Population Growth And Ecological Data Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 11, 2025 · 6 min read
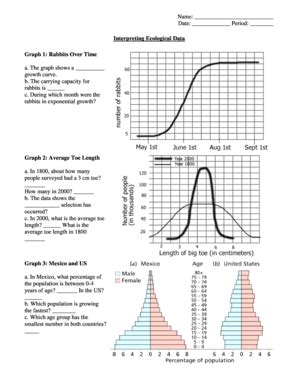
Table of Contents
Population Growth and Ecological Data: Unlocking the Answers
The relationship between population growth and ecological data is complex and multifaceted. Understanding this interplay is crucial for effective environmental management and sustainable development. This article delves into the key aspects of this relationship, exploring the data, the challenges, and the implications for our future.
Understanding Population Dynamics
Population growth, at its core, refers to the increase in the number of individuals within a specific population over time. This growth is influenced by several factors, including birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns. Analyzing these factors, using demographic data such as age pyramids and population density maps, provides vital insights into the current and future population trajectory.
Key Demographic Indicators:
- Birth Rate: The number of live births per 1,000 individuals in a population per year. High birth rates contribute significantly to population growth.
- Death Rate: The number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a population per year. Low death rates, often attributed to advancements in healthcare and sanitation, contribute to population growth.
- Migration: The movement of individuals into (immigration) or out of (emigration) a population. Net migration (immigration minus emigration) influences overall population size.
- Life Expectancy: The average number of years a newborn is expected to live. Increases in life expectancy indicate improved living conditions and healthcare.
- Age Structure: The proportion of individuals in different age groups within a population. Age pyramids visually represent this structure, revealing potential future population trends. A pyramid with a wide base indicates a young population with high potential for future growth.
Ecological Data and its Interplay with Population
Ecological data encompasses a vast array of information about the environment and the living organisms within it. This data is crucial for understanding the impact of population growth on ecosystems and for implementing effective conservation strategies. Key areas of ecological data relevant to population growth include:
1. Resource Consumption and Depletion:
A rapidly growing population places immense pressure on natural resources. This includes water, food, energy, and raw materials. Analyzing data on resource consumption per capita (per person) and resource availability helps determine the sustainability of current consumption patterns. Ecological footprint analysis, which calculates the amount of land and resources required to support a population's lifestyle, provides a valuable metric for understanding resource demand. Data on deforestation rates, water scarcity indices, and declining fish stocks directly reflect the pressures of a growing population.
2. Biodiversity Loss:
Population growth often leads to habitat destruction and fragmentation, contributing to a significant loss of biodiversity. Ecological data, such as species richness indices, species abundance data, and extinction rates, reveals the extent of this loss. The growing human footprint encroaches upon natural habitats, forcing species into smaller, more fragmented areas, reducing their ability to thrive and leading to potential population declines and even extinctions. Monitoring these changes through ecological surveys and biodiversity assessments is critical.
3. Pollution and Waste Generation:
A larger population inevitably generates more waste and pollution. Data on air and water quality, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation rates illustrates the environmental consequences of population growth. Increased industrial activity and transportation associated with population growth exacerbate pollution levels, impacting human health and ecosystem stability. Analyzing pollution data allows for the identification of pollution hotspots and the development of mitigation strategies.
4. Climate Change Impacts:
Population growth contributes significantly to climate change through increased greenhouse gas emissions. Ecological data on rising global temperatures, melting glaciers, sea-level rise, and changes in precipitation patterns highlights the impact of human activities on the planet's climate. Understanding the link between population growth, energy consumption, and climate change is crucial for implementing effective climate mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Analyzing Ecological Data: Methods and Challenges
Analyzing ecological data to understand its relationship with population growth involves several methods:
Statistical Analysis:
Statistical techniques, including regression analysis and correlation analysis, are used to establish relationships between population size and ecological indicators. For example, correlation analysis can reveal the link between population density and deforestation rates.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS):
GIS technology allows for the spatial analysis of ecological data, overlaying population density maps with maps of resource availability or pollution levels to visualize the interplay between human populations and environmental resources.
Modeling:
Population and ecological models, including agent-based models and system dynamics models, are used to simulate the future impacts of population growth on various ecological aspects. These models allow for the exploration of different scenarios and the evaluation of potential mitigation strategies.
Challenges in Data Analysis:
Despite the availability of sophisticated methods, several challenges hinder accurate analysis:
- Data Scarcity: Comprehensive and reliable ecological data is not available for many regions, particularly in developing countries.
- Data Inconsistency: Data collection methods and standards may vary across regions, making comparisons difficult.
- Complex Interactions: The interactions between population growth and ecological factors are complex and not always easily quantifiable.
- Predictive Uncertainty: Forecasting future population trends and their ecological impacts involves inherent uncertainties.
Implications and Solutions
Understanding the relationship between population growth and ecological data has significant implications for environmental policy and sustainable development. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach:
Sustainable Resource Management:
Implementing sustainable resource management practices, including water conservation, efficient energy use, and sustainable agriculture, is crucial to mitigate the environmental impact of population growth.
Biodiversity Conservation:
Protecting and restoring biodiversity through habitat conservation and species protection programs is essential to maintaining ecosystem health and resilience.
Pollution Control:
Reducing pollution through stricter emission standards, improved waste management, and promoting cleaner technologies is necessary to minimize the environmental consequences of a growing population.
Climate Change Mitigation:
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency improvements, and sustainable transportation systems is vital to combat climate change.
Family Planning and Education:
Promoting access to family planning services and education about responsible parenthood can help manage population growth in a sustainable way.
Economic Development:
Sustainable economic development that creates opportunities for education, employment, and improved living standards can contribute to lower fertility rates. This approach should prioritize equitable development that minimizes environmental impact.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Sustainability
The intricate relationship between population growth and ecological data demands a comprehensive and nuanced understanding. While population growth poses significant challenges to environmental sustainability, proactive measures, informed by robust data analysis and effective policy implementation, can pave the way for a future where human needs are met without compromising the integrity of the planet's ecosystems. A concerted global effort involving governments, organizations, and individuals is essential to navigate this complex issue and build a sustainable future for all. The continued improvement of data collection and analysis techniques, combined with the development and implementation of innovative solutions, will be critical to mitigating the potential negative consequences of population growth and safeguarding the planet's resources for generations to come. This requires a shift towards sustainable practices across all sectors, coupled with a commitment to addressing the underlying social and economic factors that influence population growth and resource consumption patterns. Only through such a holistic and collaborative approach can we ensure a sustainable and thriving future for both humanity and the environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Activity 3 1 1 Sizing Up The Universe Answers
Mar 11, 2025
-
Brave New World Chapter 4 Summary
Mar 11, 2025
-
Game Of Thrones Book Story Summary
Mar 11, 2025
-
A Partition Between A Users Computer
Mar 11, 2025
-
What Theme Is Best Revealed By This Conflict
Mar 11, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Population Growth And Ecological Data Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
