Practice Haploid V. Diploid Answer Key
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
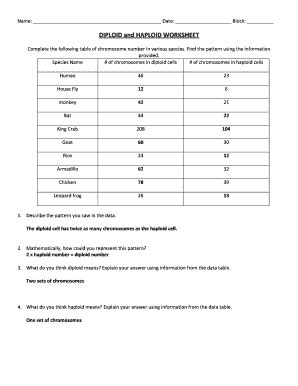
Table of Contents
Practice Haploid vs. Diploid: Answer Key and Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the difference between haploid and diploid cells is fundamental to grasping core concepts in biology, particularly genetics and cell reproduction. This comprehensive guide provides an answer key to common practice questions on haploid versus diploid cells, alongside a detailed explanation of the concepts to solidify your understanding. We'll explore the definitions, examples, processes involved, and the significance of these chromosomal states in various organisms.
What are Haploid and Diploid Cells?
Before diving into the practice questions, let's establish a firm understanding of the terms:
-
Diploid (2n): A diploid cell contains two complete sets of chromosomes. These sets are inherited from each parent, resulting in homologous pairs of chromosomes. In humans, the diploid number is 46 (23 pairs). Most somatic (body) cells are diploid.
-
Haploid (n): A haploid cell contains only one complete set of chromosomes. These cells are produced through meiosis, a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. In humans, the haploid number is 23. Gametes (sex cells – sperm and egg) are haploid.
Key Differences between Haploid and Diploid Cells
| Feature | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosome Number | Two complete sets of chromosomes | One complete set of chromosomes |
| Cell Type | Somatic cells (e.g., skin, muscle cells) | Gametes (sperm and egg cells) |
| Formation | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Function | Growth, repair, and maintenance of body | Sexual reproduction |
| Genetic Information | Two copies of each gene | One copy of each gene |
Practice Questions: Haploid vs. Diploid
Let's test your understanding with some practice questions. Remember to consider the key differences outlined above.
Question 1: Human somatic cells are diploid. What is the diploid number of chromosomes in a human somatic cell?
Answer: 46
Question 2: Human gametes (sperm and egg cells) are haploid. What is the haploid number of chromosomes in a human gamete?
Answer: 23
Question 3: During fertilization, a haploid sperm cell fuses with a haploid egg cell. What is the ploidy of the resulting zygote?
Answer: Diploid (2n) – because the zygote receives one set of chromosomes from each gamete, resulting in two complete sets.
Question 4: Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. What is the ploidy of the cells produced by meiosis?
Answer: Haploid (n)
Question 5: Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells. If the parent cell is diploid, what is the ploidy of the daughter cells?
Answer: Diploid (2n)
Question 6: A plant species has a diploid number of 12 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be found in its pollen grains (male gametes)?
Answer: 6 (n = 12/2)
Question 7: In a certain organism, the haploid number is 10. What is the diploid number?
Answer: 20 (2n = 2 * 10)
Question 8: Explain the importance of meiosis in maintaining the chromosome number across generations in sexually reproducing organisms.
Answer: Meiosis is crucial because it halves the chromosome number in gametes. When two haploid gametes fuse during fertilization, the diploid chromosome number is restored in the zygote, preventing a doubling of chromosomes with each generation.
Question 9: Differentiate between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids. How do these structures relate to haploid and diploid cells?
Answer: Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent, that carry genes for the same traits but may have different alleles (versions of the genes). Sister chromatids are identical copies of a single chromosome that are joined together until they separate during cell division. Diploid cells possess homologous chromosomes, while haploid cells have only one member of each homologous pair.
Question 10: A cell with 36 chromosomes undergoes meiosis. How many chromosomes will each resulting gamete have?
Answer: 18 (36/2)
Advanced Concepts and Applications
Beyond the basics, understanding haploid and diploid states is crucial for comprehending more advanced concepts:
-
Polyploidy: This refers to organisms having more than two complete sets of chromosomes (e.g., triploid – 3n, tetraploid – 4n). Polyploidy is common in plants and can lead to increased size and vigor.
-
Aneuploidy: This condition involves an abnormal number of chromosomes (e.g., trisomy 21, Down syndrome). Aneuploidy can arise from errors during meiosis or mitosis.
-
Genetic Diversity: Meiosis and the production of haploid gametes are essential for generating genetic diversity through the process of recombination (crossing over) and independent assortment of chromosomes. This diversity is crucial for adaptation and evolution.
-
Sex Determination: In many organisms, sex is determined by the presence or absence of certain chromosomes (e.g., the X and Y chromosomes in humans). The haploid nature of gametes plays a significant role in the inheritance of sex chromosomes.
Real-World Applications and Significance
The concepts of haploid and diploid cells are not merely theoretical; they have profound implications in various fields:
-
Agriculture: Understanding polyploidy allows scientists to develop new crop varieties with desirable traits like increased yield and disease resistance.
-
Medicine: Knowledge of aneuploidy is crucial for diagnosing genetic disorders and developing treatment strategies. Studies of haploid cells are valuable in understanding cell processes and developing new therapies.
-
Evolutionary Biology: Analyzing chromosome numbers and ploidy levels provides insights into evolutionary relationships and the mechanisms driving speciation.
Conclusion
Mastering the distinction between haploid and diploid cells is essential for a thorough grasp of fundamental biological principles. This comprehensive guide, including the answer key and detailed explanations, serves as a valuable resource for students and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of this critical concept. The applications of these principles extend far beyond the classroom, highlighting the importance of this knowledge in diverse fields. Through continued study and application, you can confidently navigate the intricacies of cellular biology and genetics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Mystery Of Edwin Drood Sparknotes
Mar 04, 2025
-
Experiment 8 The Solubility Products Of Slightly Soluble Metal Hydroxides
Mar 04, 2025
-
Neuroscience Evidence Shows That Attention Works By
Mar 04, 2025
-
Practice Test Personal Finance Chapter 4
Mar 04, 2025
-
Summary Of The Cost Of Survival
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Practice Haploid V. Diploid Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
