Rbts Must Follow Skill Acquisition Plans Exactly.
Onlines
Mar 05, 2025 · 6 min read
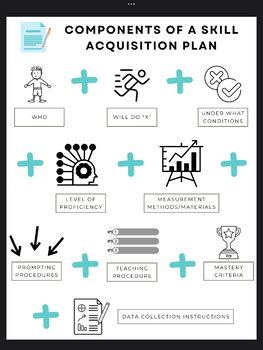
Table of Contents
RBTS Must Follow Skill Acquisition Plans Exactly: Why Precision Matters
The railway sector is a complex ecosystem demanding precision, safety, and unwavering adherence to regulations. Within this demanding environment, Railway Bridge and Tunnel Specialists (RBTS) play a crucial role, responsible for the inspection, maintenance, and repair of critical infrastructure. Their expertise directly impacts the safety and reliability of rail networks. Therefore, the meticulous execution of skill acquisition plans for RBTS is not simply recommended – it's absolutely essential. Deviation from these plans poses significant risks, undermining the very foundation of safe and efficient rail operations. This article delves into the critical reasons why RBTS must follow their skill acquisition plans exactly, examining the ramifications of non-compliance and highlighting strategies for ensuring adherence.
The Critical Importance of Skill Acquisition Plans for RBTS
Skill acquisition plans for RBTS are not arbitrary documents; they are meticulously designed roadmaps to competency. These plans detail the specific knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) required to perform tasks safely and effectively. They typically encompass:
1. Foundational Knowledge:
- Engineering Principles: A solid understanding of civil engineering principles, including structural mechanics, materials science, and hydraulics, is paramount. This knowledge forms the bedrock upon which all other skills are built.
- Railway Systems: RBTS must possess a comprehensive understanding of railway systems, including track geometry, signaling systems, and power distribution networks. This knowledge enables them to assess the impact of bridge and tunnel maintenance on the overall railway operation.
- Safety Regulations: Adherence to stringent safety regulations is non-negotiable. RBTS must be intimately familiar with all relevant safety protocols and procedures to mitigate risks and prevent accidents.
2. Practical Skills:
- Inspection Techniques: Proficient inspection techniques, including visual inspections, non-destructive testing (NDT), and data analysis, are crucial for identifying potential defects and assessing structural integrity. These skills demand both theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience.
- Repair and Maintenance Procedures: RBTS must be adept at executing various repair and maintenance procedures, ranging from minor repairs to major rehabilitation projects. This requires specialized training and practical application under the supervision of experienced professionals.
- Emergency Response: In the event of an emergency, RBTS need to be able to respond effectively and efficiently, ensuring the safety of personnel and the integrity of the infrastructure. This involves specialized training in emergency procedures and crisis management.
3. Specialized Training:
- Software Proficiency: Modern railway maintenance relies heavily on software for data analysis, modeling, and simulations. RBTS need to be proficient in using specialized software packages for bridge and tunnel assessment and management.
- Specialized Equipment Operation: RBTS often work with specialized equipment, such as inspection vehicles, NDT equipment, and heavy machinery. Safe and effective operation of this equipment necessitates specific training and certification.
- Advanced Techniques: Ongoing training in advanced techniques, such as advanced NDT methods, innovative repair technologies, and risk assessment methodologies, keeps RBTS at the cutting edge of the field.
The Consequences of Non-Compliance with Skill Acquisition Plans
Failure to adhere strictly to skill acquisition plans carries severe consequences, impacting safety, efficiency, and the overall reputation of the railway system. These consequences include:
1. Safety Risks:
- Structural Failures: Inadequate training can lead to missed defects during inspections, resulting in potential structural failures with catastrophic consequences.
- Accidents and Injuries: Improper operation of equipment or inadequate knowledge of safety procedures can cause accidents and injuries to RBTS and other railway personnel.
- Disruptions to Rail Services: Failures resulting from inadequate training can lead to significant disruptions to rail services, impacting commuters and freight transportation.
2. Financial Implications:
- Increased Maintenance Costs: Inefficient repairs or inadequate preventative maintenance stemming from skill deficiencies can lead to higher overall maintenance costs in the long run.
- Legal Liabilities: Accidents or failures due to inadequate training can result in significant legal liabilities and financial penalties.
- Loss of Reputation: Safety incidents resulting from inadequate training can damage the reputation of the railway organization and erode public trust.
3. Operational Inefficiencies:
- Delayed Projects: Lack of necessary skills can lead to delays in project completion, increasing costs and disrupting schedules.
- Reduced Productivity: Inadequate training can result in lower productivity and increased errors, impacting the overall efficiency of the maintenance process.
- Increased Downtime: Frequent breakdowns or repairs caused by inadequate training can lead to increased downtime for rail lines, disrupting services and impacting revenue.
Ensuring Adherence to Skill Acquisition Plans: Strategies for Success
Implementing robust strategies to ensure strict adherence to skill acquisition plans is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficiency of railway operations. These strategies include:
1. Comprehensive Training Programs:
- Structured Curricula: Develop comprehensive and well-structured training curricula that align precisely with the skill acquisition plan's requirements. This should include both theoretical instruction and practical, hands-on training.
- Experienced Instructors: Employ experienced and qualified instructors who can effectively deliver the training material and provide valuable feedback.
- Regular Assessments: Regular assessments, including both theoretical examinations and practical evaluations, should be conducted to monitor trainees' progress and ensure competency.
2. Mentorship and Supervision:
- Mentoring Programs: Establish mentoring programs that pair experienced RBTS with trainees, providing them with ongoing support and guidance.
- On-the-Job Training: Provide structured on-the-job training under the supervision of experienced professionals, allowing trainees to apply their knowledge and skills in a real-world setting.
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to assess the competency of RBTS and identify areas requiring further training or development.
3. Technology and Innovation:
- Simulation and Training Software: Utilize advanced simulation software to provide trainees with realistic training scenarios, allowing them to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Employ AR and VR technologies to enhance training and provide trainees with immersive experiences.
- Data Analytics and Tracking: Utilize data analytics to track training progress, identify skill gaps, and measure the effectiveness of training programs.
4. Continuous Improvement:
- Regular Reviews of Skill Acquisition Plans: Regularly review and update skill acquisition plans to reflect changes in technology, regulations, and industry best practices.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms to collect feedback from RBTS, supervisors, and other stakeholders to identify areas for improvement in the training program.
- Continuous Professional Development (CPD): Encourage and support continuous professional development through ongoing training and participation in industry events and conferences.
Conclusion: Precision is Paramount
The safety and efficiency of railway operations depend heavily on the expertise and competence of RBTS. Strict adherence to skill acquisition plans is not merely a recommendation; it's a fundamental requirement. Failure to do so exposes the railway system to significant risks, including accidents, operational disruptions, and financial liabilities. By implementing robust training programs, effective supervision, and a commitment to continuous improvement, railway organizations can ensure that their RBTS possess the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their critical duties safely and effectively, contributing to a reliable and secure railway network for all. The investment in precision and adherence to these plans is an investment in the safety and future of the railway industry itself.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Imc Unit 1 Mock 2 Dec 2022
Mar 06, 2025
-
Pobre Ana Chapter 3 English Translation
Mar 06, 2025
-
You Are Responsible For Which Of The Following
Mar 06, 2025
-
Reading Comprehension Is Difficult To Assess Through Formal Testing Alone
Mar 06, 2025
-
In This Scenario Beth Represents The
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rbts Must Follow Skill Acquisition Plans Exactly. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
