Match Each Moon Or Planet To The Most Accurate Characteristic
Onlines
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
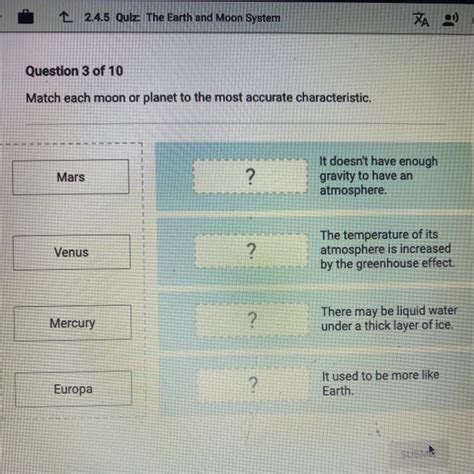
Table of Contents
Matching Celestial Bodies to Their Defining Characteristics: A Comprehensive Guide
The vastness of space harbors a captivating array of celestial bodies, each with unique characteristics that define their identities. From the terrestrial planets of our inner solar system to the gas giants and icy moons beyond, understanding these defining features is key to appreciating the intricate tapestry of our cosmos. This comprehensive guide will delve into the characteristics of various moons and planets, matching each to its most accurate description, exploring their composition, atmospheres, geological features, and potential for harboring life.
Inner Solar System: The Rocky Worlds
Our inner solar system is dominated by four terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These planets are characterized by their rocky composition, relatively small size compared to the gas giants, and, in some cases, a significant presence of geological activity.
Mercury: The Scorched Messenger
Defining Characteristic: Extreme Temperature Fluctuations.
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, experiences the most dramatic temperature swings in the solar system. Its sun-facing side can reach scorching temperatures exceeding 800°F (430°C), while the dark side plunges to frigid -290°F (-180°C). This extreme variation is due to Mercury's lack of a substantial atmosphere to regulate heat distribution. Its heavily cratered surface, a testament to its ancient history and frequent bombardment by asteroids, further emphasizes its harsh environment. The planet's metallic core, unusually large relative to its size, contributes to its weak magnetic field.
Venus: The Infernal Twin
Defining Characteristic: Runaway Greenhouse Effect.
Venus, often referred to as Earth's "twin" due to its similar size and mass, presents a stark contrast in terms of habitability. A runaway greenhouse effect has trapped heat within its dense carbon dioxide atmosphere, resulting in surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead – around 900°F (475°C). The extreme pressure and toxic atmosphere render the surface utterly inhospitable. Despite the lack of plate tectonics, Venus displays volcanic activity, hinting at a geologically active past and possibly present. Its incredibly slow rotation, taking longer than its orbital period, further adds to its unique profile.
Earth: The Blue Marble
Defining Characteristic: Abundant Liquid Water & Life.
Earth stands out as a unique celestial body due to the presence of abundant liquid water on its surface and the thriving ecosystem it supports. Its atmosphere, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, is crucial for life as we know it. Plate tectonics, a dynamic geological process, shapes the Earth's continents and oceans, constantly reshaping the landscape. The Earth's strong magnetic field protects it from harmful solar radiation, contributing to the conditions that support life.
Mars: The Red Planet
Defining Characteristic: Evidence of Past Water.
Mars, known for its reddish hue due to iron oxide in its soil, holds the compelling evidence of past liquid water on its surface. Dry riverbeds, polar ice caps, and subsurface water ice suggest a significantly wetter past. While the current Martian atmosphere is thin and cold, the potential for past or even present microbial life continues to fuel scientific exploration. Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and mountain in the solar system, dominates the Martian landscape. The planet's two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, are irregularly shaped and likely captured asteroids.
Outer Solar System: Gas Giants and Icy Moons
Beyond the asteroid belt lies the realm of the gas giants: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, along with their numerous moons, many of which hold captivating characteristics of their own.
Jupiter: The King of Planets
Defining Characteristic: Great Red Spot & Massive Size.
