Match Each Principal Function Of Management With Its Definition.
Onlines
Apr 07, 2025 · 8 min read
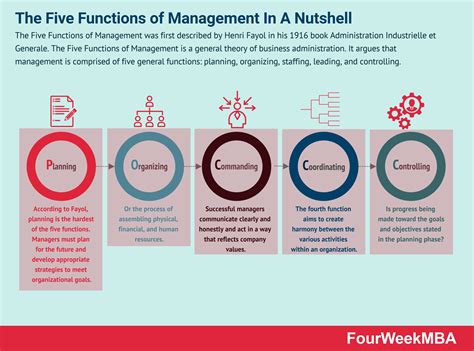
Table of Contents
- Match Each Principal Function Of Management With Its Definition.
- Table of Contents
- Match Each Principal Function of Management With Its Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
- 1. Planning: Laying the Foundation for Success
- Defining the Planning Function:
- The Importance of Effective Planning:
- 2. Organizing: Structuring for Efficiency
- Defining the Organizing Function:
- The Importance of Effective Organizing:
- 3. Leading: Motivating and Inspiring Individuals
- Defining the Leading Function:
- The Importance of Effective Leading:
- 4. Controlling: Monitoring and Adjusting Performance
- Defining the Controlling Function:
- The Importance of Effective Controlling:
- The Interdependence of Management Functions
- Conclusion: Mastering the Principal Functions for Organizational Success
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Match Each Principal Function of Management With Its Definition: A Comprehensive Guide
Effective management is the backbone of any successful organization, regardless of size or industry. Understanding the principal functions of management is crucial for anyone aspiring to lead and excel in a professional setting. These functions, often described as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling (POLC), represent a cyclical process that ensures consistent progress towards organizational goals. This comprehensive guide delves deep into each function, providing detailed definitions and illustrating their interconnectedness.
1. Planning: Laying the Foundation for Success
Planning is the first and arguably most crucial function of management. It involves setting goals, developing strategies, and outlining the actions necessary to achieve those goals. Without a well-defined plan, organizations drift aimlessly, wasting resources and missing opportunities.
Defining the Planning Function:
The planning function encompasses several key aspects:
-
Defining Objectives: Clearly stating what the organization hopes to accomplish. This includes setting both short-term (tactical) and long-term (strategic) objectives, ensuring alignment across all levels. SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) are a cornerstone of effective planning.
-
Analyzing the Environment: Conducting thorough internal and external analyses to identify opportunities and threats. This might involve SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), PESTLE analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental), or other relevant frameworks.
-
Developing Strategies: Creating a roadmap of how the organization will achieve its objectives. This involves considering resource allocation, timelines, and potential risks. Strategies should be adaptable to changing circumstances.
-
Developing Action Plans: Breaking down strategies into smaller, manageable steps. This creates a clear path for implementation and allows for easier monitoring of progress.
-
Forecasting: Predicting future trends and their potential impact on the organization. This involves analyzing data, market research, and expert opinions to anticipate challenges and opportunities.
Example: A restaurant planning to expand needs to plan its menu, location scouting, staff recruitment, marketing strategy, and financial projections. This requires detailed market research, analyzing competitor strategies, and creating a comprehensive business plan.
The Importance of Effective Planning:
Effective planning provides several key benefits:
- Reduced Uncertainty: By anticipating potential challenges, organizations can develop contingency plans and mitigate risks.
- Improved Resource Allocation: Planning ensures resources are utilized efficiently and effectively, preventing waste and maximizing returns.
- Enhanced Coordination: A well-defined plan ensures everyone is working towards the same objectives, minimizing conflict and maximizing synergy.
- Increased Productivity: Clear goals and action plans improve focus and motivation, leading to higher productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: Well-planned organizations are better positioned to respond to market changes and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
2. Organizing: Structuring for Efficiency
Organizing is the second key function of management. It involves designing the organizational structure, allocating resources, and coordinating activities to achieve the goals established in the planning phase. This entails establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting relationships within the organization.
Defining the Organizing Function:
The organizing function includes:
-
Designing Organizational Structure: Creating a framework that defines the relationships between different parts of the organization. This might involve choosing a hierarchical, flat, matrix, or network structure, depending on the organization's needs.
-
Delegating Authority and Responsibility: Assigning tasks and responsibilities to individuals and teams, ensuring that each member has the authority to complete their assigned tasks. Clear lines of authority are essential.
-
Allocating Resources: Distributing resources (financial, human, technological, etc.) effectively to support the implementation of plans. Resource allocation should be aligned with strategic priorities.
-
Establishing Communication Channels: Creating systems for information flow within the organization, ensuring effective communication between different departments and individuals.
-
Developing a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): This is a hierarchical decomposition of a project into smaller, more manageable tasks. It is a valuable tool for organizing complex projects.
Example: A software development team needs to organize itself into smaller units, each responsible for specific aspects of the project (e.g., front-end development, back-end development, testing). They will allocate resources accordingly and establish clear communication channels to ensure timely completion.
The Importance of Effective Organizing:
Effective organizing leads to:
- Improved Efficiency: Clear roles and responsibilities minimize confusion and duplication of effort, leading to increased efficiency.
- Better Coordination: A well-organized structure facilitates collaboration and communication, ensuring all parts of the organization work together effectively.
