Match The Term With Its Definition Hydrostatic Pressure
Onlines
Apr 07, 2025 · 6 min read
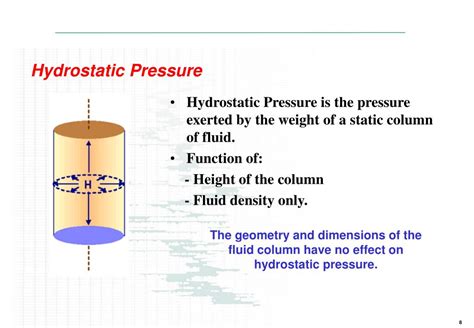
Table of Contents
Match the Term with its Definition: Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure, a fundamental concept in fluid mechanics, plays a crucial role in numerous scientific disciplines and everyday phenomena. Understanding this pressure is vital for comprehending everything from the pressure at the bottom of the ocean to the functioning of our circulatory system. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into hydrostatic pressure, explaining its definition, its calculation, and its applications in various fields. We'll also explore related concepts and address common misconceptions.
What is Hydrostatic Pressure?
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest due to the force of gravity. It's the pressure experienced at any point within a fluid, resulting from the weight of the fluid above that point. Crucially, this pressure acts equally in all directions. This is a key differentiator from other types of pressure. Imagine a submerged object; the pressure on its top surface is the same as the pressure on its bottom surface, assuming the object is entirely within the same fluid layer.
In simpler terms: Imagine a column of water. The water at the bottom of the column experiences more pressure because it's supporting the weight of all the water above it. This pressure is hydrostatic pressure. The deeper you go, the greater the pressure becomes.
Key Characteristics of Hydrostatic Pressure:
- Dependent on Depth: Hydrostatic pressure increases linearly with depth. The deeper you go into a fluid, the greater the pressure.
- Independent of Shape: The shape of the container holding the fluid doesn't affect the hydrostatic pressure at a given depth. Pressure depends solely on depth and fluid density.
- Acts in All Directions: The pressure acts equally in all directions at a given point within the fluid.
- Proportional to Density: Hydrostatic pressure is directly proportional to the density of the fluid. Denser fluids exert greater pressure at the same depth.
- Proportional to Gravity: Hydrostatic pressure is directly proportional to the acceleration due to gravity. On planets with stronger gravity, hydrostatic pressure will be higher.
Calculating Hydrostatic Pressure: The Formula
The hydrostatic pressure (P) at a depth (h) in a fluid can be calculated using the following formula:
P = ρgh
Where:
- P represents hydrostatic pressure (typically measured in Pascals, Pa).
- ρ (rho) represents the density of the fluid (typically measured in kilograms per cubic meter, kg/m³).
- g represents the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s² on Earth).
- h represents the depth within the fluid (typically measured in meters, m).
This formula is fundamental to understanding and calculating hydrostatic pressure in various situations. Let's explore how it applies in different contexts.
Applications of Hydrostatic Pressure: A Wide Range of Fields
Hydrostatic pressure is a ubiquitous phenomenon with applications across numerous scientific and engineering disciplines. Some key examples include:
1. Oceanography and Marine Science:
- Deep-sea Exploration: Understanding hydrostatic pressure is critical for designing submersibles and other equipment capable of withstanding the immense pressure at great ocean depths. The pressure increases significantly with depth, posing a significant challenge to equipment design.
- Marine Biology: Hydrostatic pressure plays a vital role in the physiology and survival of marine organisms adapted to different depths. Different species have evolved unique mechanisms to cope with the varying pressure conditions.
- Ocean Currents: Pressure differences, partly driven by hydrostatic pressure variations, contribute to ocean currents and their patterns.
2. Meteorology and Atmospheric Science:
- Atmospheric Pressure: The pressure we experience at sea level is essentially atmospheric pressure, a form of hydrostatic pressure exerted by the weight of the air above us.
- Weather Forecasting: Understanding atmospheric pressure variations is crucial for weather forecasting. Pressure systems and their movements influence weather patterns.
3. Medicine and Physiology:
- Blood Pressure: Blood pressure in our circulatory system is directly related to hydrostatic pressure. The heart pumps blood, creating pressure that helps distribute blood throughout the body. Variations in blood pressure can indicate various health problems.
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure: The pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord is also a form of hydrostatic pressure. Abnormal cerebrospinal fluid pressure can indicate neurological conditions.
4. Engineering and Technology:
- Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic systems, such as those used in construction equipment and braking systems, rely on the principles of hydrostatic pressure to transfer force and power.
- Dam Design: The design and construction of dams need to take into account the immense hydrostatic pressure exerted by the water behind them.
- Submarine Design: Submarines are designed to withstand the immense hydrostatic pressure of the ocean depths. This requires robust materials and sophisticated engineering.
Hydrostatic Pressure vs. Other Types of Pressure
It's crucial to differentiate hydrostatic pressure from other types of pressure:
- Dynamic Pressure: This pressure is associated with the movement of fluids. Unlike hydrostatic pressure, it's dependent on fluid velocity.
- Gauge Pressure: This is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. It's the pressure reading you'd get from a typical pressure gauge.
- Absolute Pressure: This is the total pressure, including atmospheric pressure. It represents the total pressure exerted at a point.
Misconceptions about Hydrostatic Pressure
Several common misconceptions surround hydrostatic pressure. Let's clarify some of them:
-
Misconception: Hydrostatic pressure only acts downwards.
- Reality: Hydrostatic pressure acts equally in all directions.
-
Misconception: The pressure at the bottom of a container depends on the container's shape.
- Reality: The pressure at a given depth only depends on the depth and fluid density, not the container's shape.
-
Misconception: Hydrostatic pressure is only relevant in liquids.
- Reality: While commonly associated with liquids, the concept applies to gases as well (e.g., atmospheric pressure).
Advanced Concepts Related to Hydrostatic Pressure:
- Pascal's Principle: This principle states that a pressure change at any point in a confined incompressible fluid is transmitted throughout the fluid such that the same change occurs everywhere. This principle is fundamental to hydraulic systems.
- Archimedes' Principle: This principle explains buoyancy, which is the upward force exerted on an object submerged in a fluid. The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
- Fluid Statics: This branch of fluid mechanics deals with fluids at rest and the forces associated with them, including hydrostatic pressure.
Conclusion: The Significance of Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications across various fields. From the depths of the ocean to the intricate workings of the human body, understanding hydrostatic pressure is vital for comprehending the world around us. By mastering the principles and calculations associated with hydrostatic pressure, we unlock the ability to analyze and solve problems across multiple disciplines, making it a cornerstone of scientific and engineering endeavors. Its importance extends beyond theoretical understanding, directly impacting the design, function, and safety of numerous technologies and systems we rely upon daily. Continued research and innovation in understanding hydrostatic pressure will undoubtedly lead to further advancements in numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Lucky Individual Won The State Lottery
Apr 08, 2025
-
Use This Crel Status To End A Members Conditional Release
Apr 08, 2025
-
The Murder Of Roger Ackroyd Characters
Apr 08, 2025
-
Identify The True And False Statements About Race
Apr 08, 2025
-
What Does Fences Symbolism In Fences
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Match The Term With Its Definition Hydrostatic Pressure . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.