), represents the profit earned from the company's core business operations. It's a crucial measure of a company's profitability, excluding the effects of financing and taxes.
6. Interest Expense
This represents the cost of borrowing money. It's deducted from operating income to arrive at income before taxes.
7. Income Tax Expense
This is the amount of income tax owed by the company based on its taxable income. It's deducted from income before taxes to arrive at net income.
8. Net Income
Net income (or net profit) is the bottom line of the income statement. It represents the company's profit after all expenses and taxes have been deducted. This is a key indicator of a company's overall financial performance and profitability.
Different Formats of Income Statements
Income statements can be presented in different formats, depending on the nature of the business and the preference of the company. Two common formats include:
1. Single-Step Income Statement
This format presents a simple calculation of total revenues and total expenses, resulting directly in the net income. It is less detailed than the multi-step format, but provides a concise overview of profitability.
2. Multi-Step Income Statement
This format presents a more detailed breakdown of revenues, costs, and expenses, providing a step-by-step calculation leading to net income. It reveals key profitability ratios like gross profit margin and operating profit margin, providing greater insights into the company's financial performance. This is the more common format used for external reporting due to its increased transparency and analytical power.
Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance in External Reporting
Preparing accurate and compliant income statements for external reporting is critical. Several measures are essential to ensure adherence to GAAP or IFRS:
-
Proper Documentation: Maintaining comprehensive documentation of all accounting transactions and the rationale behind accounting choices is vital for audits and regulatory scrutiny.
-
Internal Controls: Robust internal control systems are needed to ensure accuracy, prevent fraud, and maintain the integrity of the financial reporting process.
-
Independent Audits: Independent audits by qualified accountants are essential to verify the accuracy and compliance of the financial statements. This adds credibility and enhances the reliability of the information presented to external stakeholders.
-
Professional Judgment: Accounting often involves professional judgment, particularly in situations with complex transactions or estimates. Accountants must apply their expertise and knowledge of the accounting standards to arrive at fair and consistent accounting treatments.
-
Staying Updated: Accounting standards are constantly evolving. Companies and their accountants must stay abreast of any updates or changes to ensure compliance.
Beyond the Basic Income Statement: Additional Disclosures
While the core components of the income statement are standard, additional disclosures often enhance the understanding of the company's performance. These may include:
-
Segment Reporting: Breaking down the results into different business segments can provide deeper insights into individual performance and help investors assess risk.
-
Earnings Per Share (EPS): This metric shows the portion of net income attributable to each outstanding share of common stock.
-
Non-GAAP Measures: Companies may present non-GAAP financial measures (e.g., adjusted EBITDA) alongside GAAP measures, but these should be clearly reconciled to GAAP figures. Transparency in this aspect is vital to prevent misinterpretations.
-
Footnotes: Comprehensive footnotes provide context and further detail on specific line items in the income statement, explaining unusual transactions or accounting treatments.
Conclusion
Preparing income statements for external reporting under GAAP or IFRS requires meticulous attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the underlying accounting principles. The objective is to present a fair and accurate representation of a company's financial performance. By following established guidelines, maintaining rigorous internal controls, and ensuring independent audits, companies can generate reliable financial statements that build trust with investors, creditors, and other stakeholders, ultimately fostering a strong and transparent financial reputation. The detailed nature of these statements, offering insights beyond basic profitability, provides a comprehensive view of the company's operational efficiency, financial health, and overall success. The various formats and additional disclosures mentioned above allow for tailored presentation, catering to specific needs and increasing understanding for a wider audience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Statement Is Not True About A Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Apr 08, 2025
-
Fall Of The House Of Usher Study Guide
Apr 08, 2025
-
A Flexible Budget Performance Report Combines The
Apr 08, 2025
-
Unit 11 Probability And Statistics Answer Key
Apr 08, 2025
-
The Sieve And The Sand Part 2 Answers
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about For External Reporting Income Statements Are Generally Prepared Using . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.