Punnett Square Worksheet 2 Answer Key
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
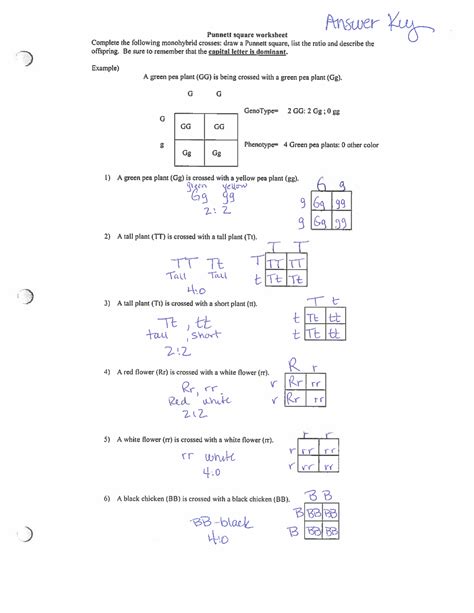
Table of Contents
Punnett Square Worksheet 2: Answers and Deep Dive into Mendelian Genetics
Welcome, future geneticists! This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Punnett squares, providing you with not just the answers to Worksheet 2 (which we'll assume covers a range of Mendelian genetics problems), but also a thorough explanation of the underlying principles. We'll explore monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, explore the concepts of homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, and unpack the nuances of dominant and recessive alleles. By the end, you'll be a Punnett Square pro!
Understanding the Fundamentals: A Quick Genetics Refresher
Before we dive into the answers, let's solidify our understanding of the basic concepts. Mendelian genetics, named after Gregor Mendel, the "father of genetics," forms the foundation of our understanding of heredity. Mendel's work revealed that traits are passed down from parents to offspring through discrete units called genes. Each gene exists in different versions called alleles.
-
Alleles: These are alternative forms of a gene that determine the characteristics of an organism. For example, a gene for flower color might have one allele for purple flowers (let's represent it with "P") and another for white flowers ("p").
-
Genotype: This refers to the genetic makeup of an organism—the combination of alleles it possesses for a particular trait. For the flower color example, an organism could have a PP (homozygous dominant), Pp (heterozygous), or pp (homozygous recessive) genotype.
-
Phenotype: This is the observable physical characteristic of an organism. In our example, PP and Pp genotypes would both result in purple flowers (the dominant phenotype), while the pp genotype would result in white flowers (the recessive phenotype).
-
Homozygous: This term describes an organism with two identical alleles for a trait (e.g., PP or pp).
-
Heterozygous: This term describes an organism with two different alleles for a trait (e.g., Pp).
-
Dominant Allele: This allele masks the expression of the recessive allele when present. In our flower example, "P" is dominant.
-
Recessive Allele: This allele is only expressed when two copies are present (homozygous recessive). In our example, "p" is recessive.
Punnett Squares: Predicting Probabilities
Punnett squares are visual tools used to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring resulting from a cross between two parents. They represent all possible combinations of alleles that can be inherited from the parents. The process involves:
- Determining Parental Genotypes: Identify the genotypes of both parents.
- Setting up the Square: Draw a square and write the alleles of one parent across the top and the alleles of the other parent down the side.
- Filling the Square: Combine the alleles to determine the genotypes of the offspring. Each box represents a possible offspring genotype.
- Analyzing Results: Determine the phenotypic ratios and genotypic ratios.
Sample Punnett Square Worksheet 2 Problems & Solutions
Let's assume your Worksheet 2 includes a variety of problems. We'll work through examples covering different scenarios:
Problem 1: Monohybrid Cross (Dominant/Recessive)
Problem: A homozygous dominant tall pea plant (TT) is crossed with a homozygous recessive short pea plant (tt). What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation?
Solution:
| T | T | |
|---|---|---|
| t | Tt | Tt |
| t | Tt | Tt |
- Genotypic Ratio: 100% Tt (heterozygous)
- Phenotypic Ratio: 100% Tall
Problem 2: Monohybrid Cross (Heterozygous x Heterozygous)
Problem: Two heterozygous tall pea plants (Tt) are crossed. What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation?
