____ Is Most Well-known For Proposing His Hierarchy Of Needs.
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
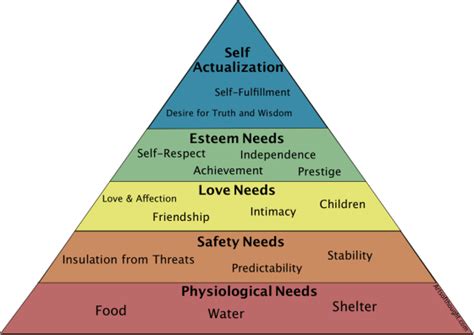
Table of Contents
Abraham Maslow: The Man Behind the Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow is most well-known for proposing his hierarchy of needs, a theory in psychology that describes the pattern of human motivations. This influential model, often depicted as a pyramid, suggests that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom and self-actualization at the peak. While Maslow's work has faced some criticisms, its impact on psychology, business, and even popular culture remains undeniable. This article will delve deep into Maslow's life, the intricacies of his hierarchy of needs, its applications, criticisms, and lasting legacy.
Maslow's Life and Influences
Born in Brooklyn, New York, in 1908, Abraham Maslow had a rather unconventional upbringing. He felt isolated and alienated during his childhood, experiencing what he later described as a feeling of being unwanted. This early experience, coupled with his later academic pursuits, profoundly shaped his understanding of human motivation and the importance of self-actualization. He initially pursued law, but his interest shifted to psychology after reading works by John B. Watson and other behaviorists. However, he was dissatisfied with the limitations of behaviorism's focus on observable behavior, ultimately gravitating towards a more humanistic approach.
His academic journey took him to the University of Wisconsin, where he earned his Bachelor's degree and then a PhD in psychology from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. It was during his time in Wisconsin that he started to develop his own unique perspectives on human psychology. His early exposure to Gestalt psychology, with its emphasis on holistic perception, likely influenced his later work. He then joined the faculty at Brooklyn College, and later, Brandeis University, where he further developed and refined his theories.
Maslow's intellectual influences extended beyond the realms of psychology. He was deeply impacted by the works of Alfred Adler and Kurt Goldstein, whose emphasis on individual growth and self-realization resonated with his own evolving ideas. He also studied the lives of individuals he considered to be self-actualized, including historical figures like Albert Einstein and Eleanor Roosevelt. This biographical approach to understanding human potential became a cornerstone of his humanistic psychology.
The Hierarchy of Needs: A Detailed Explanation
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as a pyramid. These needs are:
1. Physiological Needs: These are the most basic needs required for human survival. They include:
- Air: Essential for respiration and survival.
- Water: Crucial for hydration and bodily functions.
- Food: Provides energy and essential nutrients.
- Shelter: Protection from the elements and a safe place to rest.
- Sleep: Necessary for physical and mental restoration.
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a stable internal environment.
2. Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are met, safety needs become paramount. These involve:
- Personal Security: Freedom from fear, violence, and threats.
- Financial Security: Stability and resources to meet basic needs.
- Health and Well-being: Protection from illness and injury.
- Property: Ownership and control over possessions.
3. Love and Belonging Needs: This level focuses on social connections and the need for belonging. It includes:
- Friendship: Developing meaningful relationships with others.
- Family: Strong bonds and emotional support within the family unit.
- Intimacy: Close personal relationships with loved ones.
- Sense of Connection: Feeling a part of a group or community.
4. Esteem Needs: These needs relate to our self-worth and the recognition we receive from others. They comprise:
- Self-Esteem: Confidence, achievement, independence, and freedom.
- Respect from Others: Recognition, appreciation, and status.
5. Self-Actualization Needs: This represents the highest level in Maslow's hierarchy. It's the desire to become the best version of oneself and fulfill one's potential. This includes:
- Creativity: Expressing oneself through creative endeavors.
- Problem Solving: Tackling challenges and contributing meaningfully.
- Morality: Adhering to a personal code of ethics and values.
- Acceptance of Facts: Objective understanding of reality.
- Spontaneity: Genuine self-expression and freedom from constraint.
