Nursing Diagnosis For Jaundice In Newborn
Onlines
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
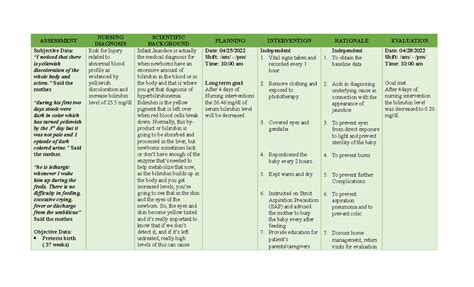
Table of Contents
Nursing Diagnoses for Jaundice in the Newborn: A Comprehensive Guide
Jaundice, characterized by yellow discoloration of the skin and sclera, is a common condition in newborns. While often benign and resolving spontaneously, it can signify underlying pathological conditions requiring prompt medical intervention. Accurate assessment and timely nursing diagnoses are crucial for effective management and improved neonatal outcomes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of nursing diagnoses associated with jaundice in newborns, encompassing physiological, psychological, and social considerations.
Understanding Neonatal Jaundice
Before delving into specific nursing diagnoses, it's crucial to understand the pathophysiology of neonatal jaundice. Jaundice occurs due to an elevated level of bilirubin, a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown. The liver plays a pivotal role in bilirubin conjugation and excretion. Immaturity of the hepatic system in newborns often leads to inefficient bilirubin processing, resulting in hyperbilirubinemia and jaundice.
Several factors can contribute to neonatal jaundice:
-
Physiological Jaundice: The most common type, it usually appears after the first 24 hours of life and resolves within 2 weeks. It's attributed to the immature hepatic system and increased bilirubin production.
-
Pathological Jaundice: This type appears within the first 24 hours of life or persists beyond 2 weeks. It suggests underlying conditions, such as hemolytic disease, infections, metabolic disorders, or biliary atresia.
-
Breastfeeding Jaundice: This type is associated with inadequate breastfeeding and subsequent dehydration, leading to increased bilirubin levels.
-
Breast Milk Jaundice: This type is linked to components in breast milk that interfere with bilirubin metabolism. It usually appears after the first week of life and can persist for several weeks.
Key Nursing Diagnoses for Neonatal Jaundice
Based on the assessment of the neonate's condition, several nursing diagnoses may be relevant. These diagnoses guide the development of an individualized care plan aimed at minimizing complications and promoting optimal outcomes.
1. Risk for Ineffective Thermoregulation
Newborns with jaundice, particularly those requiring phototherapy, are at increased risk of hypothermia. Phototherapy lamps generate heat, but their proximity can also lead to heat loss through radiation if not properly managed. Dehydration associated with jaundice further exacerbates this risk.
Nursing Interventions:
- Maintaining Skin-to-Skin Contact: Encourages thermoregulation and promotes bonding.
- Monitoring Temperature: Frequent monitoring of axillary or rectal temperature is crucial.
- Using Warm Blankets and Incubators: Maintaining a neutral thermal environment.
- Adjusting Phototherapy Lamps: Optimizing distance and intensity to minimize heat loss.
- Providing Adequate Hydration: Preventing dehydration, which exacerbates thermoregulation challenges.
2. Risk for Fluid Volume Deficit
Dehydration is a significant concern in newborns with jaundice, particularly those who are breastfeeding poorly or experiencing excessive bilirubin excretion. Fluid loss through increased stool frequency and potential vomiting can further contribute to dehydration.
Nursing Interventions:
- Monitoring Intake and Output: Closely monitoring fluid intake and output, including diapers.
- Encouraging Frequent Feedings: Promoting adequate hydration through breastfeeding or formula feeding.
- Administering Intravenous Fluids: If dehydration is severe, IV fluids may be necessary.
- Assessing for Signs of Dehydration: Monitoring for sunken fontanelles, decreased skin turgor, and dry mucous membranes.
3. Impaired Skin Integrity
Phototherapy, a common treatment for neonatal jaundice, can lead to skin irritation and dryness. The intense light can damage the skin, causing peeling, rash, and increased sensitivity to sunlight.
Nursing Interventions:
- Protecting Skin from Light: Covering areas not directly exposed to phototherapy lamps.
- Moisturizing the Skin: Applying a hypoallergenic moisturizing lotion to prevent dryness.
- Monitoring Skin for Irritation: Regularly assessing the skin for signs of damage, rash, or inflammation.