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is a gas giant dominated by hydrogen and helium. Its most striking feature is the Great Red Spot, a colossal atmospheric storm that has raged for centuries. Jupiter possesses a powerful magnetic field, and its intense radiation belts pose a significant challenge for spacecraft exploration. The planet's many moons, including the four Galilean satellites – Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto – each offer unique geological wonders.
Saturn: The Ringed Jewel
Defining Characteristic: Extensive Ring System.
Saturn is renowned for its breathtaking ring system, composed of countless icy particles ranging in size from dust grains to boulders. The rings' intricate structure and dynamics are a subject of ongoing research. Like Jupiter, Saturn is a gas giant with a powerful magnetic field and numerous moons, including Titan, a moon with a dense atmosphere and liquid methane lakes.
Uranus: The Sideways Planet
Defining Characteristic: Extreme Axial Tilt.
Uranus stands out due to its extreme axial tilt, effectively rolling on its side as it orbits the Sun. This unique orientation results in extreme seasonal variations, with each pole experiencing decades of continuous sunlight followed by decades of darkness. Uranus's atmosphere is composed mainly of hydrogen, helium, and methane, giving it a distinctive bluish-green appearance.
Neptune: The Icy Giant
Defining Characteristic: High Winds & Deep Blue Color.
Neptune, the farthest planet from the Sun, is an icy giant with a deep blue color due to methane in its atmosphere. It is characterized by extremely powerful winds, some of the fastest in the solar system. Neptune's large moon, Triton, is unique in its retrograde orbit, suggesting it may be a captured Kuiper Belt object.
Moons: Diverse Worlds in Their Own Right
Many moons in our solar system possess characteristics as fascinating as the planets themselves.
Ganymede (Jupiter's moon): Largest Moon
Defining Characteristic: Its own Magnetic Field.
Ganymede, the largest moon in our solar system, is unique for possessing its own intrinsic magnetic field, a rarity among moons. This indicates a complex internal structure and geological activity. It also has a tenuous oxygen atmosphere.
Titan (Saturn's moon): Methane Seas
Defining Characteristic: Liquid Methane Lakes and Rivers.
Titan, Saturn's largest moon, is characterized by its thick, nitrogen-rich atmosphere and the presence of liquid methane lakes and rivers on its surface. This makes it a fascinating analog for early Earth and a potential location for different forms of life.
Europa (Jupiter's moon): Subsurface Ocean
Defining Characteristic: Subsurface Ocean of Liquid Water.
Europa is considered one of the most promising locations in our solar system for finding extraterrestrial life. Strong evidence suggests a vast subsurface ocean of liquid water, potentially containing more water than all of Earth's oceans combined. This ocean is thought to be in contact with the rocky mantle, potentially providing energy sources for life.
Enceladus (Saturn's moon): Cryovolcanism
Defining Characteristic: Cryovolcanic Plumes and Subsurface Ocean.
Enceladus, a small moon of Saturn, exhibits cryovolcanism, erupting plumes of water vapor and ice particles from its south polar region. These plumes indicate a subsurface ocean interacting with the moon's rocky core, creating a potentially habitable environment.
Triton (Neptune's moon): Retrograde Orbit
Defining Characteristic: Retrograde Orbit and Cryovolcanism.
Triton, Neptune's largest moon, has a retrograde orbit, meaning it orbits in the opposite direction of its planet's rotation. This suggests that Triton may be a captured Kuiper Belt object. It also displays cryovolcanic activity, suggesting a geologically active interior.
This guide provides a glimpse into the diverse and captivating characteristics of planets and moons within our solar system. Each celestial body offers unique insights into the processes that have shaped our cosmos, and continued exploration promises to reveal even more wonders in the years to come. Further research into planetary formation, atmospheric dynamics, and the potential for extraterrestrial life continues to drive scientific inquiry and inspire our understanding of the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Summary Of A Wall Of Fire Rising
Mar 31, 2025
-
Unit 6 Study Guide Similar Triangles
Mar 31, 2025
-
Shadow Health Alcohol Use Disorder Sbar
Mar 31, 2025
-
Things Fall Apart Summary Chapter 4
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Trisubstituted Cyclohexane Compound Is Given
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match Each Moon Or Planet To The Most Accurate Characteristic . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