Solution:
| T | t | |
|---|---|---|
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | Tt | tt |
- Genotypic Ratio: 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
- Phenotypic Ratio: 3 Tall : 1 Short
Problem 3: Dihybrid Cross
Problem: A pea plant homozygous for round seeds (RR) and yellow seeds (YY) is crossed with a pea plant homozygous for wrinkled seeds (rr) and green seeds (yy). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation, assuming round and yellow are dominant?
Solution:
First, we determine the gametes (sex cells) each parent can produce. The RRYY parent produces RY gametes, and the rryy parent produces ry gametes. The Punnett square becomes:
| RY | RY | RY | RY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ry | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy |
| ry | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy |
| ry | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy |
| ry | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy | RrYy |
- Genotypic Ratio: 100% RrYy
- Phenotypic Ratio: 100% Round, Yellow Seeds
Problem 4: Dihybrid Cross (Heterozygous x Heterozygous)
Problem: Two pea plants heterozygous for both seed shape (Rr) and seed color (Yy) are crossed. What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring?
Solution: This requires a larger Punnett square (4x4):
| RY | Ry | rY | ry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RY | RRYY | RRYy | RrYY | RrYy |
| Ry | RRYy | RRyy | RrYy | Rryy |
| rY | RrYY | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
| ry | RrYy | Rryy | rrYy | rryy |
- Genotypic Ratio: 1 RRYY : 2 RRYy : 1 RRyy : 2 RrYY : 4 RrYy : 2 Rryy : 1 rrYY : 2 rrYy : 1 rryy
- Phenotypic Ratio: 9 Round, Yellow : 3 Round, Green : 3 Wrinkled, Yellow : 1 Wrinkled, Green
Problem 5: Incomplete Dominance
Problem: In snapdragons, red (R) and white (W) flower color show incomplete dominance. A red snapdragon (RR) is crossed with a white snapdragon (WW). What are the phenotypes of the F1 generation?
Solution:
| R | R | |
|---|---|---|
| W | RW | RW |
| W | RW | RW |
The RW genotype results in pink flowers. Therefore, the phenotypic ratio is 100% Pink.
Beyond the Worksheet: Advanced Concepts and Applications
While Worksheet 2 likely focused on basic Mendelian genetics, it's crucial to understand that inheritance patterns are often more complex. Several factors can influence inheritance:
- Multiple Alleles: Some genes have more than two alleles (e.g., human blood type).
- Pleiotropy: One gene can affect multiple phenotypic traits.
- Epistasis: The expression of one gene can be influenced by another gene.
- Polygenic Inheritance: Multiple genes can contribute to a single phenotypic trait (e.g., human height).
- Sex-linked Inheritance: Genes located on sex chromosomes (X and Y) show unique inheritance patterns.
- Environmental Influences: Environmental factors can significantly impact gene expression and phenotype.
Mastering Punnett Squares: Tips and Tricks
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The more Punnett squares you solve, the better you'll understand the concepts and the faster you'll become.
- Organize Your Work: Use clear labels and neatly draw your Punnett squares.
- Understand the Underlying Principles: Don't just memorize the process; understand the biological basis of inheritance.
- Use Online Resources: There are numerous online tools and resources that can help you practice and check your answers.
- Seek Help When Needed: If you're struggling with a particular concept, don't hesitate to seek help from a teacher, tutor, or online community.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Secrets of Heredity
Punnett squares are a fundamental tool in genetics. Mastering them is essential for understanding how traits are inherited and passed down through generations. While Worksheet 2 provided a foundational introduction, remember that the world of genetics is vast and complex. By continuing to explore these concepts, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of life itself. Keep practicing, keep learning, and soon you'll be confidently predicting the genetic outcomes of any cross!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Geoworld Plate Tectonics Lab Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
Hardware Lab Simulation 7 2 Clearing Dns Cache
Apr 04, 2025
-
9 1 Reference Triangles And Reciprocal Trig Functions
Apr 04, 2025
-
Mr Chen Has Heard About A Medical Savings Account
Apr 04, 2025
-
Summary Of How Much Does A Man Need
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Punnett Square Worksheet 2 Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
