Nurses Touch The Leader Case 3 Interprofessional Communication
Onlines
Apr 07, 2025 · 6 min read
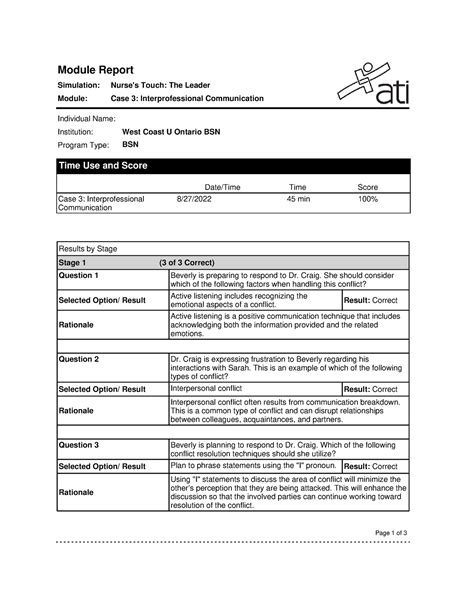
Table of Contents
Nurses Touch the Leader: Case 3 - Interprofessional Communication Breakdown and Solutions
Introduction:
Interprofessional communication (IPC) is the cornerstone of effective healthcare delivery. Miscommunication within a healthcare team can lead to adverse patient outcomes, increased stress levels for healthcare professionals, and a decline in overall patient satisfaction. Case 3 of "Nurses Touch the Leader" highlights a critical breakdown in IPC, showcasing the devastating consequences of poor communication and the crucial need for improved interprofessional collaboration. This article will delve into the specifics of the case, analyze the communication failures, explore contributing factors, and propose practical solutions to improve IPC and prevent similar incidents from recurring. We'll discuss the importance of assertive communication, active listening, shared decision-making, and the role of leadership in fostering a positive communication culture within the healthcare setting. The implications for patient safety and the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery will also be examined.
Case 3 Recap: Identifying the Communication Breakdown
(Note: Since I do not have access to the specific details of "Nurses Touch the Leader" Case 3, I will create a hypothetical case study that mirrors the general theme of interprofessional communication failure within a healthcare setting.)
Hypothetical Case 3: A 78-year-old patient, Mr. Jones, is admitted with a history of heart failure and type 2 diabetes. He is experiencing shortness of breath and chest pain. The nursing staff assesses Mr. Jones and notes a significant decrease in oxygen saturation levels. They immediately inform the attending physician, Dr. Smith, via phone. However, Dr. Smith is busy with another emergency and only briefly acknowledges the report, failing to clearly instruct the nurses on further action. The nurses, feeling unsure about the appropriate course of action, delay administering supplemental oxygen and notifying the respiratory therapist, fearing a reprimand for exceeding their scope of practice. Meanwhile, Mr. Jones' condition deteriorates, leading to respiratory distress and a subsequent cardiac arrest. Despite resuscitation efforts, Mr. Jones suffers significant neurological damage.
Analyzing the Communication Failures
This hypothetical case study demonstrates several critical communication failures:
1. Lack of Clear and Concise Communication: Dr. Smith's brief acknowledgment of the nurses' report was insufficient. He failed to provide clear instructions, leaving the nurses uncertain about the next steps. Effective communication requires clear, concise, and unambiguous language.
2. Ineffective Communication Channels: A phone call, while convenient, can be unreliable for conveying critical patient information, especially during emergencies. A more structured communication system, such as a standardized handover protocol or electronic health record (EHR) system with integrated messaging, would have been beneficial.
3. Hierarchical Communication Barriers: The power dynamic between the physician and the nurses may have inhibited the nurses from assertively advocating for Mr. Jones. They might have hesitated to question Dr. Smith's brief response due to perceived hierarchical authority. This highlights the need for a culture of open communication where all team members feel empowered to voice their concerns.
4. Lack of Shared Understanding and Situational Awareness: The lack of immediate consultation with the respiratory therapist created a critical information gap. This demonstrates the need for a team-based approach, where all relevant healthcare professionals are informed and actively involved in patient care.
5. Absence of a Formal Communication Protocol: A well-defined communication protocol would have outlined the steps to be taken in such situations, ensuring a timely and coordinated response. This includes clear escalation procedures and designated communication channels for critical patient updates.
