Questionable Business Practices According To Antitrust Agencies
Onlines
Apr 07, 2025 · 6 min read
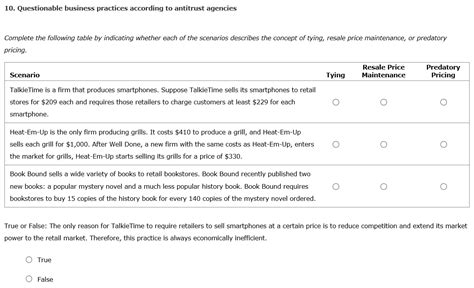
Table of Contents
Questionable Business Practices According to Antitrust Agencies
The pursuit of a competitive marketplace is a cornerstone of a healthy economy. Antitrust laws, also known as competition laws, are designed to prevent anti-competitive practices that stifle innovation, harm consumers, and ultimately undermine economic efficiency. These laws are enforced by antitrust agencies, governmental bodies tasked with investigating and prosecuting businesses engaging in questionable practices. This article delves into various business practices that frequently fall under the scrutiny of antitrust agencies worldwide, exploring the reasoning behind their condemnation and the potential consequences for offending companies.
What Constitutes a Questionable Business Practice?
Antitrust agencies scrutinize a range of business practices, often focusing on those that restrict competition and harm consumers. These practices are not always explicitly illegal; however, their impact on the market and potential to create monopolies or limit consumer choice puts them under the microscope. The specific definition of a "questionable practice" can vary slightly depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances, but several key areas consistently attract attention:
1. Price Fixing and Collusion
Price fixing, whether explicit or tacit, is a serious antitrust violation. This involves competitors agreeing on prices, either directly or indirectly, to eliminate price competition. Examples include:
- Explicit price fixing: Companies openly agree on the price they will charge for a particular product or service.
- Bid rigging: Competitors collude to manipulate bidding processes, ensuring one company wins while others submit artificially inflated bids.
- Market allocation: Competitors divide a market amongst themselves, agreeing not to compete in certain geographic areas or product segments.
Tacit collusion, while more subtle, is equally problematic. This occurs when companies indirectly coordinate their pricing strategies through subtle signals or practices, creating an environment where competition is stifled without explicit agreements.
Consequences: Penalties for price fixing are severe, including hefty fines, imprisonment for executives, and potential civil lawsuits from damaged consumers.
2. Monopolization and Abuse of Dominant Market Position
Antitrust laws aim to prevent the formation of monopolies and restrict the abuse of dominant market positions. A monopoly exists when a single firm controls a significant portion of the market, typically over 70%. Abuse of dominance involves leveraging that market power to stifle competition or harm consumers. Such abuses can include:
- Predatory pricing: Selling products below cost to drive competitors out of business, then raising prices once the competition is eliminated.
- Exclusionary practices: Employing tactics to prevent competitors from accessing essential resources, like distribution channels or key suppliers.
- Refusal to deal: Refusing to supply goods or services to competitors, even if such refusal is unjustified.
- Tying arrangements: Requiring customers to purchase a secondary product or service to obtain a desired product.
Consequences: Antitrust agencies can impose significant fines, order divestitures (selling off parts of the business), and mandate behavioral remedies to prevent future abuses.
3. Mergers and Acquisitions
While mergers and acquisitions can bring about efficiencies and innovation, antitrust agencies carefully scrutinize them to prevent mergers that would significantly reduce competition. The agencies assess the potential impact on market concentration, considering factors such as:
- Market definition: Identifying the relevant market affected by the merger.
- Market share: Calculating the combined market share of the merging entities.
- Barriers to entry: Evaluating how easy it would be for new competitors to enter the market after the merger.
- Potential for innovation: Assessing the impact on innovation and technological advancement.
Consequences: If a merger is deemed anti-competitive, agencies can block it outright or require divestitures to mitigate its anti-competitive effects.
4. Vertical Restraints
Vertical restraints involve agreements between firms at different levels of the supply chain. While some vertical restraints can be pro-competitive, others can restrict competition. Examples include:
- Resale price maintenance (RPM): Manufacturers setting minimum prices that retailers can charge for their products.
- Exclusive dealing: Requiring retailers to sell only a particular manufacturer's products.
- Territorial restrictions: Limiting the geographic area where a retailer can sell a manufacturer's products.
Consequences: Agencies may challenge vertical restraints that significantly limit competition, potentially imposing fines or ordering behavioral changes.
5. Cartels and Anti-Competitive Agreements
Cartels are agreements between competitors to coordinate their behavior in a way that restricts competition. These agreements often involve price fixing, market allocation, or output restrictions. Even seemingly innocuous meetings or information exchanges can be considered evidence of cartel activity if they lead to anti-competitive outcomes.
Consequences: Cartel activity carries severe penalties, including substantial fines and potential criminal charges against individual executives.
Global Variations in Antitrust Enforcement
While the core principles of antitrust law are similar across many jurisdictions, specific approaches and enforcement practices can vary. The United States, with its robust antitrust tradition, often serves as a benchmark, yet the European Union (EU) and other countries have their own unique regulatory frameworks and agencies.
The US Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) are the primary enforcers in the United States, while the European Commission plays a central role in the EU. These agencies differ in their enforcement priorities, investigative techniques, and the types of remedies they employ. For instance, the EU is often more aggressive in tackling mergers and acquisitions, while the US has historically focused more on prosecuting cartels and monopolization.
The Importance of Compliance and Proactive Measures
Businesses must actively strive for compliance with antitrust laws. This requires establishing robust internal compliance programs, conducting regular training for employees, and implementing systems to monitor and assess potential antitrust risks. Proactive measures, such as seeking legal counsel before entering into potentially problematic agreements, can help companies avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
The consequences of non-compliance can be devastating, encompassing significant financial penalties, reputational harm, and even criminal prosecution. Therefore, a proactive and informed approach to antitrust compliance is not merely a legal requirement but a crucial element of sound business strategy.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Antitrust Law
The world of antitrust law is complex and multifaceted. What constitutes a questionable business practice is not always immediately clear, and the line between acceptable competitive behavior and unlawful anti-competitive conduct can be blurry. However, the core principles remain consistent: fostering competition, protecting consumers, and ensuring a fair and efficient marketplace. Businesses must understand these principles, implement robust compliance programs, and actively seek legal guidance to navigate the complexities of antitrust law and avoid potential pitfalls. By doing so, they can contribute to a thriving economy while safeguarding their own long-term success. Furthermore, understanding the global variations in antitrust enforcement is also crucial for businesses operating internationally. Staying informed about the evolving regulatory landscape is essential for maintaining compliance and mitigating risk in an increasingly interconnected business world. The long-term benefits of ethical and legally sound business practices far outweigh any perceived short-term gains from engaging in questionable activities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Into The Wild Ch 6 Summary
Apr 08, 2025
-
Chapter 19 1 Measuring Recording Height And Weight Answers
Apr 08, 2025
-
A Cuantas Millas De Mexicali Queda Guadalupe Ca
Apr 08, 2025
-
This Textbooks Preferred Model Of Communication Is
Apr 08, 2025
-
Predict The Major Product Of The Reaction Shown
Apr 08, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Questionable Business Practices According To Antitrust Agencies . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.