Procedure 1 Blood Type Matching Practice
Onlines
Mar 04, 2025 · 6 min read
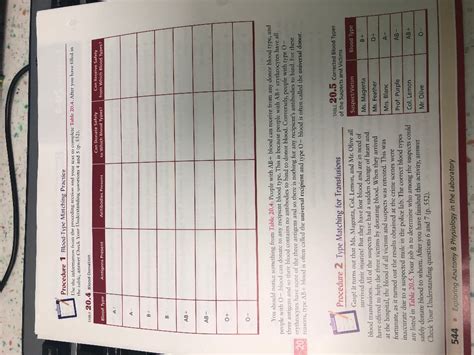
Table of Contents
Procedure 1: Blood Type Matching Practice: A Comprehensive Guide
Blood type matching is a critical procedure in healthcare, ensuring the safe transfusion of blood products. This detailed guide outlines the process, emphasizing safety and accuracy. We'll cover the theoretical basis, step-by-step practical procedures, potential pitfalls, and troubleshooting techniques. Understanding this process is fundamental for medical professionals and anyone interested in the intricacies of blood transfusion safety.
Understanding Blood Groups and the ABO System
Before delving into the practical aspects, let's review the fundamentals of blood typing. The most important system is the ABO system, classifying blood into four main groups: A, B, AB, and O. These classifications are based on the presence or absence of specific antigens (A and B antigens) on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) and the corresponding antibodies (anti-A and anti-B antibodies) present in the plasma.
- Blood Type A: Contains A antigens on RBCs and anti-B antibodies in plasma.
- Blood Type B: Contains B antigens on RBCs and anti-A antibodies in plasma.
- Blood Type AB: Contains both A and B antigens on RBCs and neither anti-A nor anti-B antibodies in plasma. This is considered the universal recipient.
- Blood Type O: Contains neither A nor B antigens on RBCs but has both anti-A and anti-B antibodies in plasma. This is considered the universal donor.
Another crucial system is the Rh factor, referring to the presence or absence of the D antigen on RBCs. Individuals with the D antigen are Rh-positive (Rh+), while those without are Rh-negative (Rh-). Rh incompatibility can lead to serious complications, particularly during pregnancy and subsequent transfusions.
Materials Required for Blood Type Matching
Performing blood type matching requires specific materials to ensure accuracy and safety. Here's a list of essential equipment:
- Blood samples: Freshly drawn blood samples from both the donor and recipient are crucial. The samples should be properly labeled and identified to avoid confusion.
- Anti-A serum: A reagent containing antibodies specific to A antigens.
- Anti-B serum: A reagent containing antibodies specific to B antigens.
- Anti-D serum (Rh factor): A reagent containing antibodies specific to the D antigen (Rh factor).
- Microscope slides or microplates: Clean, non-reactive surfaces for conducting the tests.
- Disposable pipettes or micro-pipettes: For accurate and precise transfer of reagents and blood samples.
- Positive and negative controls: To validate the accuracy of the reagents and the testing procedure.
- Applicator sticks or wooden sticks: For mixing the blood and antisera.
- Timer: To accurately time the reactions.
Step-by-Step Procedure: ABO and Rh Typing
The procedure involves a series of steps to determine both the ABO and Rh blood groups. Accuracy and adherence to proper technique are paramount to avoid errors.
Step 1: Preparation
- Clearly label the slides or microplate wells with the patient's identification number and blood type.
- Add a drop of blood sample to each designated area on the slide or microplate. This should be done using a clean pipette or micro-pipette.
Step 2: Adding Antisera
- Add a drop of anti-A serum to one well next to the blood sample.
- Add a drop of anti-B serum to another well next to the blood sample.
- Add a drop of anti-D serum (Rh factor) to a third well next to the blood sample.
Step 3: Mixing
- Use a separate clean applicator stick for each serum to gently mix the blood and serum. Avoid cross-contamination. Ensure thorough mixing.