- Minimizing Exposure Time: Balancing therapeutic effectiveness with skin protection.
4. Deficient Knowledge (regarding jaundice and its management)
Parents often experience anxiety and fear when their newborn is diagnosed with jaundice. They may lack understanding of the condition, its causes, treatment, and long-term implications. This lack of knowledge can impede their ability to provide optimal care.
Nursing Interventions:
- Providing Education: Offering comprehensive information about jaundice, its causes, treatment options, and prognosis.
- Addressing Parental Concerns: Creating a safe space for parents to express their fears and anxieties.
- Demonstrating Care Procedures: Showing parents how to manage phototherapy, monitor the infant’s condition, and recognize signs of complications.
- Providing Written Materials: Distributing pamphlets and brochures with clear explanations.
- Referring to Support Groups: Connecting parents with other families facing similar challenges.
5. Parental Anxiety Related to Newborn's Condition
Jaundice can be a significant source of stress and anxiety for parents. The uncertainty surrounding the diagnosis, the need for interventions such as phototherapy, and concerns about long-term health outcomes can lead to emotional distress.
Nursing Interventions:
- Providing Emotional Support: Offering empathy and understanding to alleviate parental anxieties.
- Encouraging Open Communication: Fostering a trusting relationship where parents feel comfortable expressing their concerns.
- Collaborating with the Healthcare Team: Working with physicians, social workers, and other professionals to provide holistic support.
- Referring to Mental Health Services: If anxiety is severe, referring parents to mental health professionals.
6. Ineffective Breastfeeding
Some newborns experience jaundice due to inadequate breastfeeding, leading to dehydration and increased bilirubin levels. Conversely, breast milk jaundice can pose challenges to breastfeeding management.
Nursing Interventions:
- Assessing Breastfeeding Techniques: Evaluating breastfeeding latch, frequency, and effectiveness.
- Providing Lactation Support: Guiding parents on optimal breastfeeding practices, latch techniques, and positioning.
- Supplementation: If necessary, supplementing with formula to ensure adequate fluid intake.
- Monitoring Weight Gain: Tracking the newborn’s weight to assess nutritional adequacy.
7. Risk for Infection
In cases of pathological jaundice, the underlying condition may be an infection. Newborns with jaundice are more susceptible to infections, potentially worsening their prognosis.
Nursing Interventions:
- Monitoring Vital Signs: Regularly assessing temperature, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
- Assessing for Signs of Infection: Observing for lethargy, irritability, poor feeding, and other indicators of infection.
- Administering Antibiotics: If infection is suspected or confirmed.
- Implementing Infection Control Measures: Adhering to strict hand hygiene and infection control protocols.
Assessment and Documentation
Accurate assessment is fundamental to formulating appropriate nursing diagnoses. The assessment should include:
- History: Prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal history, including maternal health, birth complications, and feeding patterns.
- Physical Examination: Assessing skin color, vital signs, hydration status, and neurological function.
- Laboratory Tests: Monitoring bilirubin levels, blood counts, and liver function tests.
- Monitoring Response to Treatment: Observing the effectiveness of phototherapy or other interventions.
Detailed documentation is essential to track the newborn's progress, communicate effectively among the healthcare team, and evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented care plan. Documentation should include:
- Baseline Assessment Data: Initial findings upon admission.
- Nursing Diagnoses: Clearly stated nursing diagnoses with supporting data.
- Planned Interventions: Detailed description of nursing interventions.
- Evaluation of Outcomes: Assessment of the effectiveness of interventions in achieving desired outcomes.
Conclusion
Jaundice in newborns necessitates meticulous assessment, accurate nursing diagnoses, and individualized care plans. By focusing on the physical, psychological, and social needs of the infant and parents, nurses play a crucial role in preventing complications and ensuring positive outcomes. Understanding the various nursing diagnoses related to neonatal jaundice allows for the development of targeted interventions that promote optimal health and well-being for the newborn and the family. Continuous monitoring, effective communication, and family-centered care are paramount in managing this common yet potentially serious condition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unidad 5 Leccion 2 Answer Key
Apr 02, 2025
-
Romeo And Juliet Character Map Answers
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Type Of Shock Occurs From An Antigen Antibody Response
Apr 02, 2025
-
Modules 6 8 Wan Concepts Exam
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Technology Is Shown In The Diagram
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Nursing Diagnosis For Jaundice In Newborn . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