- Enhanced Productivity: Efficient resource allocation and clear task assignments contribute to higher productivity.
- Improved Accountability: Clearly defined roles and responsibilities make it easier to hold individuals and teams accountable for their performance.
- Increased Adaptability: A flexible organizational structure allows the organization to adapt more easily to changing circumstances.
3. Leading: Motivating and Inspiring Individuals
Leading, sometimes referred to as directing, is the process of influencing and motivating individuals to work towards organizational goals. It involves setting a vision, communicating effectively, and providing support and guidance to employees.
Defining the Leading Function:
Leading encompasses several key activities:
-
Setting a Vision: Articulating a compelling vision that inspires employees and motivates them to work towards common goals. The vision should be clear, concise, and achievable.
-
Motivating Employees: Encouraging employees to perform at their best by providing incentives, recognition, and support. Effective leadership recognizes individual needs and motivations.
-
Communicating Effectively: Sharing information clearly and consistently, ensuring that all employees understand the organization's goals, strategies, and expectations. Effective communication fosters trust and collaboration.
-
Building Teamwork: Fostering a collaborative environment where employees work together effectively to achieve common goals. Effective leadership encourages open communication and mutual respect.
-
Mentoring and Coaching: Providing guidance and support to employees, helping them develop their skills and achieve their full potential. Mentorship helps to develop future leaders within the organization.
Example: A project manager needs to lead their team by setting clear objectives, providing regular feedback, resolving conflicts, and ensuring that the team has the necessary resources and support to succeed.
The Importance of Effective Leading:
Effective leadership is vital for:
- Improved Employee Morale: Effective leadership creates a positive and motivating work environment, boosting employee morale and engagement.
- Increased Productivity: Motivated and engaged employees are more productive and contribute more effectively to organizational goals.
- Enhanced Innovation: Empowering employees and encouraging creative thinking leads to increased innovation and creativity.
- Improved Employee Retention: Effective leadership helps to retain talented employees by creating a positive and rewarding work environment.
- Stronger Organizational Culture: Leadership shapes the organization's culture, influencing its values, beliefs, and behaviors.
4. Controlling: Monitoring and Adjusting Performance
Controlling is the final, yet equally crucial, function of management. It involves monitoring performance, comparing it to goals, and making necessary adjustments to ensure that the organization is on track to achieve its objectives.
Defining the Controlling Function:
Controlling includes several key steps:
-
Establishing Standards: Defining clear performance standards and metrics that will be used to measure progress towards goals. These standards should be measurable, achievable, and aligned with organizational objectives.
-
Measuring Performance: Collecting data and information on actual performance, using appropriate methods such as performance reports, feedback surveys, and direct observation.
-
Comparing Performance to Standards: Analyzing the difference between actual performance and established standards, identifying areas where performance is meeting or exceeding expectations and areas where improvement is needed.
-
Taking Corrective Action: Implementing necessary changes to improve performance, addressing any deviations from established standards. This might involve adjusting strategies, reallocating resources, or providing additional training.
-
Continuous Improvement: Using the control process to identify opportunities for improvement and implement changes to enhance organizational effectiveness.
Example: A marketing manager monitors website traffic, conversion rates, and social media engagement to assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. If performance falls short of targets, they adjust strategies and allocate resources accordingly.
The Importance of Effective Controlling:
Effective control mechanisms:
- Ensures Achievement of Goals: Regular monitoring and corrective action ensure that the organization stays on track to achieve its objectives.
- Identifies Problems Early: Early detection of deviations from standards allows for timely intervention and prevents problems from escalating.
- Improves Efficiency and Effectiveness: By identifying areas of inefficiency, organizations can implement improvements and optimize resource utilization.
- Enhances Accountability: Regular monitoring and performance evaluations enhance accountability among employees and teams.
- Facilitates Continuous Improvement: The control process provides valuable feedback, enabling organizations to continuously improve their processes and performance.
The Interdependence of Management Functions
It's crucial to understand that the four management functions are not isolated activities but rather interconnected and cyclical. Planning lays the groundwork, organizing structures the resources, leading motivates the workforce, and controlling monitors and adjusts progress. The process then repeats, ensuring continuous improvement and adaptation to the changing environment. For example, the results of the controlling function might necessitate adjustments to the planning process, highlighting the dynamic and iterative nature of management.
Conclusion: Mastering the Principal Functions for Organizational Success
Mastering the principal functions of management – planning, organizing, leading, and controlling – is essential for organizational success. By understanding the definitions, interdependencies, and importance of each function, managers can effectively guide their teams, optimize resources, and achieve their strategic objectives. This comprehensive guide provides a strong foundation for aspiring and current managers to enhance their leadership skills and contribute to the overall success of their organizations. Consistent application and adaptation of these principles are key to thriving in today's dynamic business environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Commanding Officer Can Authorize The Ep Evaluation
Apr 11, 2025
-
6 05 Quiz Poem Vs Essay Vs Interview
Apr 11, 2025
-
Drafting Contracts Tina Stark Exercise Answers
Apr 11, 2025
-
Things Fall Apart Summary Chapter 17
Apr 11, 2025
-
Introduction To The Practice Of Statistics 10th Edition
Apr 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match Each Principal Function Of Management With Its Definition. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.