Step 4: Incubation
- Allow the mixtures to incubate for approximately 1-2 minutes at room temperature. The exact incubation time will depend on the specific reagents used; always refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
Step 5: Observation and Interpretation
-
Carefully observe the reactions under a microscope or with the naked eye. Agglutination (clumping of red blood cells) indicates a positive reaction.
-
Positive Reaction: Agglutination signifies the presence of the corresponding antigen. For example, agglutination with anti-A serum indicates the presence of A antigens (blood type A).
-
Negative Reaction: The absence of agglutination suggests the absence of the corresponding antigen.
Step 6: Recording Results
- Meticulously record the results. Note the presence or absence of agglutination for each serum. This data determines the blood type.
Step 7: Cross-matching (Compatibility Testing)
After determining the ABO and Rh groups, cross-matching (compatibility testing) is performed to further ensure compatibility before transfusion. This involves mixing the recipient's serum with the donor's RBCs and vice versa. Any significant agglutination indicates incompatibility and prevents transfusion. Major crossmatch is testing the recipient’s serum with donor RBCs. Minor crossmatch is testing recipient RBCs with donor serum.
Potential Pitfalls and Troubleshooting
Several factors can influence the accuracy of blood typing. Recognizing these pitfalls and employing troubleshooting techniques is vital:
- Improper mixing: Insufficient mixing can lead to false-negative results. Ensure thorough mixing of the blood and serum.
- Contamination: Cross-contamination between reagents or samples can result in erroneous readings. Use separate applicator sticks and maintain cleanliness throughout the procedure.
- Incorrect incubation time: Deviations from the recommended incubation time can affect the reaction. Strictly adhere to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Expired reagents: Using expired reagents compromises the accuracy and reliability of the test. Always check expiration dates before use.
- Autoagglutination: Spontaneous agglutination of RBCs can occur in some individuals. This can be identified through the use of controls.
- Weak reactions: Weak or delayed reactions may be difficult to interpret. In such cases, further investigation or repeat testing might be necessary.
- Cold agglutinins: These antibodies react at lower temperatures and can interfere with results. Warming the samples to 37°C can help minimize interference.
Safety Precautions
Blood typing involves handling human samples, requiring strict adherence to safety protocols:
- Universal precautions: Treat all samples as potentially infectious and utilize appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, lab coats, and eye protection.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of all used materials, including contaminated slides, pipettes, and applicator sticks, according to established guidelines.
- Quality control: Regularly check reagents and equipment to maintain accuracy and reliability. Include positive and negative controls in each batch of tests.
Advanced Techniques and Automation
While the manual method described above is fundamental, advanced techniques and automation play an increasingly important role in blood typing. These include:
- Automated blood typing systems: These systems reduce manual handling, minimizing the risk of errors and enhancing efficiency.
- Gel card technology: This technique employs gel columns to separate agglutinated cells from non-agglutinated cells, making interpretation easier and more objective.
- Molecular techniques: These methods analyze DNA to determine blood type, providing a highly accurate and reliable method.
Conclusion
Accurate blood type matching is crucial for safe blood transfusions. Mastering the procedure, understanding potential pitfalls, and adhering to safety protocols are essential for healthcare professionals. The information presented here provides a comprehensive overview of the process, empowering individuals to perform blood typing accurately and safely. Continual training and adherence to updated guidelines ensure patient safety and the successful outcome of blood transfusions. Remember to always consult the manufacturer's instructions for specific reagents and equipment used in the procedure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cell Transport Graphic Organizer Answer Key
Mar 04, 2025
-
Dosage Calculation 3 0 Pediatric Medications Test
Mar 04, 2025
-
Ofy Unit Activity Historical Thinking Skills Pdf Ree
Mar 04, 2025
-
Parable Of The Sower Chapter Summary
Mar 04, 2025
-
The Tale Of Genji Chapter Summary
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Procedure 1 Blood Type Matching Practice . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
