Relative Mass And The Mole Pogil
Onlines
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
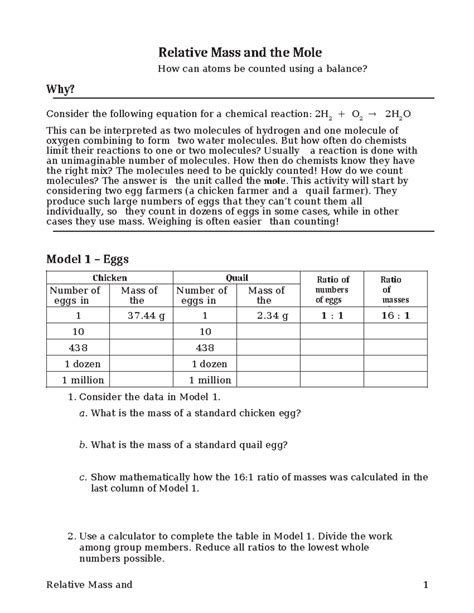
Table of Contents
Relative Mass and the Mole: A Deep Dive into POGIL Activities
The concepts of relative mass and the mole are fundamental to chemistry, forming the bedrock for understanding stoichiometry, chemical reactions, and quantitative analysis. These concepts can often seem abstract, but through practical application and hands-on activities, such as those found in Process-Oriented Guided-Inquiry Learning (POGIL) activities, these crucial ideas become much clearer and more accessible. This article delves into the intricacies of relative mass and the mole, exploring their significance and illustrating how POGIL activities can enhance learning and understanding.
Understanding Relative Atomic Mass
Before diving into the mole, it's crucial to grasp the concept of relative atomic mass (also known as atomic weight). Atoms, the building blocks of matter, are incredibly small. Precisely measuring the mass of a single atom is practically impossible using conventional methods. Instead, scientists use a relative scale.
What is Relative Atomic Mass?
Relative atomic mass is a comparison of the mass of one atom to the mass of a standard atom. The standard used is carbon-12, which is assigned a relative mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu). Therefore, the relative atomic mass of any element represents how many times heavier or lighter its atom is compared to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. For example, an oxygen atom is roughly 16 amu, meaning it's 16/12 or 4/3 times heavier than 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom. This is crucial because it allows us to make comparisons between the masses of different atoms.
Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass:
The relative atomic mass of an element found on the periodic table is actually a weighted average of the masses of its isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron number leads to slight variations in mass. The weighted average accounts for the natural abundance of each isotope. For instance, chlorine has two main isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37. Chlorine-35 is more abundant, so the average atomic mass of chlorine is closer to 35 amu than to 37 amu. This weighted average is the value used in most chemical calculations.
The Significance of Relative Atomic Mass in Chemical Calculations
Relative atomic mass plays a vital role in many chemical calculations. It is used to:
- Determine the molar mass of a compound: Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. It's calculated by adding up the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule.
- Calculate the empirical formula of a compound: Empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. Relative atomic masses are used to determine this ratio from experimental data.
- Carry out stoichiometric calculations: Stoichiometry involves using balanced chemical equations to determine the amounts of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Relative atomic masses are essential for converting between mass and moles in these calculations.
The Mole: A Chemist's Counting Unit
The mole is arguably the most important concept in quantitative chemistry. It's a unit that provides a bridge between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world of laboratory measurements.
What is a Mole?
A mole (mol) is defined as the amount of substance containing Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>) of entities. These entities can be atoms, molecules, ions, or any other specified particles. Avogadro's number is a fundamental constant in chemistry, much like the speed of light in physics. Think of it like a dozen—a dozen eggs contains 12 eggs, a mole of atoms contains approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> atoms.
Molar Mass and its Relationship to the Mole:
The molar mass of a substance is numerically equal to its relative molecular mass (or formula mass) but expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). For example, the relative molecular mass of water (H₂O) is approximately 18 amu (1 x 2 + 16). Therefore, the molar mass of water is 18 g/mol. This means that one mole of water weighs 18 grams and contains approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> water molecules.
The Importance of the Mole in Chemical Calculations
The mole is essential for several reasons:
- Converting between mass and number of particles: It allows chemists to easily convert between the mass of a substance (measured in grams) and the number of atoms or molecules present.