Contributing Factors to Poor IPC
Several factors can contribute to poor interprofessional communication, including:
- Professional Hierarchy: Rigid hierarchical structures can create communication barriers, preventing junior healthcare professionals from openly expressing concerns to senior colleagues.
- Time Constraints: Heavy workloads and time pressure can lead to rushed communication, increasing the risk of misunderstandings and errors.
- Cultural Differences: Differences in cultural background, communication styles, and professional training can contribute to misunderstandings.
- Lack of Teamwork and Collaboration: A lack of trust and collaboration among team members can hinder communication and decision-making.
- Insufficient Training: Inadequate training in IPC skills, such as assertive communication and active listening, can impede effective communication.
Implementing Solutions for Improved IPC
To prevent similar incidents and improve interprofessional communication, several strategies can be implemented:
1. Structured Communication Techniques: Implementing structured communication techniques, such as the SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) method, provides a standardized framework for exchanging critical patient information. This ensures clear and concise communication, reducing the risk of misunderstandings.
2. Enhancing Teamwork and Collaboration: Promoting team-based care through shared decision-making and collaborative problem-solving improves communication flow and coordination. Regular team meetings, case discussions, and interprofessional education opportunities can foster a stronger sense of teamwork.
3. Leveraging Technology: Using electronic health records (EHRs) with integrated communication tools, such as secure messaging and alerts, streamlines communication and ensures timely access to patient information.
4. Training in IPC Skills: Investing in comprehensive training programs focused on IPC skills, including assertive communication, active listening, conflict resolution, and effective teamwork, is crucial. This training should be integrated into both initial and ongoing professional development programs.
5. Fostering a Culture of Open Communication: Creating a culture where all healthcare professionals feel comfortable expressing their concerns and opinions, regardless of their professional role, is essential. This requires leadership commitment to promoting open communication and a just culture where errors are seen as learning opportunities.
6. Standardized Handover Protocols: Implementing standardized handover protocols ensures that critical information is consistently and accurately communicated between shifts or teams. This reduces the risk of communication breakdowns and ensures continuity of care.
7. Regular Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing formal mechanisms for feedback and evaluation helps identify areas where communication can be improved. This includes regular team debriefings after significant events, patient safety huddles, and anonymous feedback surveys.
8. Addressing Hierarchy Issues: Healthcare organizations need to actively address hierarchical barriers that might prevent junior staff from freely communicating with senior colleagues. This may involve establishing clear communication pathways, empowering junior staff, and promoting a culture of respect and mutual support.
Implications for Patient Safety and Efficiency
Effective interprofessional communication significantly impacts patient safety and the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery. Improved IPC leads to:
- Reduced Medical Errors: Clear communication reduces the risk of medication errors, diagnostic errors, and treatment errors.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Efficient and effective communication leads to faster diagnosis, timely interventions, and better patient outcomes.
- Increased Patient Satisfaction: Patients are more satisfied when they feel that their healthcare team is working collaboratively and effectively.
- Enhanced Healthcare Team Morale: A positive communication environment fosters a stronger sense of teamwork, increased morale, and reduced stress among healthcare professionals.
- Improved Efficiency and Resource Utilization: Effective IPC streamlines workflow, reduces redundancies, and optimizes resource utilization.
Conclusion: The Importance of Proactive IPC Strategies
The hypothetical Case 3, mirroring the spirit of "Nurses Touch the Leader," highlights the critical role of interprofessional communication in ensuring patient safety and delivering high-quality care. Poor communication can have devastating consequences, leading to adverse patient outcomes and impacting the overall efficiency of the healthcare system. Therefore, a proactive approach to improving IPC is essential. This involves implementing structured communication techniques, fostering a culture of open communication, providing comprehensive training in IPC skills, and leveraging technology to enhance communication flow. By addressing the contributing factors to poor IPC and implementing effective solutions, healthcare organizations can create a safer and more efficient environment for both patients and healthcare professionals. Investing in robust interprofessional communication strategies is not merely a best practice; it is a fundamental requirement for achieving optimal patient care and a high-performing healthcare system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Wingate Company A Wholesale Distributor Of Electronic Equipment
Apr 09, 2025
-
Match Each Excerpt To Its Poetic Style
Apr 09, 2025
-
Research Suggests That Adult Males Are Socialized Around
Apr 09, 2025
-
Measuring With Metric Lab Answer Key
Apr 09, 2025
-
A Business Plan Is A Document That Outlines Blank
Apr 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Nurses Touch The Leader Case 3 Interprofessional Communication . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.