Mixtures Fuels Solvents Paints And Dusts
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
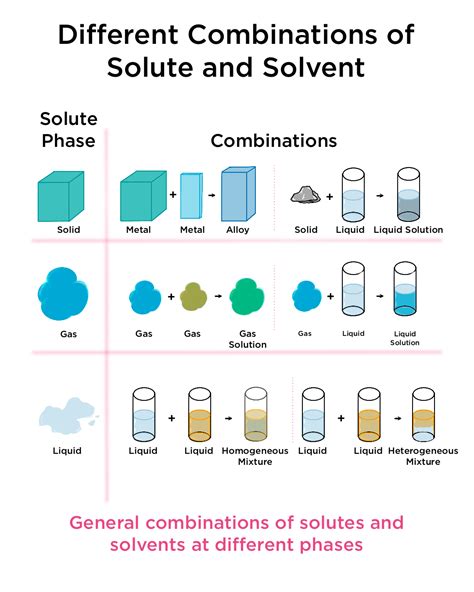
Table of Contents
Mixtures, Fuels, Solvents, Paints, and Dusts: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Properties and Hazards
Understanding the properties and potential hazards of mixtures, fuels, solvents, paints, and dusts is crucial for ensuring safety and complying with regulations across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into the characteristics of each category, exploring their composition, uses, and associated risks. We'll also examine the importance of proper handling, storage, and disposal to minimize potential harm to individuals and the environment.
Mixtures: A Diverse Group of Substances
A mixture is a substance composed of two or more components not chemically bonded. These components retain their individual chemical properties and can be separated by physical means like filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures are ubiquitous in our daily lives, ranging from the air we breathe to the food we eat. The characteristics of a mixture depend heavily on the properties of its constituent components and their proportions.
Types of Mixtures:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: In these mixtures, the components are uniformly distributed, meaning the composition is the same throughout. Examples include saltwater, air, and sugar dissolved in water.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures exhibit a non-uniform composition, with distinct regions having different properties. Examples include sand and water, oil and water, and a salad.
Significance in Various Industries:
Mixtures play a vital role in various industries. In the food industry, mixtures are essential for creating diverse food products, while in the pharmaceutical industry, they are used to formulate medications. The chemical industry relies extensively on mixtures for various manufacturing processes. Understanding the behavior of mixtures is critical for optimizing these processes and ensuring product quality.
Fuels: Powering Our World
Fuels are substances that release energy when they undergo combustion. This energy release is typically in the form of heat and light, making fuels essential for various applications, from powering vehicles and generating electricity to heating homes.
Types of Fuels:
- Fossil Fuels: These are fuels derived from ancient organic matter, including coal, petroleum, and natural gas. They are a significant source of energy but contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
- Biofuels: These are fuels derived from renewable biological sources, such as ethanol from corn or sugarcane and biodiesel from vegetable oils. They offer a more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Nuclear Fuels: These fuels, such as uranium, undergo nuclear fission to release immense amounts of energy. Nuclear power plants utilize this energy to generate electricity.
Fuel Properties and Considerations:
The efficiency and effectiveness of a fuel depend on various properties, including its energy density, flammability, and environmental impact. Energy density refers to the amount of energy released per unit mass or volume. Flammability relates to how easily a fuel ignites and burns. Environmental concerns related to fuel use include greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
Solvents: Dissolving and Cleaning
Solvents are substances capable of dissolving other substances, creating a homogeneous solution. They are widely used in various applications, including cleaning, extraction, and as components in paints and coatings.
Types of Solvents:
- Organic Solvents: These solvents are derived from organic compounds and are often volatile and flammable. Examples include acetone, ethanol, and toluene. Many organic solvents pose significant health risks, necessitating careful handling and proper ventilation.
- Inorganic Solvents: These solvents are derived from inorganic compounds and are generally less volatile and flammable than organic solvents. Water is the most common inorganic solvent.
Solvent Selection and Safety:
Choosing the appropriate solvent for a particular application requires considering factors such as the solubility of the substance to be dissolved, the solvent's toxicity, flammability, and environmental impact. Safety precautions, including proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE), are crucial when working with solvents.
Paints: Coating and Protection
Paints are mixtures of pigments, binders, solvents, and additives that create a colored coating on surfaces. They serve various purposes, including protection from environmental factors, aesthetic enhancement, and marking.
Paint Components:
- Pigments: These provide the color and opacity of the paint.
- Binders: These substances bind the pigments together and adhere the paint to the surface.
- Solvents: These thin the paint and aid in its application.
- Additives: These improve the paint's properties, such as its flow, drying time, and durability.
Paint Types and Applications:
Various paint types exist, each suited to different applications. Oil-based paints are durable and provide a hard finish, while water-based paints (latex paints) are easier to clean up and offer lower VOC emissions. Powder coatings are applied as a dry powder and cured using heat, offering excellent durability and scratch resistance.
Dusts: Airborne Particulates
Dusts are fine solid particles suspended in the air. They can originate from various sources, including industrial processes, construction activities, and natural events like windstorms. Dusts pose various health and environmental risks.
Types of Dusts:
- Mineral Dusts: These dusts are composed of mineral particles, such as silica, asbestos, and coal dust. Inhaling these dusts can cause serious respiratory diseases like silicosis and asbestosis.
- Organic Dusts: These dusts are composed of organic particles, such as wood dust, grain dust, and cotton dust. They can trigger allergic reactions and respiratory problems.
- Metal Dusts: These dusts are composed of metal particles, such as iron, lead, and aluminum. Exposure to metal dusts can cause various health problems, depending on the specific metal.
Dust Control and Mitigation:
Controlling dust is crucial in various settings to minimize health risks and environmental impacts. Methods for dust control include engineering controls like ventilation systems, administrative controls such as work practices, and personal protective equipment like respirators.
Synergistic Effects and Combined Hazards
It's crucial to understand that the combined effects of mixtures, fuels, solvents, paints, and dusts can be more hazardous than the individual components alone. Synergistic effects occur when the combined effect of two or more substances is greater than the sum of their individual effects. For example, the combination of certain solvents can increase their toxicity or flammability. Similarly, the presence of dust in a flammable atmosphere can increase the risk of explosion.
Regulations and Safety Practices
Handling, storing, and disposing of mixtures, fuels, solvents, paints, and dusts require strict adherence to regulations and safety practices. These regulations vary depending on the specific substance and location, but generally focus on minimizing risks to human health and the environment. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) provide crucial information on the hazards associated with specific materials and the necessary safety precautions. Proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response plans are vital for ensuring safety.
Conclusion: Responsible Handling is Key
Understanding the properties and potential hazards of mixtures, fuels, solvents, paints, and dusts is paramount for safety and environmental protection. Proper handling, storage, disposal, and adherence to regulations are crucial for minimizing risks in various industries and protecting both human health and the environment. Continuous education and awareness are key to promoting responsible use and preventing accidents. By understanding the intricacies of these substances and implementing appropriate safety measures, we can mitigate potential risks and ensure a safer working environment for everyone.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements About Group Writing Are True
Apr 04, 2025
-
11 3 Practice Problems Continued Chemistry Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Sentences Contain Redundant Words Or Phrases
Apr 04, 2025
-
Pal Cadaver Endocrine System Lab Practical Question 1
Apr 04, 2025
-
Common With Norming Is Intergroup Conflict
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Mixtures Fuels Solvents Paints And Dusts . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
