Match The Psychological Perspective To The Proper Description.
Onlines
Mar 14, 2025 · 7 min read
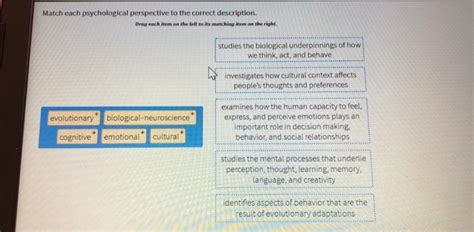
Table of Contents
Match the Psychological Perspective to the Proper Description: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the vast landscape of psychology requires familiarity with its diverse perspectives. These perspectives, or schools of thought, offer unique lenses through which to examine human behavior, thought, and emotion. This comprehensive guide will explore the major psychological perspectives, providing clear descriptions and examples to help you accurately match each perspective to its corresponding description.
Key Psychological Perspectives: A Detailed Overview
This section will delve into the core principles and tenets of each major psychological perspective. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial for correctly associating them with specific descriptions.
1. Psychodynamic Perspective
The psychodynamic perspective, rooted in the work of Sigmund Freud, emphasizes the influence of the unconscious mind on behavior. It posits that our early childhood experiences, particularly our relationships with our parents, shape our personality and influence our adult behavior. Key concepts include:
- The Id, Ego, and Superego: Freud's structural model of the personality, depicting the interplay between primal urges (Id), rational thought (Ego), and moral conscience (Superego).
- Defense Mechanisms: Unconscious strategies used by the ego to protect itself from anxiety-provoking thoughts and feelings (e.g., repression, denial, projection).
- Psychosexual Stages: Freud's theory suggesting that personality develops through a series of psychosexual stages (oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital), with fixation at a particular stage leading to specific personality traits.
Example: A psychodynamic therapist might explore a patient's current relationship problems by examining their early childhood experiences with their parents, looking for patterns of attachment and unresolved conflicts that are influencing their present-day relationships.
2. Behavioral Perspective
The behavioral perspective focuses on observable behaviors and how they are learned through environmental interactions. It largely discards internal mental states, emphasizing the role of conditioning and reinforcement in shaping behavior. Major concepts include:
- Classical Conditioning: Learning through association, where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a naturally occurring stimulus to elicit a conditioned response (Pavlov's dogs).
- Operant Conditioning: Learning through consequences, where behaviors are strengthened or weakened depending on whether they are followed by reinforcement or punishment (Skinner's box).
- Social Learning Theory: An extension of behaviorism that acknowledges the role of observation and imitation in learning (Bandura's Bobo doll experiment).
Example: A behavioral therapist might use techniques like systematic desensitization (gradually exposing a patient to a feared stimulus) or token economies (rewarding desirable behaviors with tokens that can be exchanged for privileges) to treat phobias or other behavioral problems.
3. Cognitive Perspective
The cognitive perspective emphasizes mental processes such as thinking, memory, perception, and problem-solving. It examines how these internal processes influence our behavior and emotions. Key concepts include:
- Information Processing: The analogy of the human mind as a computer, processing information through various stages.
- Schemas: Mental frameworks that organize and interpret information, shaping our understanding of the world.
- Cognitive Biases: Systematic errors in thinking that can affect our judgments and decisions.
Example: A cognitive therapist might help a patient identify and challenge negative thought patterns contributing to depression or anxiety. They might teach techniques like cognitive restructuring to replace negative thoughts with more realistic and positive ones.
4. Biological Perspective
The biological perspective focuses on the physiological and genetic factors underlying behavior and mental processes. It explores the influence of the brain, nervous system, hormones, and genes on our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Key concepts include:
- Neuroscience: The study of the nervous system, including the brain and its functions.
- Genetics: The study of how genes influence behavior and mental health.
- Evolutionary Psychology: The application of evolutionary principles to understanding human behavior.
Example: A biological psychologist might investigate the role of neurotransmitters in depression or study the genetic predisposition to certain mental illnesses.
