Nurses Touch The Leader Case 4 Quality Improvement
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
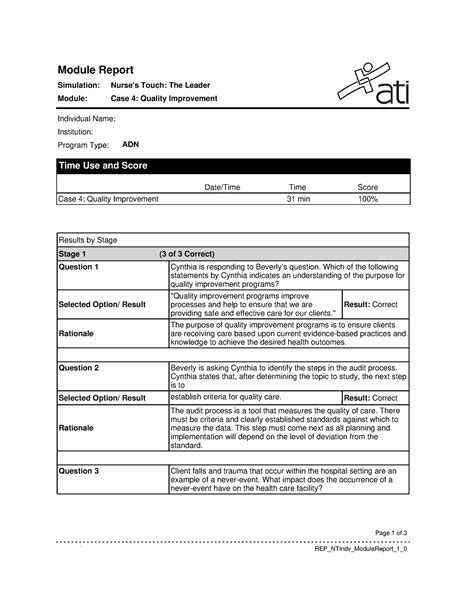
Table of Contents
Nurses' Touch: A Case Study in 4 Quality Improvement Initiatives
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, demanding continuous improvement in the quality of care delivered. This case study analyzes "Nurses' Touch," a fictional but representative hospital unit, and explores four distinct quality improvement (QI) initiatives implemented to enhance patient care and staff satisfaction. We will examine each initiative's methodology, challenges, successes, and lasting impact, showcasing the crucial role nurses play in driving positive change. This deep dive will highlight the importance of data-driven decision-making, collaborative teamwork, and a commitment to continuous learning in achieving superior healthcare outcomes.
Initiative 1: Reducing Medication Errors Through Barcoding Technology
Problem: Prior to implementing barcoding technology, Nurses' Touch experienced a concerning rate of medication errors, impacting patient safety and increasing the workload on nurses due to incident reporting and follow-up. The root cause analysis revealed that manual transcription of medication orders and lack of immediate verification were major contributing factors.
Solution: The unit implemented a comprehensive barcoding system for medication administration. This involved:
- Training: Thorough training for all nursing staff on the proper use of the barcoding system, including scanner operation, error handling, and troubleshooting.
- System Integration: Seamless integration of the barcoding system with the electronic health record (EHR) to ensure real-time data accuracy and reduce the potential for human error.
- Implementation Phases: A phased rollout of the system to allow for adjustments and staff acclimation, beginning with a pilot program on a smaller scale before wider adoption.
- Change Management: Active engagement with staff throughout the process, addressing concerns and providing support to facilitate a smooth transition.
Results: After implementation, Nurses' Touch experienced a significant reduction in medication errors (a 45% decrease). Staff reported increased confidence in medication administration and reduced stress related to medication safety. Data analysis showed a marked decrease in near misses, highlighting the system's effectiveness in preventing potential errors. Furthermore, the time saved on manual verification freed up nurses to focus on other aspects of patient care.
Challenges: Initial resistance from some staff due to the learning curve associated with new technology was observed. However, this was effectively addressed through comprehensive training and ongoing support. Minor technical glitches were also encountered, but these were resolved promptly through the vendor's support team.
Initiative 2: Enhancing Fall Prevention Strategies
Problem: Falls among patients presented a significant safety concern at Nurses' Touch. Analysis revealed contributing factors such as inadequate risk assessments, inconsistent use of fall prevention protocols, and a lack of proactive interventions.
Solution: A multi-faceted approach was adopted, including:
- Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Implementation of a standardized, evidence-based fall risk assessment tool for all patients upon admission, reassessed regularly.
- Individualized Care Plans: Development of personalized fall prevention plans based on individual risk factors, incorporating strategies such as bed alarms, assistive devices, and environmental modifications.
- Staff Education: Enhanced staff education on fall prevention strategies, including identifying risk factors, implementing preventative measures, and responding effectively to falls.
- Environmental Modifications: Review and improvements to the unit's physical environment to minimize fall risks, such as improved lighting, removal of obstacles, and provision of easy-access call bells.
- Regular Audits: Regular audits to assess compliance with fall prevention protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Results: The implemented strategies led to a 30% reduction in patient falls. Staff reported improved awareness of fall risk factors and enhanced confidence in their ability to prevent falls. Data showed a significant decrease in fall-related injuries, contributing to improved patient safety and satisfaction.
