Radioactive Dating Game Lab Answer Key
Onlines
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
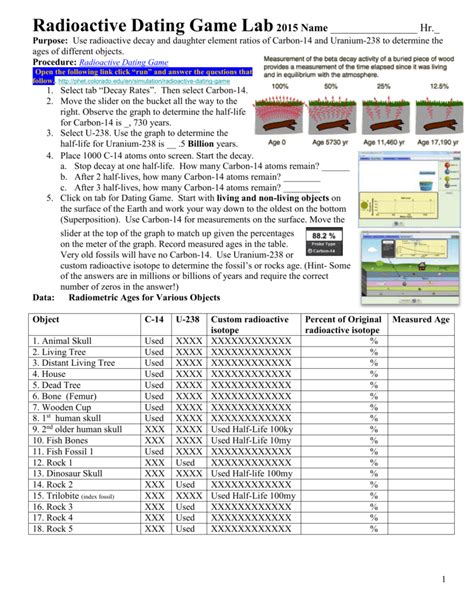
Table of Contents
Decoding the Radioactive Dating Game: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Applying Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, also known as radioactive dating, is a powerful technique used to determine the age of materials, particularly those of geological origin. It's a cornerstone of geology, archaeology, and paleontology, providing crucial insights into Earth's history and the evolution of life. While the concept might seem complex, understanding the underlying principles allows for a deeper appreciation of this invaluable scientific tool. This comprehensive guide will explore the fundamentals of radioactive dating, address common misconceptions, and delve into practical applications.
What is Radiometric Dating?
Radiometric dating relies on the predictable and consistent decay of radioactive isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are unstable, meaning they spontaneously undergo radioactive decay, transforming into a different element over time. This decay process follows a precise, exponential pattern, characterized by a half-life.
The half-life is the time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample of a radioactive isotope to decay. Each radioactive isotope has a unique and constant half-life, ranging from fractions of a second to billions of years. By measuring the ratio of the parent isotope (the original radioactive atom) to the daughter isotope (the product of decay), scientists can calculate the age of the sample.
Key Isotope Pairs in Radiometric Dating
Several isotope pairs are commonly used in radiometric dating, each suited to different materials and time scales:
-
Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) Dating: Used for dating organic materials (wood, bone, etc.) up to approximately 50,000 years old. ¹⁴C decays into ¹⁴N (nitrogen-14) with a half-life of 5,730 years. This method relies on the constant production of ¹⁴C in the atmosphere through cosmic ray interactions.
-
Potassium-Argon (⁴⁰K-⁴⁰Ar) Dating: Used for dating volcanic rocks and minerals millions to billions of years old. ⁴⁰K decays into ⁴⁰Ar (argon-40) with a half-life of 1.25 billion years. This method is particularly useful because argon is a gas that escapes from molten rock, effectively resetting the clock when the rock melts.
-
Uranium-Lead (U-Pb) Dating: Used for dating zircon crystals in igneous and metamorphic rocks, providing ages ranging from millions to billions of years. Several uranium isotopes (²³⁸U and ²³⁵U) decay through a series of steps to different lead isotopes (²⁰⁶Pb and ²⁰⁷Pb). The multiple decay pathways offer powerful cross-checking capabilities.
-
Rubidium-Strontium (⁸⁷Rb-⁸⁷Sr) Dating: Similar to U-Pb dating, this method is employed for dating very old rocks and minerals, providing ages over billions of years. ⁸⁷Rb decays into ⁸⁷Sr (strontium-87) with a half-life of 48.8 billion years.
Understanding the Radioactive Dating Game Lab
Many educational labs use simplified models to illustrate the principles of radioactive dating. These models typically involve a set of objects representing radioactive isotopes and their decay products. Students manipulate these objects to simulate the decay process over several half-lives and then calculate the age of the simulated sample based on the remaining parent and daughter isotopes.
The "answer key" for such a lab doesn't necessarily provide a single numerical answer. Instead, it should guide students through the steps of:
- Understanding the initial conditions: How many "parent" isotopes are present at the start of the simulation?
- Simulating decay: Students randomly remove "parent" isotopes according to the probability defined by the half-life. This can be achieved through various methods, such as coin flips or random number generators. Each removal represents a decay event, creating a "daughter" isotope.
- Measuring the ratios: After each simulated half-life, students record the number of remaining "parent" and accumulated "daughter" isotopes.
- Plotting the data: A graph showing the decay curve can visually represent the exponential decay process.
- Calculating the age: Based on the ratio of parent to daughter isotopes and the known half-life, students can estimate the age of the simulated sample. This calculation typically involves logarithmic functions or can be done using a pre-made chart or online calculator.
Addressing Common Misconceptions:
-
Contamination: Contamination of the sample with parent or daughter isotopes can skew the results. Rigorous laboratory techniques are essential to minimize this risk.
-
Closed System: The dating method assumes a closed system – no addition or loss of parent or daughter isotopes after the sample's formation. Geologic processes that alter the sample can affect its accuracy.
-
Dating the Event: Radiometric dating provides the age of the material being dated, not necessarily the precise age of the event that formed it. For example, dating a fossil only provides the age of the rock surrounding it, not the exact time the organism lived.
-
Multiple Dating Methods: The use of multiple dating methods on the same sample can provide a more robust and reliable age determination, helping to cross-check results and account for potential uncertainties.
Practical Applications of Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating is crucial for a wide range of scientific disciplines:
-
Geology: Determining the age of rocks and minerals provides a timescale for Earth's geological history, revealing the sequence of events that have shaped the planet.
-
Paleontology: Dating fossils allows scientists to reconstruct the evolutionary history of life, establishing the chronological order of species appearance and extinction.
-
Archaeology: Dating artifacts and settlements allows for a more precise understanding of human history and cultural development.
-
Anthropology: Dating human remains helps to trace human migration patterns and understand the evolution of human populations.
-
Cosmochemistry: Dating meteorites helps to determine the age of the solar system and provide insights into the formation of planets.
Advanced Considerations and Techniques
The process of radiometric dating is not simply a matter of measuring isotope ratios. It involves sophisticated techniques for sample preparation, measurement, and data analysis. These include:
-
Mass Spectrometry: Precisely measures the relative abundances of isotopes using various techniques like thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
-
Isochron Dating: A powerful technique that accounts for initial variations in isotope ratios, particularly useful when dealing with samples that have undergone complex geologic processes.
-
Error Analysis: Quantifies the uncertainty associated with radiometric age determinations, considering factors such as measurement errors, decay constant uncertainties, and potential contamination.
Conclusion
Radiometric dating is a fundamental tool for understanding Earth's history and the evolution of life. While its application can be complex, the core principle—measuring the predictable decay of radioactive isotopes—is relatively straightforward. By understanding the basics of radioactive decay, the various dating methods, and potential sources of error, we can appreciate the significant role this technique plays in reconstructing our planet's past and informing our understanding of the natural world. The "answer key" to a radioactive dating game lab isn’t a single number; it’s the journey of learning and applying these principles to solve scientific puzzles. Through this process, students gain a tangible understanding of a powerful scientific method that continues to shape our understanding of time itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Coming Of Age In Mississippi Book Summary
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Researcher Is Conducting A Written Survey
Apr 04, 2025
-
Summary Of Ethan Frome Chapter 1
Apr 04, 2025
-
1 7 Study Guide And Intervention Answer Key
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Twentieth Century Poetic Revolution Mastery Test
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Radioactive Dating Game Lab Answer Key . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
