Match The Situation With The Appropriate Use Of Network Media.
Onlines
Mar 17, 2025 · 7 min read
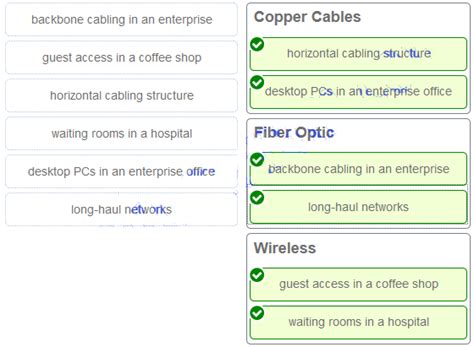
Table of Contents
- Match The Situation With The Appropriate Use Of Network Media.
- Table of Contents
- Matching the Situation with the Appropriate Use of Network Media
- Understanding Network Media: A Quick Overview
- Guided Media
- Unguided Media
- Matching Network Media to Specific Situations
- Case Studies: Matching Media to Specific Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Home Network
- Scenario 2: Small Office Network
- Scenario 3: Large Enterprise Network
- Scenario 4: Long-Distance Data Transmission
- Scenario 5: Industrial Automation Network
- Scenario 6: Connecting Remote Locations with Limited Infrastructure
- Factors Affecting Media Choice: A Deeper Dive
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Matching the Situation with the Appropriate Use of Network Media
Choosing the right network media is crucial for optimal network performance and efficiency. The wrong choice can lead to bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and ultimately, a poorly functioning network. This article delves deep into various network media types, their characteristics, and how to match them with specific situations to ensure your network runs smoothly and securely. We'll explore the strengths and weaknesses of each, helping you make informed decisions for your network infrastructure.
Understanding Network Media: A Quick Overview
Network media, also known as transmission media, refers to the physical path used to transmit data between network devices. These media can be broadly categorized into two main types: guided media and unguided media.
Guided Media
Guided media, also called wired media, provide a physical path along which signals are transmitted. This provides better security and higher bandwidth compared to unguided media. Key examples include:
-
Twisted-Pair Cable: This is the most common type of network cable, consisting of two insulated copper wires twisted together. It's inexpensive and readily available, making it suitable for many applications. However, it's susceptible to interference and has a limited bandwidth compared to other options. Variations include shielded twisted-pair (STP) and unshielded twisted-pair (UTP), with STP offering better protection against interference.
-
Coaxial Cable: Coaxial cable consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer, a metallic shield, and an outer jacket. It offers better shielding and bandwidth than twisted-pair cable, making it suitable for applications requiring higher data rates, like cable television and older Ethernet networks. However, it's less flexible and more expensive than twisted-pair.
-
Fiber-Optic Cable: This type of cable uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light. It offers superior bandwidth, security, and distance capabilities compared to copper cables. It's ideal for long-distance transmission and high-bandwidth applications like high-speed internet and backbone networks. However, it's more expensive and requires specialized equipment for installation and termination.
Unguided Media
Unguided media, also called wireless media, uses radio waves or other electromagnetic signals to transmit data. They offer flexibility and mobility but are more susceptible to interference and security breaches. Examples include:
-
Radio Waves: These are used in various wireless technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks. The range and bandwidth vary depending on the frequency and technology used. They are prone to interference from other devices and environmental factors.
-
Microwaves: These are high-frequency radio waves used for point-to-point communication, often in long-distance wireless links. They require line-of-sight transmission and are susceptible to atmospheric conditions.
-
Infrared (IR): IR uses infrared light to transmit data over short distances. It's commonly used in remote controls and some short-range wireless communication systems. However, it's easily blocked by obstacles.
Matching Network Media to Specific Situations
The optimal choice of network media depends on several factors, including:
-
Distance: For short distances, twisted-pair cable is often sufficient. For longer distances, fiber-optic cable or microwave links might be necessary.
-
Bandwidth: High-bandwidth applications require media capable of supporting high data rates, such as fiber-optic cable or high-quality coaxial cable.
-
Cost: Twisted-pair cable is generally the most affordable option, while fiber-optic cable is the most expensive.
-
Security: Guided media generally offer better security than unguided media due to the physical nature of the connection.
-
Environment: The environmental conditions can affect the choice of media. For example, fiber-optic cable is less susceptible to electromagnetic interference than copper cables.
-
Scalability: Consider the future needs of your network. Choose a media type that can support future expansion and upgrades.