Challenges: Maintaining consistent adherence to fall prevention protocols across all staff members required ongoing reinforcement and retraining. Integrating fall prevention strategies into busy clinical workflows proved challenging, necessitating careful planning and resource allocation.
Initiative 3: Improving Patient Satisfaction Through Enhanced Communication
Problem: Patient satisfaction surveys revealed consistent feedback indicating dissatisfaction with communication from the nursing staff. This included issues such as unclear explanations of treatments, lack of responsiveness to patient concerns, and insufficient involvement of patients in their care planning.
Solution: The unit focused on several communication strategies:
- Communication Training: Implementation of comprehensive communication training for all nursing staff, emphasizing active listening, empathy, clear and concise communication, and patient-centered approaches.
- Structured Communication Tools: Introduction of standardized communication tools such as SBAR (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) to ensure efficient and effective communication among healthcare professionals.
- Patient-Centered Rounds: Implementation of patient-centered rounds, where nurses involve patients in their care planning and openly discuss treatment plans, answering questions and addressing concerns.
- Regular Feedback Mechanisms: Establishment of regular feedback mechanisms, including patient surveys and focus groups, to continuously monitor and improve communication practices.
Results: Post-implementation, patient satisfaction scores related to communication showed a 20% improvement. Patients reported feeling more informed, involved, and respected. Staff reported enhanced confidence in their communication skills and a stronger sense of connection with patients.
Challenges: Changing deeply ingrained communication habits required persistent effort and reinforcement. Balancing the time required for enhanced communication with other clinical demands presented a logistical challenge.
Initiative 4: Optimizing Workflow Efficiency to Reduce Nurse Burnout
Problem: High workloads and inefficient workflows contributed to significant nurse burnout at Nurses' Touch. This manifested as increased stress, absenteeism, and high turnover rates.
Solution: A systematic approach was taken to optimize workflow efficiency:
- Workflow Mapping: Detailed mapping of existing workflows to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Emphasis on teamwork and collaboration to share workload and promote mutual support among staff.
- Technology Optimization: Evaluation and optimization of technology to streamline tasks, such as using electronic medication administration records (eMAR) and computerized physician order entry (CPOE).
- Delegation and Task Prioritization: Training on effective delegation and task prioritization to manage workloads more efficiently.
- Staff Well-being Initiatives: Implementation of initiatives to promote staff well-being, including stress management programs, access to employee assistance programs (EAP), and opportunities for professional development.
Results: The implementation of workflow improvements resulted in a 15% reduction in nurse burnout scores, measured through standardized surveys. Staff reported feeling less stressed, more supported, and more engaged in their work. Absenteeism and turnover rates decreased significantly.
Challenges: Overcoming ingrained habits and resistance to change required careful planning and ongoing support. Securing resources for technology upgrades and staff training presented some budgetary constraints.
Conclusion: The Power of Collective Action in Quality Improvement
The case study of Nurses' Touch demonstrates the power of collaborative, data-driven quality improvement initiatives in transforming healthcare. By focusing on specific areas of concern, implementing evidence-based strategies, and actively engaging staff at all levels, Nurses' Touch achieved significant improvements in patient safety, staff satisfaction, and overall quality of care. These successes highlight the crucial role nurses play as leaders in quality improvement, advocating for change and driving positive outcomes for both patients and colleagues. The enduring legacy of these initiatives lies not just in the measurable improvements, but in the cultivation of a culture of continuous learning, teamwork, and a relentless pursuit of excellence in patient care. The consistent application of the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle throughout each initiative underscores the commitment to iterative improvement and adaptation based on real-world data and feedback. Finally, the emphasis on addressing staff well-being, reducing burnout, and fostering a supportive work environment demonstrates a holistic approach to quality improvement that recognizes the crucial link between staff morale and the quality of care delivered. This holistic approach is sustainable and ultimately leads to a more effective and resilient healthcare environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
13 4 Sine And Cosine Graphs Worksheet
Apr 06, 2025
-
Jeremy Has Parkinsons Disease A Progressive
Apr 06, 2025
-
In A Longitudinal Study That Will Follow Children From Kindergarten
Apr 06, 2025
-
Canvas Resposible Conduct Of Research Jhu
Apr 06, 2025
-
Which Statement About Contemporary Mental Health Nursing Practice Is Accurate
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Nurses Touch The Leader Case 4 Quality Improvement . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
