Occupational Prestige Means That Jobs Are
Onlines
Apr 02, 2025 · 6 min read
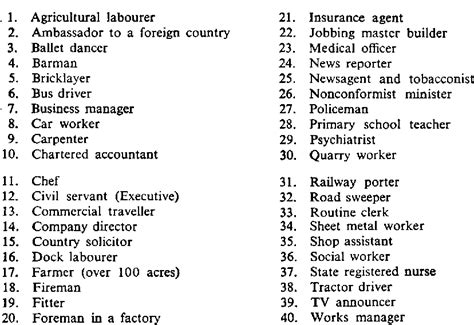
Table of Contents
Occupational Prestige: What It Means and Why It Matters
Occupational prestige is a complex social phenomenon reflecting societal views on the value and importance of different jobs. It's not simply about salary, although income often correlates with prestige. Instead, it's a multifaceted assessment encompassing factors like education level required, skill complexity, autonomy, and perceived social contribution. Understanding occupational prestige means understanding how society values work, shapes career aspirations, and influences social stratification.
What Does Occupational Prestige Mean?
Occupational prestige refers to the social honor and respect accorded to specific jobs or professions within a given society. This ranking is subjective and varies across cultures, time periods, and even individual perspectives. However, certain professions consistently garner high prestige across diverse societies, while others remain lower in the hierarchy.
Key factors influencing occupational prestige include:
- Education and Training: Occupations requiring extensive education and specialized training, such as medicine or law, tend to hold higher prestige.
- Skill Complexity and Autonomy: Jobs demanding a high level of skill, expertise, and independent decision-making usually rank higher. Think of surgeons, engineers, or research scientists.
- Income and Wealth: While not the sole determinant, higher salaries often correlate with greater prestige, suggesting a societal valuation of financial success within a career.
- Social Contribution: Professions perceived as contributing significantly to society, such as teachers, nurses, and firefighters, often garner considerable respect.
- Working Conditions: The physical and emotional demands of a job also play a role. Dangerous or stressful jobs might receive less prestige than those perceived as safer and less demanding.
- Historical and Cultural Context: The prestige associated with specific occupations can change over time due to societal shifts, technological advancements, and evolving cultural values.
Measuring Occupational Prestige
Sociologists and researchers utilize various methods to measure occupational prestige. One common approach involves conducting surveys where respondents rate the prestige of different occupations on a scale. These surveys often reveal consistent patterns across different demographics, though some variations exist depending on factors like age, education, and social class. Analyzing these survey results generates an occupational prestige scale, providing a ranked list of jobs from highest to lowest prestige.
These scales are crucial for research in several areas, including social stratification, social mobility, and the study of inequality. They highlight how societal perceptions of work influence individual choices, career aspirations, and the overall distribution of resources and opportunities.
The Impact of Occupational Prestige
The impact of occupational prestige extends beyond mere societal ranking. It significantly influences various aspects of individuals' lives, including:
- Self-Esteem and Identity: Individuals often derive a sense of self-worth and identity from their profession. Working in a high-prestige occupation can boost self-esteem and foster a strong sense of professional accomplishment.
- Social Status and Relationships: Occupational prestige influences social networks and relationships. Individuals in high-prestige professions often associate with others in similar positions, leading to social circles with shared values and opportunities.
- Marriage and Family: Occupational prestige can play a role in mate selection and family dynamics. Individuals may seek partners with similar or complementary professional standing.
- Income and Economic Well-Being: While not directly equivalent, occupational prestige often correlates with higher salaries, benefits, and career advancement opportunities.
- Access to Resources and Opportunities: High-prestige occupations often provide access to networks, resources, and opportunities that are less readily available to those in lower-prestige jobs.
- Political Influence and Social Power: Individuals in high-prestige professions often wield more social and political influence, shaping public policies and societal norms.
Occupational Prestige and Social Stratification
Occupational prestige is a fundamental element of social stratification – the hierarchical arrangement of individuals and groups based on social factors like wealth, power, and prestige. Jobs with higher prestige tend to cluster at the top of the social hierarchy, while those with lower prestige occupy the lower rungs. This stratification has significant implications for social mobility, equality, and the overall structure of society.
Social Mobility and Occupational Prestige
Social mobility, the ability to move up or down the social hierarchy, is closely tied to occupational prestige. Individuals in low-prestige occupations often face significant barriers to upward mobility, while those in high-prestige positions often have greater opportunities for advancement. Education, skills, and networking all play crucial roles, but the starting point determined by initial occupational prestige can significantly shape the trajectory of social mobility.
Inequality and Occupational Prestige
The disparities in occupational prestige contribute to broader social inequalities. Differences in income, wealth, power, and access to resources are often reflected in the hierarchical ranking of occupations. Addressing this inequality requires acknowledging the role of occupational prestige and working towards a more equitable system that values contributions across a broader range of professions.
Changing Perceptions of Occupational Prestige
Occupational prestige is not static; it evolves over time, reflecting societal shifts, technological advancements, and changes in values. For instance, the prestige associated with certain manual labor professions has declined in some societies, while the prestige of technology-related jobs has risen significantly.
The Impact of Technology
Technological advancements have reshaped the occupational landscape, leading to the emergence of new professions and the decline of others. The demand for skilled workers in technology-related fields has driven up their prestige, while the automation of certain tasks has diminished the perceived value of some traditional occupations.
Shifting Social Values
Changing social values also impact occupational prestige. Increased emphasis on social responsibility and environmental sustainability has led to a rise in prestige for professions associated with these values. This reflects a broader societal shift towards valuing contributions that benefit society as a whole.
Occupational Prestige and Career Choices
Understanding occupational prestige is crucial for making informed career choices. Aspiring professionals consider not only salary and benefits but also the social standing and respect associated with different career paths. This involves a complex interplay between personal values, aspirations, and societal expectations.
The Role of Education and Training
The pursuit of higher education often reflects a desire to access high-prestige occupations. Investing in advanced education and training can enhance career prospects and lead to positions with greater prestige and social standing. However, access to education is not always equal, creating inequalities in the pursuit of high-prestige careers.
The Importance of Networking
Networking plays a significant role in career advancement, especially within high-prestige professions. Building relationships with individuals in desired fields can provide access to opportunities, mentorship, and support in achieving career goals. This underscores the social aspect of occupational prestige and the importance of leveraging social networks for career success.
Conclusion: Occupational Prestige in a Changing World
Occupational prestige remains a significant factor in shaping individual lives, social structures, and societal values. While it’s not solely about income, its impact on self-esteem, social status, and access to opportunities is undeniable. Understanding the multifaceted nature of occupational prestige, its historical and cultural contexts, and its influence on social stratification is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern job market and promoting a more equitable and just society. As societies evolve and technology continues to transform the work landscape, the perceptions and rankings of occupational prestige will continue to shift, demanding ongoing analysis and critical reflection on the values we place on different forms of work. The future of work necessitates a deeper understanding of the interplay between prestige, social mobility, and the creation of a more inclusive and rewarding work environment for everyone.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Theme Of The Novel Oliver Twist
Apr 03, 2025
-
Monomers And Polymers Worksheet Answer Key
Apr 03, 2025
-
Select All Of The Following That Describe Meiosis
Apr 03, 2025
-
Dosage Calculation Rn Pediatric Nursing Online Practice Assessment 3 2
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Hours Did Miriam Stop To Rest
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Occupational Prestige Means That Jobs Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