- Stoichiometric calculations: The mole is crucial for solving stoichiometry problems, enabling the determination of reactant and product quantities in chemical reactions.
- Concentration calculations: Molarity (moles per liter) is a common unit of concentration, highlighting the importance of the mole in expressing solution composition.
- Gas laws: The ideal gas law relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas, illustrating the mole's relevance in gas chemistry.
POGIL Activities: Enhancing Understanding of Relative Mass and the Mole
POGIL activities offer a student-centered approach to learning, encouraging collaborative problem-solving and deeper conceptual understanding. These activities guide students through a series of questions and challenges, prompting them to actively construct their knowledge rather than passively receiving it. In the context of relative mass and the mole, POGIL activities are particularly effective.
How POGIL Activities Help:
- Active Learning: Instead of lecturing, POGIL activities encourage students to actively engage with the material. They work collaboratively, discussing concepts, and solving problems together.
- Conceptual Understanding: The emphasis is on understanding the underlying concepts, not just memorizing formulas. Students are prompted to explain their reasoning and justify their answers.
- Problem-Solving Skills: POGIL activities present a range of problems of varying difficulty, honing students' problem-solving skills in a supportive environment.
- Critical Thinking: Students are challenged to analyze information, identify patterns, and draw conclusions, fostering critical thinking abilities.
- Collaboration: Working in groups enhances communication skills and allows students to learn from each other.
Examples of POGIL Activities related to Relative Mass and the Mole:
A POGIL activity on relative mass might begin by asking students to calculate the relative atomic mass of an element given the masses and abundances of its isotopes. This would be followed by progressively challenging problems involving molar mass calculations, the conversion between mass and number of particles, and simple stoichiometric calculations. A sophisticated activity could introduce the concept of limiting reactants and percent yield, tying together the concepts of relative mass and the mole within the context of a chemical reaction. Other activities could use real-world examples, such as calculating the number of atoms in a gold nugget or determining the amount of a specific element in a compound found in everyday life. The activities could progressively increase in complexity, introducing more intricate scenarios and challenging the students to critically evaluate and analyze data. For example, an advanced activity could involve determining the empirical and molecular formula of a compound given experimental data, requiring students to integrate multiple concepts and apply their problem-solving skills comprehensively.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several common misconceptions arise when studying relative mass and the mole:
- Confusing atomic mass with mass number: Atomic mass is a weighted average of isotopic masses, while the mass number refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in a specific isotope.
- Incorrectly using units: Students often make mistakes in unit conversions, particularly when dealing with grams, moles, and Avogadro's number.
- Difficulty with stoichiometric calculations: Many students struggle to apply the mole concept in stoichiometric calculations, particularly when dealing with limiting reactants and percent yield. POGIL activities can help address this by providing numerous opportunities for practice and peer feedback.
- Failure to relate macroscopic measurements to the microscopic world: Students sometimes struggle to connect the measurable mass of a substance to the vast number of atoms or molecules it contains. Visual aids and analogies can help to bridge this gap.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
The concepts of relative mass and the mole are crucial for success in chemistry. POGIL activities offer an engaging and effective approach to mastering these fundamental concepts. By actively participating in these activities, students develop a deeper understanding, improve problem-solving skills, and build a stronger foundation for more advanced chemical concepts. The collaborative nature of POGIL encourages communication and critical thinking, enhancing the overall learning experience and preparing students for success in future chemistry endeavors. Furthermore, the iterative nature of POGIL activities, allowing students to revisit and refine their understanding through progressive challenges, solidifies their grasp of the fundamental principles of relative mass and the mole, paving the way for a more comprehensive understanding of chemistry as a whole. The integration of real-world examples into POGIL activities not only contextualizes the learning process but also helps students appreciate the practical applications of these crucial chemical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Letter To My Mother That She Will Never Read
Apr 05, 2025
-
Mapping Genes To Traits In Dogs Using Snps
Apr 05, 2025
-
1 05 Quiz Poetry Of The Modern Period
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Statements Best Describes The Sprint Test
Apr 05, 2025
-
Select All The Correct Statements About Sending A Bad News Message
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Relative Mass And The Mole Pogil . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
