In Parallelogram Rstu What Is Su
Onlines
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
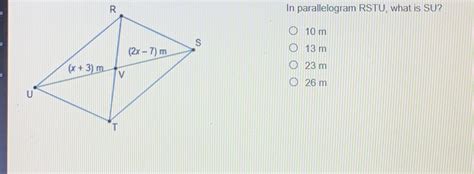
Table of Contents
Decoding Parallelograms: Understanding the Properties of SU in Parallelogram RSTU
Parallelograms, fundamental shapes in geometry, hold a special place in mathematics due to their inherent properties and applications. This article delves deep into the characteristics of parallelograms, focusing specifically on determining the length and nature of side SU in parallelogram RSTU. We'll explore various approaches, leveraging different geometric principles and theorems, to fully understand this seemingly simple yet insightful problem.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Parallelograms
Before we tackle the specific question of determining the length of SU, let's solidify our understanding of parallelograms. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) with two pairs of parallel sides. This fundamental property leads to several other crucial characteristics:
-
Opposite sides are equal in length: In parallelogram RSTU, RS = UT and RT = SU. This is a direct consequence of the parallel sides.
-
Opposite angles are equal: ∠R = ∠T and ∠S = ∠U. This arises from the properties of parallel lines intersected by transversals.
-
Consecutive angles are supplementary: This means that the sum of any two consecutive angles is 180 degrees. For example, ∠R + ∠S = 180°, ∠S + ∠T = 180°, and so on.
-
Diagonals bisect each other: The diagonals of a parallelogram intersect at a point called the centroid, where each diagonal is divided into two equal parts.
Methods to Determine the Length of SU
The length of SU in parallelogram RSTU cannot be determined solely from the name of the parallelogram. We need additional information. The methods to find the length of SU will vary depending on the information provided. Let's explore several scenarios:
Scenario 1: Given the Length of RS and the Angle ∠R
If we know the length of side RS and the measure of angle ∠R, we can use trigonometry to determine the length of SU. Remember, in a parallelogram, opposite sides are equal, so RS = UT. However, SU and RT are not necessarily equal to RS unless the parallelogram is a rectangle (or a square, which is a special type of rectangle).
Let's assume:
- RS = 10 units
- ∠R = 60°
Since RS and RT are adjacent sides, we can't directly use the length of RS to find SU. However, we can use the parallelogram's properties. If we were to draw a diagonal, say RT, we would create two congruent triangles (ΔRST and ΔUT). Then, using the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines within one of these triangles, we could find the length of SU, but we would require more information like the length of RT or another angle.
Scenario 2: Given the Length of RS and RT
If we know the lengths of RS and RT, we can use the Parallelogram Law. The Parallelogram Law states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the four sides of a parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of its two diagonals. Mathematically:
2(RS² + RT²) = SU² + UT²
Since RS = UT, the equation simplifies to:
2(RS² + RT²) = SU² + RS²
Solving for SU:
SU² = RS² + 2RT²
SU = √(RS² + 2RT²)
This allows us to calculate SU directly using the given lengths of RS and RT.
Scenario 3: Given the Coordinates of the Vertices
If we know the coordinates of the vertices R, S, T, and U in a Cartesian coordinate system, we can use the distance formula to determine the length of SU. The distance formula calculates the distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) as:
Distance = √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²)
By applying this formula to the coordinates of points S and U, we can directly calculate the length of SU.
Scenario 4: Given the Area and the Height
The area of a parallelogram is given by the formula:
Area = base * height
If we are given the area of the parallelogram and the length of one side (which serves as the base), we can calculate the height. Then, using the height and applying trigonometric functions, and assuming we know one of the angles, we might be able to calculate the length of SU. But this would again require additional information to create solvable right triangles.
Scenario 5: Special Cases
-
Rectangle: If RSTU is a rectangle, then all angles are 90°, and opposite sides are equal. Therefore, SU = RT. If the length of RT is known, then SU is also known.
-
Rhombus: If RSTU is a rhombus, then all sides are equal in length. Thus, RS = ST = TU = UR = SU. Knowing the length of any side immediately gives us the length of SU.
-
Square: If RSTU is a square, it's both a rectangle and a rhombus, so all sides are equal and all angles are 90°. Therefore, SU = RS = ST = TU = UR.
The Importance of Additional Information
It's crucial to emphasize that simply knowing that a quadrilateral is a parallelogram isn't sufficient to determine the length of any specific side. More information, such as the length of another side, an angle, the coordinates of the vertices, or the area of the parallelogram, is always necessary to solve for the unknown side length. The methods outlined above provide various approaches depending on the specific data available.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The study of parallelograms extends beyond basic geometry. Concepts such as vectors and linear algebra provide alternative and often more powerful tools for analyzing parallelograms and solving related problems. Vectors can represent the sides of the parallelogram, and vector operations can be used to calculate the lengths and angles.
Conclusion
Determining the length of SU in parallelogram RSTU requires more than just the name of the parallelogram. This article has comprehensively explored various scenarios and methodologies, highlighting the importance of additional information. Whether using trigonometry, the parallelogram law, coordinate geometry, or leveraging special cases, understanding the inherent properties of parallelograms and applying appropriate geometric principles are key to successful problem-solving. The methods outlined here provide a robust framework for tackling such geometric challenges and highlight the versatility and significance of parallelograms in mathematics and related fields. Remember, the key lies in carefully analyzing the given information and selecting the most appropriate approach to calculate the length of SU.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
An Out Of Network Provider Calls And Tells You
Mar 13, 2025
-
Learning Through Art Functions Of Membrane Proteins
Mar 13, 2025
-
Alienation Is Defined By The Text As
Mar 13, 2025
-
Yo Un Poco Porque Tengo Un Examen Manana
Mar 13, 2025
-
An Organization That Pursues A Single Product Strategy
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In Parallelogram Rstu What Is Su . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