-
Ease of Installation: Twisted-pair cabling is relatively easy to install, while fiber-optic cable requires specialized expertise.
Case Studies: Matching Media to Specific Scenarios
Let's explore several scenarios and identify the most appropriate network media:
Scenario 1: Home Network
Situation: A small home network with two computers, a smart TV, and several mobile devices. The devices are located within a single house, and the primary use is for web browsing, streaming, and file sharing.
Appropriate Media: Unshielded twisted-pair cable (UTP) Category 5e or Category 6 for wired connections and Wi-Fi (802.11ac or 802.11ax) for wireless connections. UTP is cost-effective and provides sufficient bandwidth for typical home network activities. Wi-Fi offers flexibility for mobile devices.
Scenario 2: Small Office Network
Situation: A small office with 10-15 computers, a server, and a printer, all located within a single building. The network needs to support file sharing, email, and internet access.
Appropriate Media: A combination of UTP Category 6 cabling for wired connections and potentially Wi-Fi for mobile devices. Category 6 provides better performance than Category 5e, especially with a larger number of devices.
Scenario 3: Large Enterprise Network
Situation: A large enterprise with hundreds or thousands of computers, servers, and network devices spread across multiple buildings or even cities. The network needs to support high-bandwidth applications like video conferencing, data storage, and cloud computing.
Appropriate Media: A combination of fiber-optic cable for the backbone network and UTP for local area networks (LANs). Fiber optics offer the high bandwidth and long-distance capabilities needed for a large-scale network. UTP can be used for shorter distances within buildings. Wireless solutions like Wi-Fi might supplement the wired infrastructure for mobile devices.
Scenario 4: Long-Distance Data Transmission
Situation: Transmitting large amounts of data over a long distance, such as between two geographically distant data centers.
Appropriate Media: Fiber-optic cable is the clear choice. Its high bandwidth and low signal attenuation make it ideal for long-distance transmission. Microwave links could also be considered, but they are more susceptible to interference and environmental conditions.
Scenario 5: Industrial Automation Network
Situation: A factory floor with various machines and sensors needing to communicate in real-time. Reliability, resilience, and resistance to electromagnetic interference are crucial.
Appropriate Media: Shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable or fiber-optic cable could be suitable depending on the specific requirements. STP offers better protection against electromagnetic interference than UTP. Fiber optics provide the best reliability and bandwidth. Wireless solutions might be used in specific areas, but wired connections are preferred for critical applications.
Scenario 6: Connecting Remote Locations with Limited Infrastructure
Situation: Connecting two remote offices or locations with limited existing infrastructure, such as in a rural area with poor wired connectivity.
Appropriate Media: A wireless solution, such as a microwave link or a satellite link, might be the only feasible option. However, these solutions are often more expensive and can be less reliable than wired connections.
Factors Affecting Media Choice: A Deeper Dive
Beyond the basic scenarios, several more nuanced factors should influence your network media selection:
-
Cost of Installation and Maintenance: While fiber optics offer superior performance, the initial investment and specialized skills required for installation can be significantly higher. Ongoing maintenance costs should also be factored in.
-
Scalability and Future-Proofing: Consider the future growth of your network. Choosing a media capable of handling increased bandwidth and a larger number of devices is essential for long-term cost savings and avoiding costly upgrades.
-
Security Considerations: Wireless networks, while convenient, are more vulnerable to unauthorized access compared to wired networks. Consider implementing robust security measures if using wireless technology. The physical nature of wired connections provides an inherent level of security.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Certain industries and applications might have regulatory requirements that dictate the type of network media allowed. Understanding these regulations is crucial for compliance.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate network media is a crucial decision impacting network performance, security, scalability, and cost. By carefully considering the factors outlined in this article, including distance, bandwidth needs, cost, security concerns, and environmental factors, you can effectively match the right network media to your specific situation. Remember to consider not just the immediate needs but also the future scalability and potential upgrades your network might require. A well-planned network infrastructure ensures smooth operations, efficient data transmission, and robust security for years to come. Choosing the right media is the cornerstone of a successful and reliable network.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Su Casa Es Muy Grande Ellos
Mar 18, 2025
-
Lesson 4 Student Activity Sheet Answers
Mar 18, 2025
-
Mrs Duarte Is Enrolled In Original Medicare
Mar 18, 2025
-
Choose The Function Whose Graph Is Given Below
Mar 18, 2025
-
National Geographic Secrets Of The Body Farm Answers
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Situation With The Appropriate Use Of Network Media. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