The Pyramid Analogy: The pyramid structure visually represents the hierarchical nature of these needs. Maslow argued that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before they can focus on higher-level ones. For instance, someone struggling with hunger (physiological need) will likely prioritize finding food over pursuing creative endeavors (self-actualization). However, it's crucial to understand this is not a rigid, linear progression. Individuals may experience needs simultaneously or regress to lower levels during periods of stress or crisis.
Applications of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's hierarchy has found extensive application in various fields, including:
1. Business and Management: Understanding employee motivation is crucial in any organization. Businesses can use Maslow's hierarchy to tailor compensation packages, create a supportive work environment, offer opportunities for advancement (esteem needs), and foster teamwork (belonging needs).
2. Education: Educators can utilize this theory to create a learning environment that addresses students' various needs. Providing a safe and supportive classroom (safety needs), encouraging collaboration (belonging needs), and recognizing student achievements (esteem needs) can significantly enhance the learning experience.
3. Marketing and Advertising: Understanding consumer needs is essential for effective marketing. Companies can tailor their messages to resonate with different levels of Maslow's hierarchy, emphasizing safety, belonging, or self-actualization depending on the product or service being offered.
4. Health and Wellness: In healthcare, the hierarchy can help professionals understand patients' motivations and barriers to health-seeking behavior. Addressing basic needs like food security or housing (physiological and safety) can be critical in promoting overall well-being.
5. Personal Development: Individuals can use the hierarchy for self-reflection and personal growth. By identifying their unmet needs, they can develop strategies to address them and work towards self-actualization.
Criticisms of Maslow's Hierarchy
Despite its widespread influence, Maslow's hierarchy has faced several criticisms:
1. Lack of Empirical Evidence: While Maslow based his theory on observations and case studies, robust empirical evidence supporting the strict hierarchical structure is limited. People often pursue higher-level needs even when lower-level needs are unmet.
2. Cultural Bias: The hierarchy is often criticized for being culturally biased towards Western individualism. In collectivist cultures, social needs (belonging) might outweigh individual needs (esteem and self-actualization).
3. Oversimplification: The hierarchy is a simplification of complex human motivations. It doesn't fully account for the interplay of various factors influencing human behavior.
4. Difficulty in Measuring: The concepts of self-actualization and other higher-level needs are difficult to measure objectively, making empirical testing challenging.
5. Limited Applicability: The hierarchy's application may be limited in specific contexts like extreme poverty or trauma, where basic survival needs override all others.
Maslow's Legacy and Ongoing Relevance
Despite these criticisms, Maslow's hierarchy of needs remains a remarkably influential theory. Its impact on various fields is undeniable, offering a valuable framework for understanding human motivation. The concept of self-actualization, in particular, has profoundly influenced positive psychology and the pursuit of personal growth. While the rigid hierarchical structure may be debated, the underlying principles of basic needs, social connection, and the pursuit of self-fulfillment continue to resonate with individuals and organizations worldwide. Maslow's work provides a fundamental understanding of human nature and aspirations, providing valuable insights for various disciplines to create environments conducive to human flourishing. Further research, incorporating nuanced cultural perspectives and addressing the limitations of the original model, will continue to shape our understanding of human needs and motivations, building upon Maslow's foundational contribution to the field. His enduring legacy lies in his pioneering work in humanistic psychology and his enduring influence on the study of human motivation. The hierarchy of needs, though subject to revision and refinement, continues to serve as a valuable tool for understanding and promoting individual and societal well-being. It remains a powerful starting point for discussions about human potential and the pursuit of a meaningful life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Should Service Technicians Be Familiar With Company Pricing Policies
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Bride Comes To Yellow Sky Summary
Apr 06, 2025
-
The Legend Of Sleepy Hollow Literary Analysis
Apr 06, 2025
-
Where Are You Going Where Have You Been Theme
Apr 06, 2025
-
Lucia Probo Entremeses Y Platos Principales En Los Dos Restaurantes
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about ____ Is Most Well-known For Proposing His Hierarchy Of Needs. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