5. Humanistic Perspective
The humanistic perspective emphasizes human potential, free will, and self-actualization. It focuses on the individual's subjective experience and their capacity for personal growth. Key concepts include:
- Self-Actualization: The innate drive to reach one's full potential.
- Unconditional Positive Regard: Acceptance and support without judgment.
- Self-Concept: The individual's perception of themselves.
Example: A humanistic therapist might use client-centered therapy, focusing on empathy, unconditional positive regard, and helping the client explore their own feelings and experiences to foster self-acceptance and personal growth.
6. Sociocultural Perspective
The sociocultural perspective examines the influence of social and cultural factors on behavior and mental processes. It highlights the impact of social norms, cultural values, and societal expectations on individual behavior. Key concepts include:
- Social Norms: The unwritten rules that govern behavior in a society.
- Cultural Values: The beliefs and principles that guide behavior within a culture.
- Social Influence: The impact of others on our behavior and attitudes.
Example: A sociocultural psychologist might research the influence of cultural norms on gender roles or study the impact of social media on self-esteem.
7. Evolutionary Perspective
The evolutionary perspective views human behavior through the lens of natural selection and adaptation. It suggests that many of our behaviors and psychological traits have evolved over time to enhance survival and reproduction. Key concepts include:
- Adaptation: Traits that have evolved to increase survival and reproductive success.
- Natural Selection: The process by which organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- Sexual Selection: The process by which traits that enhance mating success are selected for.
Example: Evolutionary psychologists might explain aggression as an adaptive trait that increased survival in ancestral environments or investigate mate preferences in terms of reproductive fitness.
Matching Perspectives to Descriptions: Practice Exercises
Now, let's test your understanding with some practice exercises. For each description below, identify the corresponding psychological perspective:
Exercise 1: This perspective emphasizes the role of unconscious conflicts and early childhood experiences in shaping personality and behavior. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Psychodynamic Perspective
Exercise 2: This perspective focuses on observable behaviors and how they are learned through conditioning and reinforcement. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Behavioral Perspective
Exercise 3: This perspective explores how mental processes such as thinking, memory, and perception influence behavior and emotion. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Cognitive Perspective
Exercise 4: This perspective examines the physiological and genetic factors underlying behavior and mental processes, focusing on the brain, nervous system, hormones, and genes. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Biological Perspective
Exercise 5: This perspective highlights the importance of human potential, free will, and self-actualization, emphasizing individual subjective experience and personal growth. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Humanistic Perspective
Exercise 6: This perspective examines the influence of social and cultural factors on behavior and mental processes, considering the impact of social norms, cultural values, and societal expectations. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Sociocultural Perspective
Exercise 7: This perspective explains human behavior through the lens of natural selection and adaptation, suggesting that many of our behaviors and traits have evolved to enhance survival and reproduction. Which perspective is this?
Answer: Evolutionary Perspective
Integrating Perspectives: A Holistic Approach
It's important to note that these perspectives are not mutually exclusive. A comprehensive understanding of human behavior often requires integrating insights from multiple perspectives. For example, understanding depression might involve considering biological factors (neurotransmitter imbalances), cognitive factors (negative thought patterns), and social factors (stressful life events). By integrating different perspectives, we gain a richer and more nuanced understanding of the complexity of human experience.
Conclusion: Mastering Psychological Perspectives
Mastering the various psychological perspectives is key to a deeper understanding of human behavior and mental processes. By understanding the core principles of each perspective and its unique approach to studying the mind, you can accurately analyze and interpret human actions, thoughts, and emotions. This guide provides a solid foundation for further exploration and application of these crucial concepts. Remember to continuously learn and expand your knowledge to refine your understanding of this fascinating field. The human mind is a complex and evolving entity, and staying updated on the latest research and theories is essential for a comprehensive understanding of psychology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Sun Also Rises Summary By Chapter
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Banner Requires 1 1 3
Mar 14, 2025
-
Secondary Math 3 Module 6 Modeling Periodic Behavior 6 1 Answers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Silvina Tuvo Un Accidente En Su Automovil
Mar 14, 2025
-
Print Reading For Construction Answer Key
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Psychological Perspective To The Proper Description. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
